J Korean Med Sci.
2012 Aug;27(8):948-952. 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.8.948.
Mosaic Ring Chromosome 6 in an Infant with Significant Patent Ductus Arteriosus and Multiple Congenital Anomalies
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Chonnam National University Medical School, Chonnam National University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea. youngcx@hanmail.net
- KMID: 1714209
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2012.27.8.948
Abstract
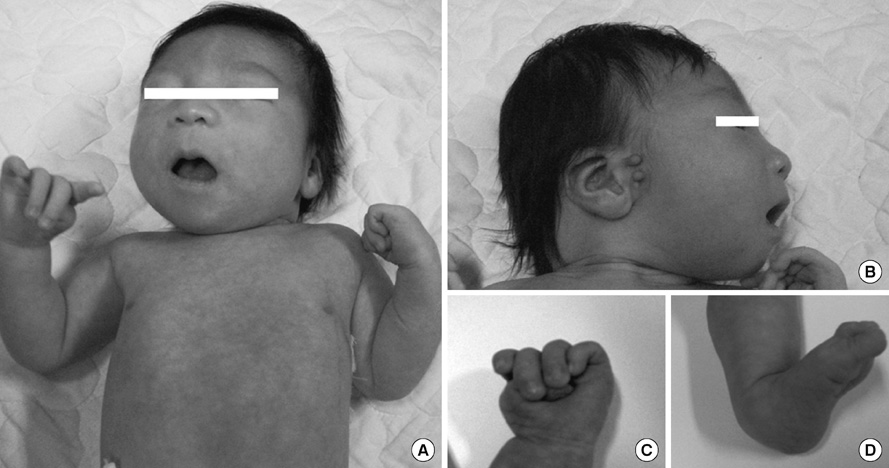
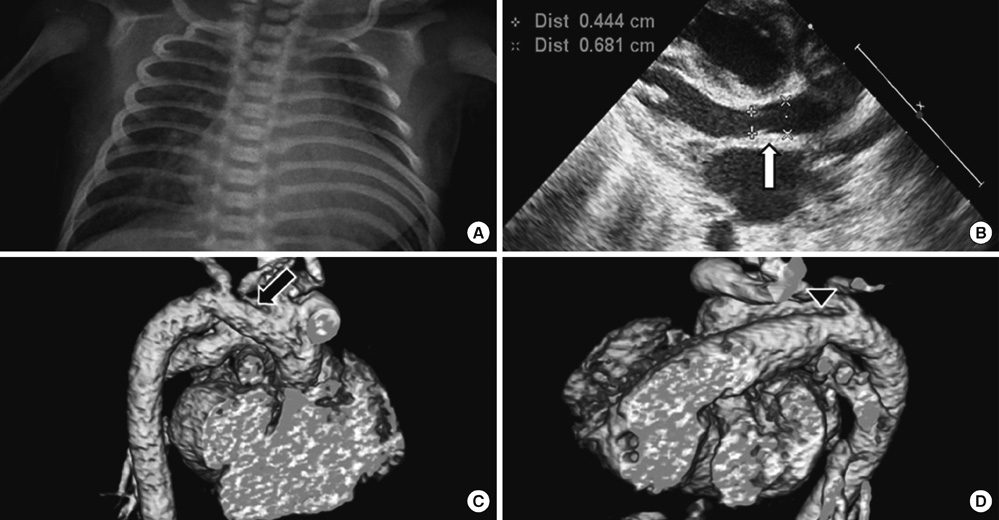
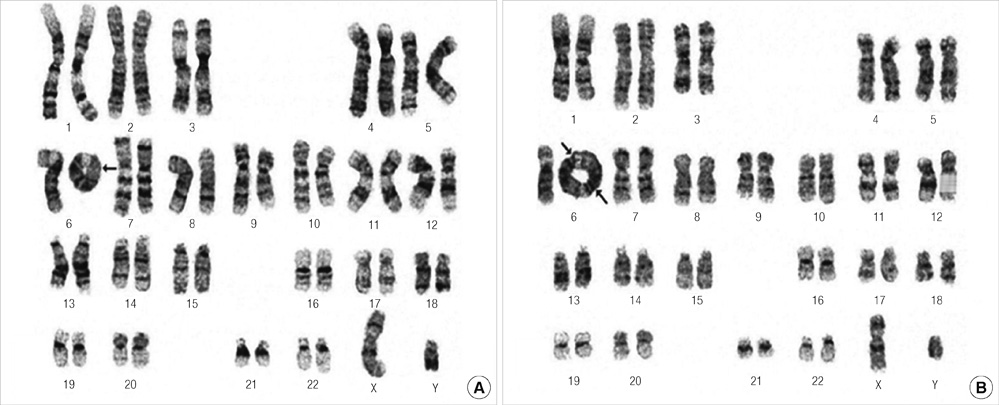
- The clinical features of ring chromosome 6 include central nervous system anomalies, growth retardation, facial dysmorphism and other congenital anomalies. Ring chromosome 6 occurs rarely and manifests as various phenotypes. We report the case of mosaic ring chromosome 6 by conventional karyotyping in a 7-day-old male infant diagnosed with a large patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) with hypoplasia of aortic valve and aortic arch. These have not been previously reported with ring chromosome 6. He recovered from heart failure symptoms after ligation of the PDA. He showed infantile failure to thrive and delayed milestone in a follow-up evaluation. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of a Korean individual with ring chromosome 6 and hemodynamically significant PDA.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Abnormalities, Multiple/*diagnosis/genetics/radiography
Aorta, Thoracic/radiography
Aortic Valve/ultrasonography
Chromosome Disorders/*diagnosis/genetics
Chromosomes, Human, Pair 6/genetics
Ductus Arteriosus, Patent/*diagnosis/genetics/radiography
Humans
Infant
Karyotyping
Male
Ring Chromosomes
Tomography, X-Ray Computed
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ahzad HA, Ramli SF, Loong TM, Salahshourifar I, Zilfalil BA, Yusoff NM. De novo ring chromosome 6 in a child with multiple congenital anomalies. Kobe J Med Sci. 2010. 56:E79–E84.2. Andrieux J, Devisme L, Valat AS, Robert Y, Frnka C, Savary JB. Prenatal diagnosis of ring chromosome 6 in a fetus with cerebellar hypoplasia and partial agenesis of corpus callosum: case report and review of the literature. Eur J Med Genet. 2005. 48:199–206.3. Moore CM, Heller RH, Thomas GH. Developmental abnormalities associated with a ring chromosome 6. J Med Genet. 1973. 10:299–303.4. Peeden JN, Scarbrough P, Taysi K, Wilroy RS, Finley S, Luthardt F, Martens P, Howard-Peebles PN. Ring chromosome 6: variability in phenotype expression. Am J Med Genet. 1983. 16:563–573.5. Salamanca-Gonez F, Nava S, Armendares S. Ring chromosome 6 in a malformed boy. Clin Genet. 1975. 8:370–375.6. Römke C, Heyne K, Stewens J, Schwinger E. Erroneous diagnosis of fetal alcohol syndrome in a patient with ring chromosome 6. Eur J Pediatr. 