Yonsei Med J.
2006 Jun;47(3):359-366. 10.3349/ymj.2006.47.3.359.
Antiallodynic Effects of Acupuncture in Neuropathic Rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physiology, Yonsei Univ. College of Med., Seoul, Korea. bhlee@yumc.yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Brain Korea 21 Project for Med. Sci., Yonsei Univ. College of Med., Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Med., Yonsei Univ. College of Med., Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Integrative Med., College of Med., The Catholic Univ. of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Oriental Med. Sci., Graduate School of East-West Medical Science, Kyung Hee Univ., Yongin, Korea.
- 6Department of Medical Research, Korea Institute of Oriental Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- KMID: 1715854
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2006.47.3.359
Abstract
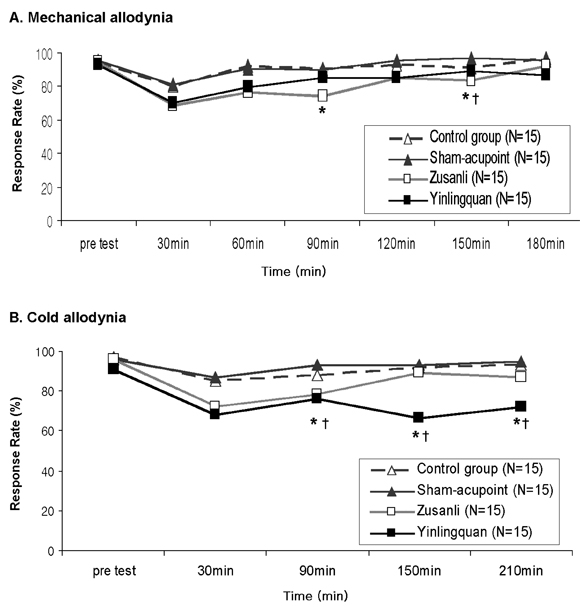
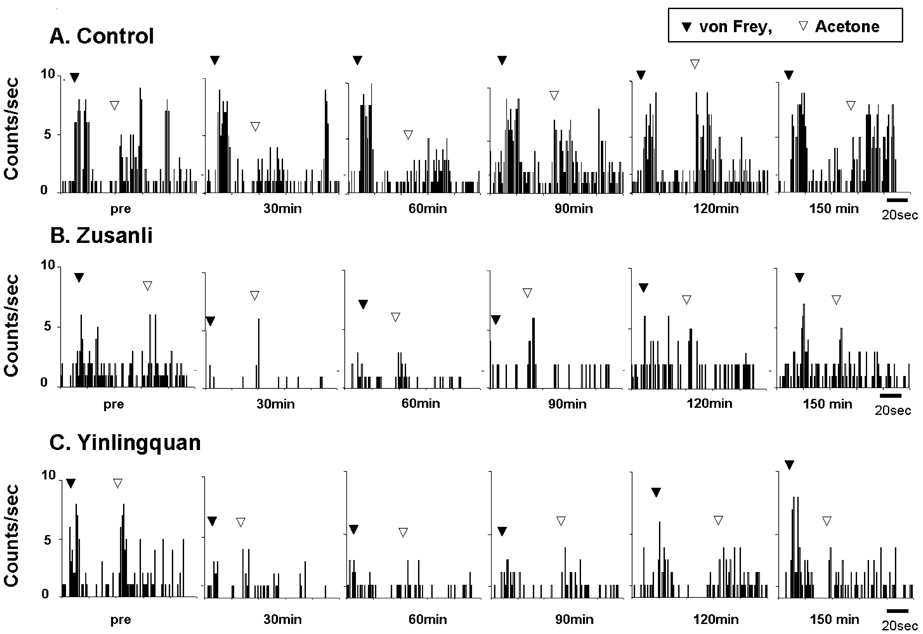
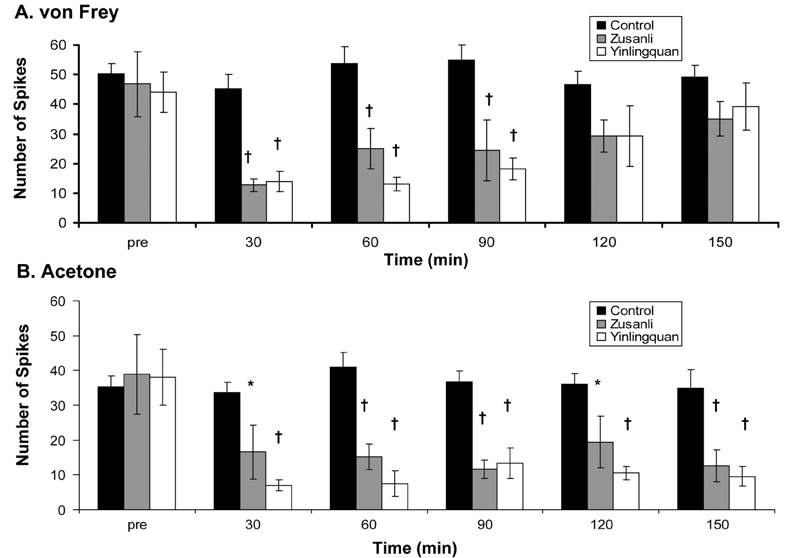
- Peripheral nerve injury often results in abnormal neuropathic pain such as allodynia or hyperalgesia. Acupuncture, a traditional Oriental medicine, has been used to relieve pain and related symptoms. However, the efficiency of acupuncture in relieving neuropathic pain is not clear. The aim of this study was to investigate the anti-allodynic effects of acupuncture through behavioral and electrophysiological examinations. Male Sprague-Dawley rats were subjected to neuropathic surgery consisting of a tight ligation and transection of the left tibial and sural nerves, under pentobarbital anesthesia. The acupuncture experiment consisted of four different groups, one treated at each of three different acupoints (Zusanli (ST36), Yinlingquan (SP9), and a sham-acupoint) and a control group. Behavioral tests for mechanical allodynia and cold allodynia were performed for up to two weeks postoperatively. Extracellular electrophysiological recordings were made from the dorsal roots using platinum wire electrodes. Mechanical and cold allodynia were significantly reduced after acupuncture treatment at the Zusanli and Yinlingquan acupoints, respectively. Electrophysiological neural responses to von Frey and acetone tests were also reduced after acupuncture at the same two acupoints. These results suggest that acupuncture may be beneficial in relieving neuropathic pain.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Effects of Acupuncture Stimulation at Different Acupoints on Formalin-Induced Pain in Rats
Kyung Ha Chang, Sun Joon Bai, Hyejung Lee, Bae Hwan Lee
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2014;18(2):121-127. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2014.18.2.121.Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, acupuncture, and spinal cord stimulation on neuropathic, inflammatory and, non-inflammatory pain in rat models
Karina Laurenti Sato, Luciana Sayuri Sanada, Morgana Duarte da Silva, Rodrigo Okubo, Kathleen A. Sluka
Korean J Pain. 2020;33(2):121-130. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2020.33.2.121.
Reference
-
1. Talmoush AJ. Causalgia: Redefinition as a clinical pain syndrome. Pain. 1981. 10:187–197.2. Arner S, Meyerson BA. Lack of analgesic effect of opioids on neuropathic and idiopathic forms of pain. Pain. 1988. 33:11–23.3. Vincent CA, Richardson PH. The evaluation of therapeutic acupuncture: concepts and methods. Pain. 1986. 24:1–13.4. Berman BM, Singh BB, Lao L, Langenberg P, Li H, Hadhazy V, et al. A randomized trial of acupuncture as an adjunctive therapy in osteoarthritis of the knee. Rheumatology (Oxford). 1999. 38:346–354.5. Birch S, Hammerschlag R, Berman BM. Acupuncture in the treatment of pain. J Altern Complement Med. 1996. 2:101–124.6. Ezzo J, Hadhazy V, Birch S, Lao L, Kaplan G, Hochberg M, et al. Acupuncture for osteoarthritis of the knee: a systematic review. Arthritis Rheum. 2001. 44:819–825.7. Koo ST, Park YI, Lim KS, Chung K, Chung JM. Acupuncture analgesia in a new rat model of ankle sprain pain. Pain. 2002. 99:423–431.8. Richardson PH, Vincent CA. Acupuncture for the treatment of pain: a review of evaluative research. Pain. 1986. 24:15–40.9. Dai Y, Kondo E, Fukuoka T, Tokunaga A, Miki K, Noguchi K. The effect of electroacupuncture on pain behaviors and noxious stimulus-evoked Fos expression in a rat model of neuropathic pain. J Pain. 2001. 2:151–159.10. Huang C, Li HT, Shi YS, Han JS, Wan Y. Ketamine potentiates the effect of electroacupuncture on mechanical allodynia in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Neurosci Lett. 2004. 368:327–331.11. Hwang BG, Min BI, Kim JH, Na HS, Park DS. Effects of electroacupuncture on the mechanical allodynia in the rat model of neuropathic pain. Neurosci Lett. 2002. 320:49–52.12. Sung HJ, Kim YS, Kim IS, Jang SW, Kim YR, Na DS, et al. Proteomic analysis of differential protein expression in neuropathic pain and electroacupuncture treatment models. Proteomics. 2004. 4:2805–2813.13. Oh JH, Bai SJ, Cho ZH, Han HC, Min SS, Shim I, et al. Pain relieving effects of acupuncture and electroacupuncture in an animal model of arthritic pain. Int J Neurosci. 2006. in press.14. Lee BH, Won R, Baik EJ, Lee SH, Moon CH. An animal model of neuropathic pain employing injury to the sciatic nerve branches. Neuroreport. 2000. 11:657–661.15. Gordon DB, Love G. Pharmacologic management of neuropathic pain. Pain Manag Nurs. 2004. 5(4):Suppl 1. 19–33.16. Harden N, Cohen M. Unmet needs in the management of neuropathic pain. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2003. 25(5):Suppl. S12–S17.17. Chong MS, Bajwa ZH. Diagnosis and treatment of neuropathic pain. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2003. 25(5):Suppl. S4–S11.18. Hyodo M. An objective approach to acupuncture. 1975. Japan: Ryodoraku (Automomic Nerve Society).19. Hyodo M. Liptonand S, Miles J, editors. Modern scientific acupuncture, as practiced in Japan. Persistent Pain. 1985. Olrando: Grune & Stratton;129–156.20. Gunn CC, Milbrandt WE, Little AS, Mason KE. Dry needling of muscle motor points for chronic low-back pain: a randomized clinical trial with long-term follow-up. Spine. 1980. 5:279–291.21. Li AH, Zhang JM, Xie YK. Human acupuncture points mapped in rats are associated with excitable muscle/skin-nerve complexes with enriched nerve endings. Brain Res. 2004. 1012:154–159.22. Ezzo J, Berman B, Hadhazy VA, Jadad AR, Lao L, Singh BB. Is acupuncture effective for the treatment of chronic pain? A systematic review. Pain. 2000. 