Korean J Gastroenterol.
2010 Nov;56(5):329-333. 10.4166/kjg.2010.56.5.329.
Case of Malarial Hepatitis by Plasmodium Vivax
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Pohang St. Mary's Hospital, Pohang, Korea. yyhhsung@hanmail.net
- KMID: 1718376
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2010.56.5.329
Abstract
- Malarial infection is one of the most important tropical diseases, but also increasing in the temperate regions. Severe malaria with organ dysfunction is commonly associated with Plasmodium falciparum, but rarely with Plasmodium vivax. Malarial hepatitis is also unusual in P. falciparum and very rare in P. vivax. Only 3 cases of malarial hepatitis caused by P. vivax have been reported in the world. Because the presence of hepatitis in malaria indicates a more severe illness with higher incidence of other complications and poor prognosis, malarial patients should be meticulously monitored for hepatic dysfunction with or without jaundice. We report here a case of malarial hepatitis caused by P. vivax that was presented by fever, general ache, nausea, fatigue, and significant elevation of aminotransferase and bilirubin.
MeSH Terms
-
Abdomen/ultrasonography
Antimalarials/therapeutic use
Erythrocytes/immunology/parasitology
Fatigue/etiology
Hepatitis/*diagnosis/etiology/ultrasonography
Humans
Malaria, Vivax/complications/*diagnosis/drug therapy
Male
Mefloquine/therapeutic use
Nausea/etiology
Plasmodium vivax/isolation & purification
Primaquine/therapeutic use