1987. 146:443.7. Ivanovich JL, Watson MS, Whelan AJ. An 11-year-old boy with mosaic ring chromosome 6 and dilated aortic root. Am J Med Genet. 2001. 98:182–184.8. Carnevale A, Blanco B, Castillo J, del Castillo V, Dominguez D. Ring chromosome 6 in a child with minimal abnormalities. Am J Med Genet. 1979. 4:271–277.9. Nishi Y, Yoshimura O, Ohama K, Usui T. Ring chromosome 6: case report and review. Am J Med Genet. 1982. 12:109–114.10. Chitayat D, Hahm SY, Iqbal M, Nitowsky H. Ring chromosome 6: report of a patient and literature review. Am J Med Genet. 1987. 26:145–151.11. Callen DF, Eyre HJ, Ringenbergs ML, Freemantle CJ, Woodroffe P, Haan EA. Chromosomal origin of small ring marker chromosomes in man: characterization by molecular genetics. Am J Hum Genet. 1991. 48:769–782.12. Pezzolo A, Gimelli G, Cohen A, Lavaggetto A, Romano C, Fogu G, Zuffardi O. Presence of telomeric and subtelomeric sequences at the fusion points of ring chromosomes indicates that the ring syndrome is caused by ring instability. Hum Genet. 1993. 92:23–27.13. Kosztolányi G. Does "ring syndrome" exist? An analysis of 207 case reports on patients with a ring autosome. Hum Genet. 1987. 75:174–179.14. Davies AF, Mirza G, Sekhon G, Turnpenny P, Leroy F, Speleman F, Law C, van Regemorter N, Vamos E, Flinter F, et al. Delineation of two distinct 6p deletion syndromes. Hum Genet. 1999. 104:64–72.15. Hopkin RJ, Schorry E, Bofinger M, Milatovich A, Stern HJ, Jayne C, Saal HM. New insights into the phenotype of 6q deletions. Am J Med Genet. 1997. 70:377–386.16. Pierpont ME, Basson CT, Benson DW Jr, Gelb BD, Giglia TM, Goldmuntz E, McGee G, Sable CA, Srivastava D, Webb CL. Genetic basis for congenital heart defects: current knowledge: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Congenital Cardiac Defects Committee, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young: endorsed by the American Academy of Pediatrics. Circulation. 2007. 115:3015–3038.17. Fried K, Rosenblatt M, Mundel G, Krikler R. Mental retardation and congenital malformations associated with a ring chromosome 6. Clin Genet. 1975. 7:192–196.18. Van den Berghe H, Fryns JP, Cassiman JJ, David G. Ring chromosome 6. Karotype 46, XY, r(6)-45, XY,-6. Ann Genet. 1974. 17:29–35.19. Wurster D, Pomeroy J, Benirschke K, Hoefnagel D. Mental deficiency and malformations in a boy with a group-C ring chromosome: 46,XY, Cr. J Ment Defic Res. 1969. 13:184–190.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Indomethacin therapy in premature infants with patent ductus arteriosus
- PDA Clipping by Using 2mm Thoracoscope
- A case of coaretation of the aorta associated with the patent ductus arteriosus and the persistent leftsuperior vena cava
- Nonsurgical closure of patent ductus arteriosus with the rashkind PDA occluder system
- Congenital absence of ductus arteriosus: an autopsy case