86:217–225.23. Ernst E, White A. Acupuncutre: a scientific appraisal. 1999. Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann.24. Woollam CH, Jackson AO. Acupuncture in the management of chronic pain. Anaesthesia. 1998. 53:593–595.25. Kim HW, Kwon YB, Han HJ, Yang IS, Beitz AJ, Lee JH. Antinociceptive mechanisms associated with diluted bee venom acupuncture (apipuncture) in the rat formalin test: involvement of descending adrenergic and serotonergic pathways. Pharmacol Res. 2005. 51:183–188.26. Lee BH, Park SH, Won R, Park YG, Sohn JH. Antiallodynic effects produced by stimulation of the periaqueductal gray matter in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Neurosci Lett. 2000. 291:29–32.27. Cheng RS, Pomeranz B. Monoaminergic mechanism of electroacupuncture analgesia. Brain Res. 1981. 215:77–92.28. Han JS, Terenius L. Neurochemical basis of acupuncture analgesia. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1982. 22:193–220.29. Mayer DJ. Biological mechanisms of acupuncture. Prog Brain Res. 2000. 122:457–477.30. Takeshige C, Sato T, Mera T, Hisamitsu T, Fang J. Descending pain inhibitory system involved in acupuncture analgesia. Brain Res Bull. 1992. 29:617–634.31. Yonehara N. Influence of serotonin receptor antagonists on substance P and serotonin release evoked by tooth pulp stimulation with electro-acupuncture in the trigeminal nucleus cudalis of the rabbit. Neurosci Res. 2001. 40:45–51.32. Altman S. Techniques and instrumentation. Probl Vet Med. 1992. 4:66–87.33. Felhendler D, Lisander B. Pressure on acupoints decreases postoperative pain. Clin J Pain. 1996. 12:326–329.34. Chu J. The local mechanism of acupuncture. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi (Taipei). 2002. 65:299–302.35. Noguchi E, Ohsawa H, Kobayashi S, Shimura M, Uchida S, Sato Y. The effect of electro-acupuncture stimulation on the muscle blood flow of the hindlimb in anesthetized rats. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1999. 75:78–86.36. Sandberg M, Lindberg LG, Gerdle B. Peripheral effects of needle stimulation (acupuncture) on skin and muscle blood flow in fibromyalgia. Eur J Pain. 2004. 8:163–171.37. Cao X. Scientific bases of acupuncture analgesia. Acupunct Electrother Res. 2002. 27:1–14.38. Brunelli B, Gorson KC. The use of complementary and alternative medicines by patients with peripheral neuropathy. J Neurol Sci. 2004. 218:59–66.39. Phillips KD, Skelton WD, Hand GA. Effect of acupuncture administered in a group setting on pain and subjective peripheral neuropathy in persons with human immunodeficiency virus disease. J Altern Complement Med. 2004. 10:449–455.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Antiallodynic Effects between Intrathecal Cholinesterase Inhibitors and NMDA Antagonists on Two Neuropathic Pain Rat Models
- Comparison of the Antiallodynic Effects of Intrathecal Lidocaine and MK-801 on Mechanical Allodynia in Two Neuropathic Pain Rat Models
- Antiallodynic effects of intrathecal tianeptine in a neuropathic pain rat
- Antiallodynic Effect of Pregabalin in Rat Models of Sympathetically Maintained and Sympathetic Independent Neuropathic Pain
- The Mechanical Antiallodynic Effect of intrathecal Morphine and R-Phenylisopropyl-Adenosine in Rats with Spinal Nerve Ligation