Young Adult
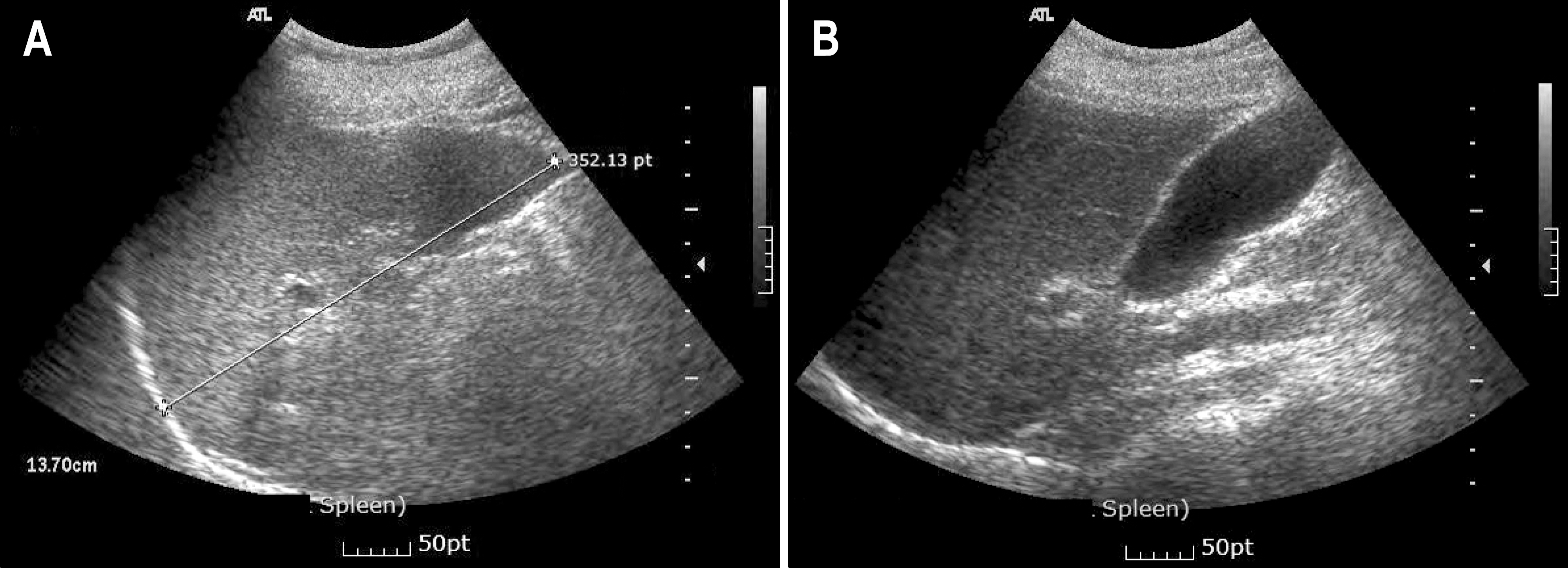
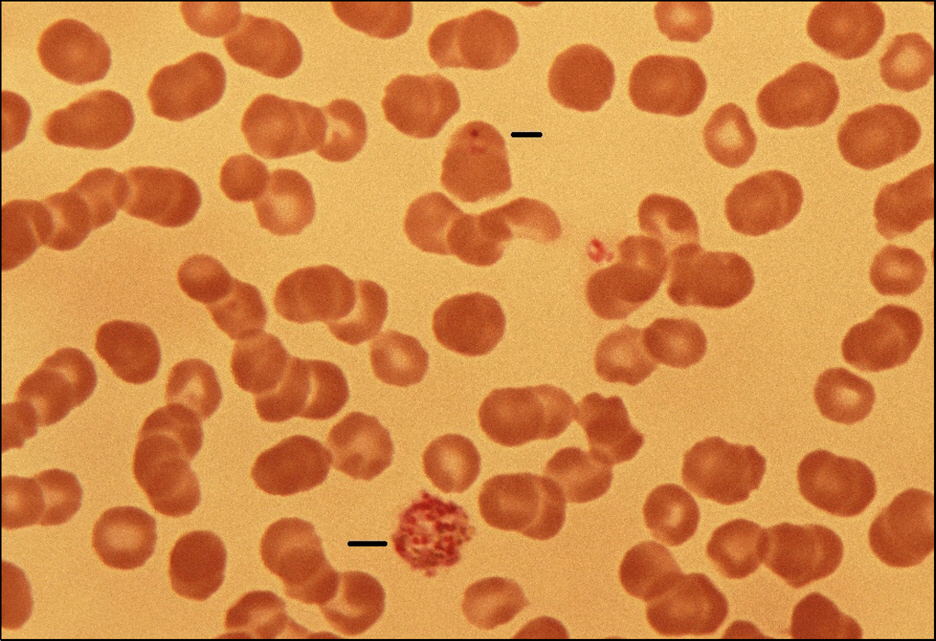
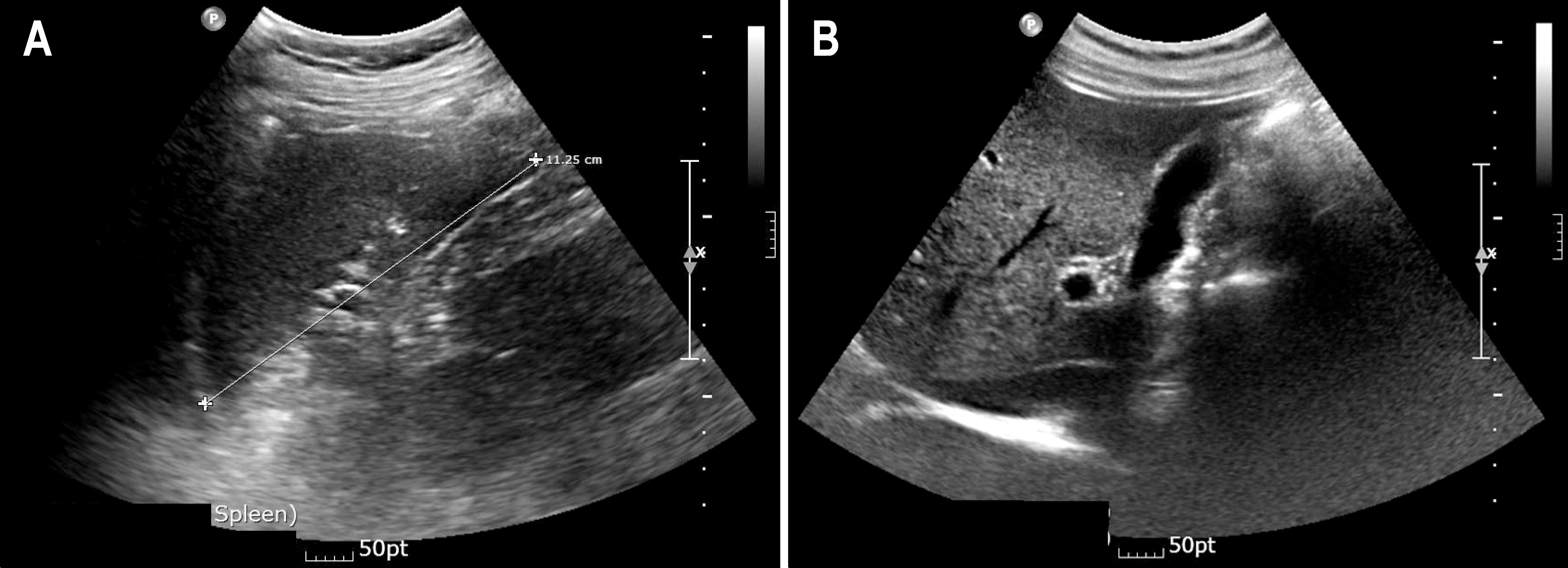
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee DY, Kim SY, Hwang SC, Lee JS, Kang JS. Clinical observation in 21 cases of imported malaria. Korean J Intern Med. 1988; 34:660–665.2. Chai JY. Re-emerging Plasmodium vivax malaria in the Republic of Korea. Korean J Parasitol. 1999; 37:129–143.3. Kho WG. Reemergence of malaria in Korea. J Korean Med Assoc. 2007; 50:959–966.
Article4. Song HH, Oh SO, Kim SH, et al. Clinical features of Plasmodium vivax malaria. Korean J Intern Med. 2003; 18:220–224.5. Park MH, Cha JG, Koo WH, Rho JH, Cho CK, Kim HJ. Spontaneous rupture of spleen in a patient with malarial infection. J Korean Surg Soc. 2000; 59:562–566.6. Chung HS, Eun CR, Choi HJ, et al. A case of splenic infarction during acute malaria. Korean J Med. 2007; 73(suppl 3):S1061–S1065.7. World Health Organization. Severe falciparum malaria. World Health Organization, Communicable Diseases Cluster. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2000; 94(suppl 1):S1–S90.8. Srivastava A, Khanduri A, Lakhtakia S, Pandey R, Choudhuri G. Falciparum malaria with acute liver failure. Trop Gastroenterol. 1996; 17:172–174.9. Nautiyal A, Singh S, Parmeswaran G, DiSalle M. Hepatic dysfunction in patient with Plasmodium vivax infection. MedGenMed. 2005; 7:8.10. Kochar DK, Saxena V, Singh N, Kochar SK, Kumar SV, Das A. Plasmodium vivax malaria. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005; 11:132–134.11. Anand AC, Puri P. Jaundice in malaria. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005; 20:1322–1332.
