J Korean Med Sci.
2010 Jan;25(1):176-179. 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.1.176.
Cervical Epidural Abscess in Haemodialysis Patients by Catheter Related Infection: Report of Two Cases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Abant lzzet Baysal University, Bolu, Turkey. ruchanergun@hotmail.com
- KMID: 1713854
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.1.176
Abstract
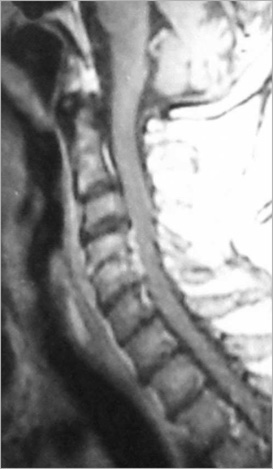
- Despite advances in neuroimaging and neurosurgical treatment modalities, spinal epidural abscess remains a challenging problem. Early diagnosis is often difficult and treatment is always delayed. Spinal epidural abscess usually develops in patients with predisposing factors such as IV drug abuse, senillity, diabetes mellitus, spinal attempts, alcoholism, immunosuppression, liver diseases and catheterizations. It is rarely seen in cervical region. A successful treatment is only possible with early diagnosis and accurate surgical and medical treatment. Optimal management is unclear and morbidity and mortality are significant. We present two adult haemodialysis patients with end-stage renal insufficiency who developed cervical epidural abscess following central venous catheter placement. Early surgical intervention is mandatory in cases those have progressive neurological deficit and spinal deformity, and this is also increases the success rate of medical therapy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ahl T, Hedstrom M, von Heijne A, Hammers Stiernstedt S. Acute spinal epidural abscess without concurrent spondylodiscitis. Successful closed treatment in 10 cases. Acta Orthop Scand. 1999. 70:199–202.
Article2. Kimura T, Hashizume K, Tanaka T, Yonemasu Y. A case of acute cervical epidural abscess. No To Shinkei. 1997. 49:359–363.3. Lu CH, Chang WN, Lui CC, Lui CC, Lee PY, Chang HW. Adult spinal epidural abscess: clinical features and prognostic factors. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2002. 104:306–310.
Article4. Mann S, Schutze M, Sola S, Piek J. Nonspecific pyogenic spondylodiscitis: clinical manifestations, surgical treatment, and outcome in 24 patients. Neurosurg Focus. 2004. 17:E3.
Article5. Reihsaus E, Waldbaur H, Seeling W. Spinal epidural abscess: a metaanalysis of 915 patients. Neurosurg Rev. 2000. 23:175–204.
Article6. Sugimoto M, Tamaki N, Nagashima T, Kokunai T, Tomita H, Sakagami Y. Cervical spinal epidural abscess caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). No Shinkei Geka. 1994. 22:973–976.7. Khan SH, Hussain MS, Griebel RW, Hattingh S. Title comparison of primary and secondary spinal epidural abscesses: a retrospective analysis of 29 cases. Surg Neurol. 2003. 59:28–33.8. Rigamonti D, Liem L, Sampath P, Knoller N, Namaguchi Y, Schreibman DL, Sloan MA, Wolf A, Zeidman S. Spinal epidural abscess: contemporary trends in etiology, evaluation, and management. Surg Neurol. 1999. 52:189–196.
Article9. Sampath P, Rigamonti D. Spinal epidural abscess: a review of epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment. J Spinal Disord. 1999. 12:89–93.10. Valero R, Castaneda O, de Francisco AL, Pinera C, Rodrigo E, Arias M. Clinical suspicion of vertebral osteomielitis: back pain in patients with hemodyalisis by catheter related infection. Nefrologia. 2004. 24:583–588.11. Chelsom J, Solberg CO. Vertebral osteomyelitis at a Norwegian university hospital 1987-97: clinical features, laboratory findings and outcome. Scand J Infect Dis. 1998. 30:147–151.12. Fieseler HG, Kumm D, Braun M. An important differential diagnosis for persistent back pain. Schmerz. 2001. 15:110–115.13. Priest DH, Peacock JE Jr. Hematogenous vertebral osteomyelitis due to Staphylococcus aureus in the adult: clinical features and therapeutic outcomes. South Med J. 2005. 98:854–862.
Article14. Kolmos HJ. Spinal epidural abscess in patients on maintenance haemodialysis: a presentation of two cases. Int Urol Nephrol. 1979. 11:249–253.
Article15. Philipneri M, Al-Aly Z, Amin K, Gellens ME, Bastani B. Routine replacement of tunneled, cuffed, hemodialysis catheters eliminates paraspinal/vertebral infections in patients with catheter-associated bacteremia. Am J Nephrol. 2003. 23:202–207.
Article16. Torda AJ, Gottlieb T, Bradbury R. Pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis: analysis of 20 cases and review. Clin Infect Dis. 1995. 20:320–328.
Article17. Lang IM, Hughes DG, Jenkins JP, St Clair Forbes W, McKenna F. MR imaging appearances of cervical epidural abscess. Clin Radiol. 1996. 50:466–471.
Article18. Muffolerro AJ, Nader R, Westmark RM, Nauta HJ, Garges KJ, Hadjipavlou AG. Hematogenous pyogenic facet joint infection of the subaxial cervical spine: a report of two cases and review of the literature. J Neurosurg. 2001. 95:1 suppl. 135–138.19. Lam KS, Pande KC, Mehdian H. Surgical decompression: a life-saving procedure for an extensive spinal epidural abscess. Eur Spine J. 1997. 6:332–335.
Article20. Tang HJ, Lin HJ, Liu YC, Li CM. Spinal epidural abscess experience with 46 patients and evaluation of prognostic factors. J Infection. 2002. 45:76–81.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Epidural Abscess after Epidural Block for Pain Management: A report of 3 cases
- Spinal Subdural Abscess Following epidural Catheterization: A case report
- Epidural Abscess following Longterm Epidural Catheterization
- Epidural Abscess after Implantation of Epidural Port in Cancer Pain Patient: A case report
- Chronic Spinal Epidural Abscess after Epidural Analgesia: Case Report