J Korean Med Sci.
2008 Apr;23(2):328-331. 10.3346/jkms.2008.23.2.328.
Identification of Proteolipid Protein 1 Gene Duplication by Multiplex Ligation-Dependent Probe Amplification: First Report of Genetically Confirmed Family of Pelizaeus-Merzbacher Disease in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, College of Medicine, Korea University, Seoul, Korea. rehab46@korea.ac.kr
- 2Department of Diagnostic Radiology, College of Medicine, Korea University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, College of Medicine, Korea University, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1713470
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2008.23.2.328
Abstract
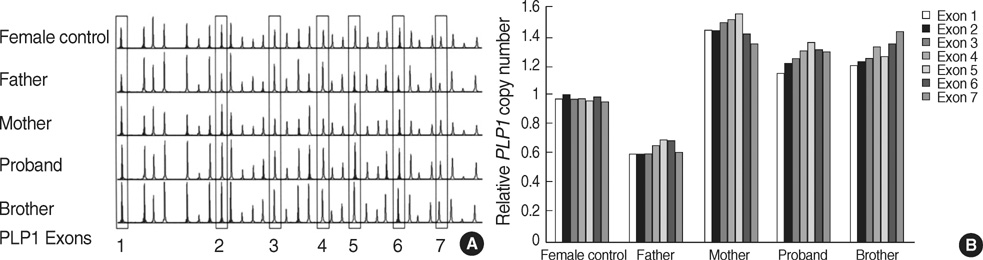
- Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease (PMD) is a rare X-linked recessive disorder with a prototype of a dysmyelinating leukodystrophy that is caused by a mutation in the proteolipid protein 1 (PLP1) gene on the long arm of the X chromosome in band Xq22. This mutation results in abnormal expression or production of PLP. We here present a Korean boy with spastic quadriplegia, horizontal nystagmus, saccadic gaze, intentional tremor, head titubation, ataxia, and developmental delay. The brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed abnormally high signal intensities in the white matter tract, including a subcortical U fiber on the T2-weighted and fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) image. The chromosomal analysis was normal; however, duplication of the PLP1 gene in chromosome Xq22 was detected when the multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA) method was used. We also investigated the pedigree for a genetic study related to PMD. This case suggests that the duplication mutation of the PLP1 gene in patients with PMD results in a mild clinical form of the disorder that mimics the spastic quadriplegia of cerebral palsy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Brain/*pathology
Child, Preschool
Chromosome Mapping
Chromosomes, Human, X
Developmental Disabilities/diagnosis/genetics
Exons
Gene Duplication
Humans
Korea
Magnetic Resonance Imaging/methods
Mutation
Myelin Proteolipid Protein/genetics
Myelin Sheath/chemistry
Pelizaeus-Merzbacher Disease/*diagnosis/*genetics
Polymerase Chain Reaction/*methods
Figure
Reference
-
1. Inoue K. PLP1-related inherited dysmyelinating disorders: pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease and spastic paraplegia type 2. Neurogenetics. 2005. 6:1–16.
Article2. Koeppen AH, Robitaille Y. Pelizaeus-Merzbacher Disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2002. 61:747–759.
Article3. Golomb MR, Walsh LE, Carvalho KS, Christensen CK, DeMyer WE. Clinical findings in Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. J Child Neurol. 2004. 19:328–331.
Article4. Kang HS, Oh SW, Park YW, Lee CG, Kim SW, Lee GJ. Two cases of Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 2000. 43:561–566.5. Kim SM, Lee BC, Kwon KH, Kim SY, Yoo KH, Jung S, Jung JW. Pelizaeus Merzbacher disease: two cases in family diagnosed by the clinical features and magnetic resonance imaging. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 1995. 13:115–122.6. Moon JL, Kang SY, Lee SE, Yoo KB. Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease: a case report. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2002. 26:108–112.7. Lee ES, Moon HK, Park YH, Garbern J, Hobson GM. A case of complicated spastic paraplegia 2 due to a point mutation in the proteolipid protein 1 gene. J Neurol Sci. 2004. 224:83–87.
Article8. Barkovich AJ. Concepts of Myelin and Myelination in Neuroradiology. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000. 21:1099–1109.9. Sistermans EA, de Coo RF, De Wijs IJ, Van Oost BA. Duplication of the proteolipid protein gene is the major cause of Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. Neurology. 1998. 50:1749–1754.
Article10. Woodward K, Kendall E, Vetrie D, Malcolm S. Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease: identification of Xq22 proteolipid-protein duplications and characterization of breakpoints by interphase FISH. Am J Hum Genet. 1998. 63:207–217.
Article11. Lee JA, Cheung SW, Ward PA, Inoue K, Lupski JR. Prenatal diagnosis of PLP1 copy number by array comparative genomic hybridization. Prenat Diagn. 2005. 25:1188–1191.12. Inoue K, Osaka H, Sugiyama N, Kawanishi C, Onishi H, Nezu A, Kimura K, Yamada Y, Kosaka K. A duplicated PLP gene causing Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease detected by comparative multiplex PCR. Am J Hum Genet. 1996. 59:32–39.13. Wolf NI, Sistermans EA, Cundall M, Hobson GM, Davis-Williams AP, Palmer R, Stubbs P, Davies S, Endziniene M, Wu Y, Chong WK, Malcolm S, Surtees R, Garbern JY, Woodward KJ. Three or more copies of the proteolipid protein gene PLP1 cause severe Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. Brain. 2005. 128:743–751.
Article14. Gao Q, Thurston VC, Vance GH, Dlouhy SR, Hodes ME. Genetic diagnosis of PLP gene duplications/deletions in patients with Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. Clin Genet. 2005. 68:466–467.
Article15. Combes P, Bonnet-Dupeyron MN, Gauthier-Barichard F, Schiffmann R, Bertini E, Rodriguez D, Armour JA, Boespflug-Tanguy O, Vaurs-Barriere C. PLP1 and GPM6B intragenic copy number analysis by MAPH in 262 patients with hypomyelinating leukodystrophies: Identification of one partial triplication and two partial deletions of PLP1. Neurogenetics. 2006. 7:31–37.
Article16. Warshawsky I, Chernova OB, Hubner CA, Stindl R, Henneke M, Gal A, Natowicz MR. Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification for rapid detection of proteolipid protein 1 gene duplications and deletions in affected males and carrier females with Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. Clin Chem. 2006. 52:1267–1275.
Article17. Sellner LN, Taylor GR. MLPA and MAPH: new techniques for detection of gene deletions. Hum Mutat. 2004. 23:413–419.
Article18. Takata M, Suzuki T, Ansai S, Kimura T, Shirasaki F, Hatta N, Saida T. Genome profiling of melanocytic tumors using multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA): its usefulness as an adjunctive diagnostic tool for melanocytic tumors. J Dermatol Sci. 2005. 40:51–57.
Article19. Wolf NI, Sistermans EA, Cundall M, Hobson GM, Davis-Williams AP, Palmer R, Stubbs P, Davies S, Endziniene M, Wu Y, Chong WK, Malcolm S, Surtees R, Garbern JY, Woodward KJ. Three or more copies of the proteolipid protein gene PLP1 cause severe Pelizaeus-merzbacher disease. Brain. 2005. 128:743–751.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pelizaeus-Merzbacher Disease with PLP1 Exon 1 Duplication, Previously Misdiagnosed as Cerebral Palsy: a Case Report
- Two Cases of Pelizaeus-Merzbacher Disease
- Magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopic analysis in 5 cases of Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease: metabolic abnormalities as diagnostic tools
- Pelizaeus-Merzbacher Disease: A case report
- Dental Treatment of a Patient with Pelizaeus-Merzbacher Disease under Outpatient General Anesthesia: A Case Report