Clin Orthop Surg.
2012 Dec;4(4):256-262. 10.4055/cios.2012.4.4.256.
Comparison of the Clinical Outcomes after Total Knee Arthroplasty with the LCS Rotating Platform Mobile Bearing Knee System and the PFC Sigma RP-F Mobile Bearing Knee System
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Murup Hospital, Changwon, Korea.
- 3Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Hyundae General Hospital, Namyangju, Korea. jungyb2000@paran.com
- KMID: 1719292
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2012.4.4.256
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
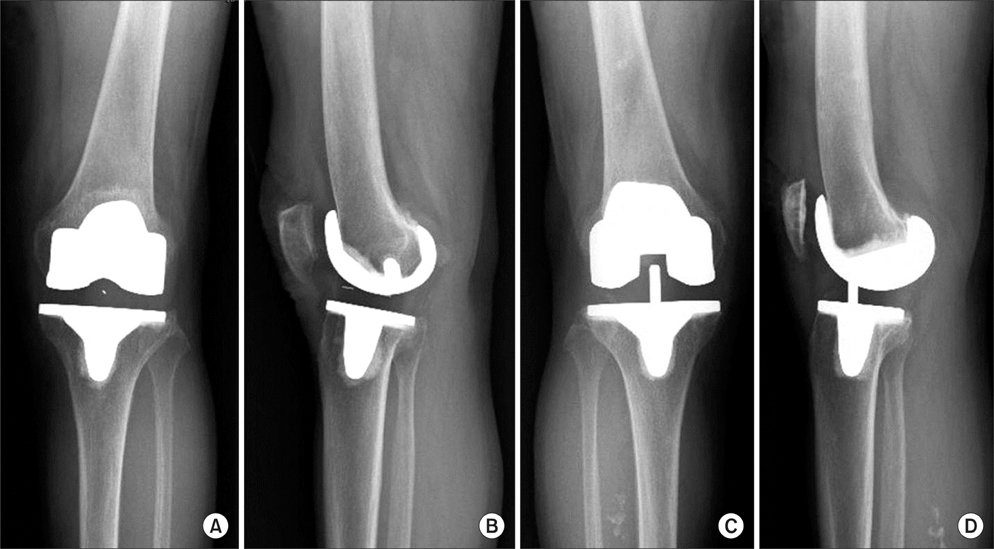
We compared clinical outcomes after total knee arthroplasty with the Low Contact Stress (LCS) rotating platform mobile bearing knee system and the Press Fit Condylar Sigma rotating platform high flexion (PFC Sigma RP-F) mobile bearing knee system.
METHODS
Fifty cases of total knee arthroplasty were performed with the PFC Sigma RP-F mobile bearing knee system and sixty-one cases were performed with the LCS mobile bearing total knee arthroplasty. The average duration of follow-up was 2.9 years.
RESULTS
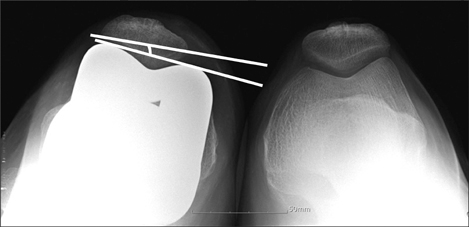
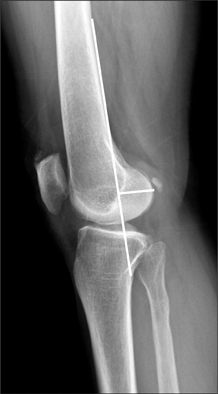
The mean Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) knee score was 62.1 (range, 52 to 75) in the LCS group and 61.9 (range, 50 to 74) in the Sigma RP-F group preoperatively, and 90.1 (range, 84 to 100) in the LCS group and 89.8 (range, 83 to 100) in the Sigma RP-F group at the final follow-up. The mean preoperative flexion contracture was 6.7degrees (range, 0degrees to 10degrees) in the LCS group and 9.3degrees (range, 0degrees to 15degrees) in the Sigma RP-F group preoperatively. The mean range of motion was 124.6degrees (range, 105degrees to 150degrees) in the LCS group and 126.1degrees (range, 104degrees to 145degrees) in the Sigma RP-F group at the final follow-up.
CONCLUSIONS
After a minimum duration of follow-up of two years, we found no significant differences between the two groups with regard to the range of knee motion or the clinical or radiographic results.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mulholland SJ, Wyss UP. Activities of daily living in non-Western cultures: range of motion requirements for hip and knee joint implants. Int J Rehabil Res. 2001. 24(3):191–198.
Article2. Schurman DJ, Parker JN, Ornstein D. Total condylar knee replacement: a study of factors influencing range of motion as late as two years after arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1985. 67(7):1006–1014.
Article3. Seon JK, Song EK, Lee JY. Comparison of range of motion of high-flexion prosthesis and mobile-bearing prosthesis in total knee arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2005. 28:10 Suppl. s1247–s1250.
Article4. Yamazaki J, Ishigami S, Nagashima M, Yoshino S. Hy-Flex II total knee system and range of motion. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2002. 122(3):156–160.
Article5. Jung YB, Lee YS, Lee EY, Jung HJ, Nam CH. Comparison of the modified subvastus and medial parapatellar approaches in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2009. 33(2):419–423.
Article6. Buechel FF, Pappas MJ. The New Jersey Low-Contact-Stress Knee Replacement System: biomechanical rationale and review of the first 123 cemented cases. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1986. 105(4):197–204.
Article7. Kim YH, Kook HK, Kim JS. Comparison of fixed-bearing and mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasties. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001. (392):101–115.
Article8. Sorrells RB, Stiehl JB, Voorhorst PE. Midterm results of mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasty in patients younger than 65 years. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001. (390):182–189.
Article9. Dennis DA, Komistek RD, Mahfouz MR, Walker SA, Tucker A. A multicenter analysis of axial femorotibial rotation after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004. (428):180–189.
Article10. Kuster MS, Spalinger E, Blanksby BA, Gachter A. Endurance sports after total knee replacement: a biomechanical investigation. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2000. 32(4):721–724.
Article11. Anouchi YS, McShane M, Kelly F Jr, Elting J, Stiehl J. Range of motion in total knee replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996. (331):87–92.
Article12. Li G, Most E, Sultan PG, et al. Knee kinematics with a high-flexion posterior stabilized total knee prosthesis: an in vitro robotic experimental investigation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004. 86(8):1721–1729.
Article13. Miner AL, Lingard EA, Wright EA, Sledge CB, Katz JN. Kinemax Outcomes Group. Knee range of motion after total knee arthroplasty: how important is this as an outcome measure? J Arthroplasty. 2003. 18(3):286–294.
Article14. Meneghini RM, Pierson JL, Bagsby D, Ziemba-Davis M, Berend ME, Ritter MA. Is there a functional benefit to obtaining high flexion after total knee arthroplasty? J Arthroplasty. 2007. 22:6 Suppl 2. 43–46.
Article15. Kim YH, Kim JS. Comparison of anterior-posterior-glide and rotating-platform low contact stress mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasties. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004. 86(6):1239–1247.
Article16. Kim YH, Sohn KS, Kim JS. Range of motion of standard and high-flexion posterior stabilized total knee prostheses: a prospective, randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005. 87(7):1470–1475.
Article17. Ranawat CS. Design may be counterproductive for optimizing flexion after TKR. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003. (416):174–176.
Article18. Puloski SK, McCalden RW, MacDonald SJ, Rorabeck CH, Bourne RB. Tibial post wear in posterior stabilized total knee arthroplasty: an unrecognized source of polyethylene debris. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001. 83(3):390–397.19. Morra EA, Rosca M, Greenwald JF, Greenwald AS. The influence of contemporary knee design on high flexion: a kinematic comparison with the normal knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008. 90 Suppl 4:195–201.
Article20. Mikulak SA, Mahoney OM, dela Rosa MA, Schmalzried TP. Loosening and osteolysis with the press-fit condylar posterior-cruciate-substituting total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001. 83(3):398–403.
Article21. Mestha P, Shenava Y, D'Arcy JC. Fracture of the polyethylene tibial post in posterior stabilized (Insall Burstein II) total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2000. 15(6):814–815.
Article22. Mauerhan DR. Fracture of the polyethylene tibial post in a posterior cruciate-substituting total knee arthroplasty mimicking patellar clunk syndrome: a report of 5 cases. J Arthroplasty. 2003. 18(7):942–945.
Article23. Chiu YS, Chen WM, Huang CK, Chiang CC, Chen TH. Fracture of the polyethylene tibial post in a NexGen posterior-stabilized knee prosthesis. J Arthroplasty. 2004. 19(8):1045–1049.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Condylar Lift Off in Fixed and Mobile Bearing Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Moderate to Severe Varus Deformity in Total Knee Arthroplasty: PFC Sigma Fixed Bearing Versus Rotating Platform
- A Comparison of the Clinical and Radiographic Results of Press Fit Condylar Rotating-Platform High-Flexion and Low Contact Stress Mobile Bearing Prosthesis in Total Knee Arthroplasty: Short term Results
- Total Knee Arthroplasty using LCS Mobile Bearing System
- Mobile Bearing Subluxation after Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty Treated by Arthroscopy : A Case Report