Article12. Montse R, Pedro LA. Malaria. Joan R, Jean-Pierre B, Mario R, editors. Textbook of hepatology: from basic science to clinical practice. I:3rd ed.Malden: Blackwell;2007. p. 1029–1033.13. Anand AC, Ramji C, Narula AS, Singh W. Malarial hepatitis: a heterogeneous syndrome? Natl Med J India. 1992; 5:59–62.14. Gilles HM. The malaria parasites. Gilles HM, Warrell DA, Bruce-Chwatt LJ, editors. eds.Bruce-Chwatt's essential malariology. 3rd ed.London: Arnold;1993. p. 13–34.15. Bhalla A, Suri V, Singh V. Malarial hepatopathy. J Postgrad Med. 2006; 52:315–320.16. Guha M, Kumar S, Choubey V, Maity P, Bandyopadhyay U. Apoptosis in liver during malaria: role of oxidative stress and implication of mitochondrial pathway. FASEB J. 2006; 20:1224–1226.
Article17. Seth AK, Nijhawan VS, Bhandari MK, Dhaka RS. Malarial hepatitis: Incidence and liver morphology. Indian J Gastroenterol. 1997; 16(suppl 2):A107.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Spontaneous Splenic Rupture in Vivax Malaria
- A Case of Plasmodium vivax Infection Diagnosed after Treatment of Imported Falciparum Malaria
- A Case of Mixed Malarial Infection with Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax
- Plasmodium vivax Infection Accompanied by Acute Renal Failure
- Two Cases of Vivax Malaria Recurred at 38 and 40 Days after Hydoxychloroquine Therapy