J Korean Med Sci.
2010 May;25(5):734-737. 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.5.734.
Optimal Waist Circumference Cutoff Values for Metabolic Syndrome Diagnostic Criteria in a Korean Rural Population
- Affiliations
-
- 1Health Promotion Center, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Preventive Medicine and Institute of Genomic Cohort, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea. cchung@yonsei.ac.kr
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea. cchung@yonsei.ac.kr
- 4Department of Preventive Medicine, Chosun University College of Medicine, Gwangju, Korea.
- 5Department of Preventive Medicine, Chungnam National University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- KMID: 1713958
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.5.734
Abstract
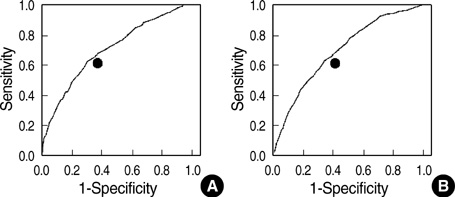
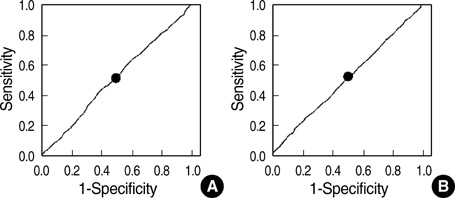
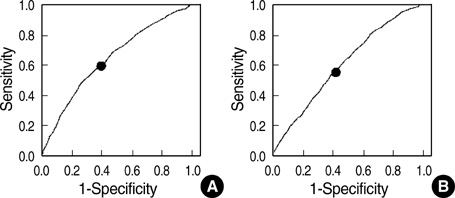
- The Korean Society for the Study of Obesity (KSSO) has defined the waist circumference cutoff value of central obesity as 90 cm for men and 85 cm for women. The purpose of this investigation was to determine the corresponding waist circumference values. A total of 3,508 persons in the Korean Rural Genomic Cohort Study were enrolled in this survey. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was used to find appropriate waist circumference cutoff values in relation to insulin resistance determined by homeostasis model assessment for insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), body mass index (BMI), and components of metabolic syndrome. The optimal waist circumference cutoff values were 87 cm for men and 83 cm for women by ROC analysis to HOMA-IR and 86 cm for men and 83 cm for women by ROC analysis to value with more than two components of metaobolic syndrome. By using a BMI > or =25 kg/m2, 86 cm for men and 82 cm for women were optimal waist circumference cutoff values. In this study, we suggest that the most reasonable waist circumference cutoff values are 86-87 cm for men and 82-83 cm for women.
MeSH Terms
-
Cohort Studies
Diagnosis, Computer-Assisted/*methods
Female
*Health Status Indicators
Humans
Korea/epidemiology
Male
Metabolic Syndrome X/*diagnosis/*epidemiology
Middle Aged
Physical Examination/methods/statistics & numerical data
Prevalence
Reproducibility of Results
Risk Assessment/methods
Risk Factors
Rural Population/*statistics & numerical data
Sensitivity and Specificity
*Waist Circumference
Figure
Reference
-
1. Reaven GM. Banting lecture 1988. Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes. 1988. 37:1595–1607.
Article2. Isomaa B, Almgren P, Tuomi T, Forsen B, Lahti K, Nissen M, Taskinen MR, Groop L. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality associated with the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Care. 2001. 24:683–689.
Article3. Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults. Executive Summary of the third report of the national cholesterol education program (NCEP) expert panel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA. 2001. 285:2486–2497.4. Alberti KG, Zimmet PZ. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabet Med. 1998. 15:539–553.
Article5. Beck-Nielsen H. General characteristics of the insulin resistance syndrome: prevalence and heritability. European Group for the study of Insulin Resistance (EGIR). Drugs. 1999. 58:Suppl 1. 7–10.6. Bloomgarden ZT. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists (AACE) consensus conference on the insulin resistance syndrome: 25-26 August 2002, Washington, DC. Diabetes Care. 2003. 26:1297–1303.
Article7. Alberti KG, Zimmet P, Shaw J. The metabolic syndrome--a new worldwide definition. Lancet. 2005. 366:1059–1062.
Article8. Lee SY, Park HS, Kim DJ, Han JH, Kim SM, Cho GJ, Kim DY, Kwon HS, Kim SR, Lee CB, Oh SJ, Park CY, Yoo HJ. Appropriate waist circumference cutoff points for central obesity in Korean adults. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007. 75:72–80.
Article9. Stern MP, Williams K, Gonzalez-Villalpando C, Hunt KJ, Haffner SM. Does the metabolic syndrome improve identification of individuals at risk of type 2 diabetes and/or cardiovascular disease? Diabetes Care. 2004. 27:2676–2681.
Article10. Lakka HM, Laaksonen DE, Lakka TA, Niskanen LK, Kumpusalo E, Tuomilehto J, Salonen JT. The metabolic syndrome and total and cardiovascular disease mortality in middle-aged men. JAMA. 2002. 288:2709–2716.
Article11. Lemieux I, Pascot A, Couillard C, Lamarche B, Tchernof A, Alméras N, Bergeron J, Gaudet D, Tremblay G, Prud'homme D, Nadeau A, Després JP. Hypertriglyceridemic waist: a marker of the atherogenic metabolic triad (hyperinsulinemia; hyperapolipoprotein B; small, dense LDL) in men? Circulation. 2000. 102:179–184.12. Perry AC, Applegate EB, Allison ML, Miller PC, Signorile JF. Relation between anthropometric measures of fat distribution and cardiovascular risk factors in overweight pre- and postmenopausal women. Am J Clin Nutr. 1997. 66:829–836.
Article13. Han TS, van Leer EM, Seidell JC, Lean ME. Waist circumference action levels in the identification of cardiovascular risk factors: prevalence study in a random sample. BMJ. 1995. 311:1401–1405.
Article14. Lear SA, Chen MM, Frohlich JJ, Birmingham CL. The relationship between waist circumference and metabolic risk factors: cohorts of European and Chinese descent. Metabolism. 2002. 51:1427–1432.
Article15. Li G, Chen X, Jang Y, Wang J, Xing X, Yang W, Hu Y. Obesity, coronary heart disease risk factors and diabetes in Chinese: an approach to the criteria of obesity in the Chinese population. Obes Rev. 2002. 3:167–172.
Article16. Steering Committee of the WHO Western Pacific Region, IASO & IOTF. The Asia-Pacific perspective: Redefining obesity and its treatment. 2000. Austrlia:17. Lee S, Choi S, Kim HJ, Chung YS, Lee KW, Lee HC, Huh KB, Kim DJ. Cutoff values of surrogate measures of insulin resistance for metabolic syndrome in Korean non-diabetic adults. J Korean Med Sci. 2006. 21:695–700.
Article18. Ryu S, Sung KC, Chang Y, Lee WY, Rhee EJ. Spectrum of insulin sensitivity in the Korean population. Metabolism. 2005. 54:1644–1651.
Article19. Kim JA, Choi CJ, Yum KS. Cut-off values of visceral fat area and waist circumference: diagnostic criteria for abdominal obesity in a Korean population. J Korean Med Sci. 2006. 21:1048–1053.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Optimal Cutoffs of Cardiometabolic Risk for Postmenopausal Korean Women
- Optimal Waist Circumference Cutoff Value Reflecting Insulin Resistance as a Diagnostic Criterion of Metabolic Syndrome in a Nondiabetic Korean Population Aged 40 Years and Over: The Chungju Metabolic Disease Cohort (CMC) Study
- Gender Differences in Diagnostic Values of Visceral Fat Area and Waist Circumference for Predicting Metabolic Syndrome in Koreans
- Prevalence of the Metabolic Syndrome and Its associated Factors among Elders in a Rural Community
- Cut-off Values of Waist Circumference for Abdominal Obesity among Koreans