J Korean Med Sci.
2008 Apr;23(2):232-235. 10.3346/jkms.2008.23.2.232.
Korean Ginseng-Induced Occupational Asthma and Determination of IgE Binding Components
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. youyoung@plaza.snu.ac.kr
- 2Institute of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Seoul National University Medical Research Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 1713454
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2008.23.2.232
Abstract
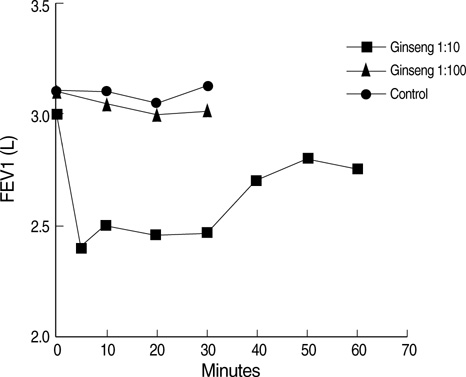
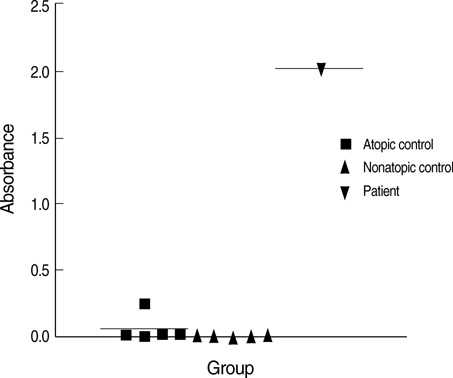
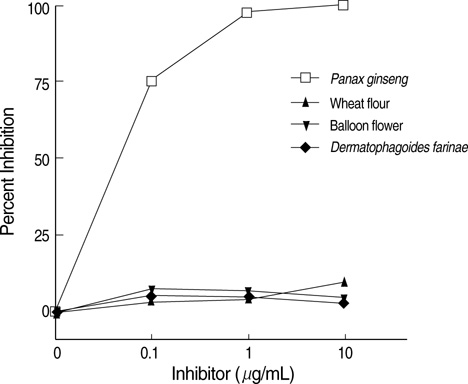
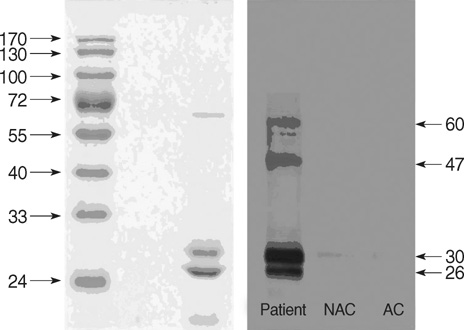
- A number of case reports on occupational asthma caused by herbal medicines have been issued, for example, on Sanyak, Chunkung, Banha, and Brazilian ginseng. Recently, cases of occupational asthma induced by Sanyak and Korean ginseng have been reported, but the pathogenic mechanisms involved are unknown. This study was carried out to evaluate the immunologic mechanism underlying Korean ginseng-induced occupational asthma. A patient engaged in Korean ginseng wholesale was referred for recurrent dyspnea, wheezing, and nasal symptoms, which were aggravated at work. Allergen bronchial provocation testing to Korean ginseng extract showed a typical immediate response, and skin prick testing to Korean ginseng extract also showed a strong positive response. Moreover, serum-specific IgE levels to Korean ginseng extract were significantly higher than in controls. Enzymelinked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) inhibition tests showed a dose-dependent inhibition by Korean ginseng, but not by Dermatophagoides farinae, wheat flour, or Chinese balloon flower. Sodium dodecylsulfate-poly-acrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and immunoblotting revealed four specific Immunoglobulin E (IgE) binding components at 26, 30, 47, and 60 kDa, which were not bound by control sera. These results strongly suggest that occupation asthma induced by Korean ginseng is induced via an IgE-mediated mechanism.
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Asthma/diagnosis/*etiology/*immunology
Bronchi/metabolism
Electrophoresis, Polyacrylamide Gel
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay/methods
Flour
Flowers
Humans
Hypersensitivity/*diagnosis
Immunoglobulin E/analysis/*chemistry
Korea
Occupational Diseases/diagnosis/*etiology/*immunology
Panax/*adverse effects
Pyroglyphidae/metabolism
*Skin Tests
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Past, Present, and Future of Allergy in Korea
You-Young Kim
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2010;2(3):155-164. doi: 10.4168/aair.2010.2.3.155.
Reference
-
1. Park HS, Kim MJ, Moon HB. Occupational asthma caused by two herb materials Dioscorea batatas and Pinellia ternata. Clin Exp Allergy. 1994; 24:575–581.
Article2. Lee SK, Cho HK, Cho SH, Kim SS, Nahm DH, Park HS. Occupational asthma and rhinitis caused by multiple herbal agents in a pharmacist. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2001; 86:469–474.
Article3. Kim SH, Jeong H, Kim YK, Cho SH, Min KU, Kim YY. IgE-mediated occupational asthma induced by herbal medicine, Banha (Pinellia ternata). Clin Exp Allergy. 2001; 31:779–781.
Article4. Subiza J, Subiza JL, Escribano PM, Hinojosa M, Garcia R, Jerez M, Subiza E. Occupational asthma caused by Brazil ginseng dust. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1991; 88:731–736.
Article5. Lee JY, Lee YD, Bahn JW, Park HS. A case of occupational asthma and rhinitis caused by Sanyak and Korean ginseng dusts. Allergy. 2006; 61:392–393.
Article6. Park HK, Jeon SG, Kim TB, Kang HR, Chang YS, Kim YK, Cho SH, Min KU, Kim YY. Occupational asthma and rhinitis induced by a herbal medicine, Wonji. J Korean Med Sci. 2005; 20:46–49.7. Kiefer D, Pantuso T. Panax ginseng. Am Fam Physician. 2003; 68:1539–1542.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Heterogeneity of IgE response to TDI-HSA conjugates by ELISA in toluene diisocyanate (TDI) -induced occupational asthma (OA) patients
- Occupational asthma and IgE antibodies to reactive dyes
- