Korean J Gastroenterol.
2012 Jul;60(1):61-63. 10.4166/kjg.2012.60.1.61.
Actinomycosis in Pancreas and Psoas Muscle
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jongk.lee@samsung.com
- KMID: 1718469
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2012.60.1.61
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
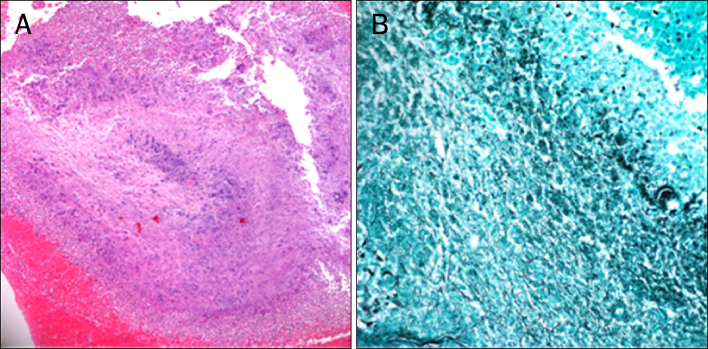
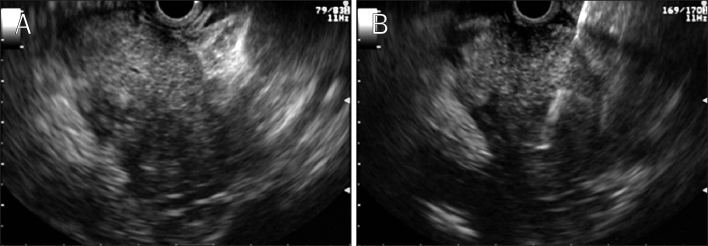
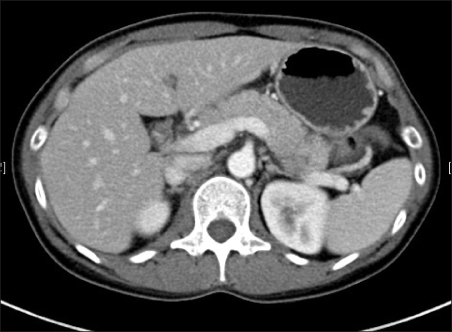
Figure
Reference
-
1. Russo T. Mandell GL, Douglas RG, Bennett JE, editors. Agents of actinomycosis. Principles and practice of infectious diseases. 2010. Volume 2. New York: Elsevier Churchill Livingstone;3209–3219.2. Wong VK, Turmezei TD, Weston VC. Actinomycosis. BMJ. 2011. 343:d6099.3. Fowler RC, Simpkins KC. Abdominal actinomycosis: a report of three cases. Clin Radiol. 1983. 34:301–307.4. Piper MH, Schaberg DR, Ross JM, Shartsis JM, Orzechowski RW. Endoscopic detection and therapy of colonic actinomycosis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1992. 87:1040–1042.5. Jha A. Actinomycosis of the pancreas: a case report and review. Gastroenterol Res. 2010. 3:134–138.6. Lewis RP, Sutter VL, Finegold SM. Bone infections involving anaerobic bacteria. Medicine (Baltimore). 1978. 57:279–305.7. Cintron JR, Del Pino A, Duarte B, Wood D. Abdominal actinomycosis. Dis Colon Rectum. 1996. 39:105–108.8. Harris LA, DeCosse JJ, Dannenberg A. Abdominal actinomycosis: evaluation by computed tomography. Am J Gastroenterol. 1989. 84:198–200.9. Lee IJ, Ha HK, Park CM, et al. Abdominopelvic actinomycosis involving the gastrointestinal tract: CT features. Radiology. 2001. 220:76–80.10. Ferrari TC, Couto CA, Murta-Oliveira C, Conceição SA, Silva RG. Actinomycosis of the colon: a rare form of presentation. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2000. 35:108–109.11. Weese WC, Smith IM. A study of 57 cases of actinomycosis over a 36-year period. A diagnostic 'failure' with good prognosis after treatment. Arch Intern Med. 1975. 135:1562–1568.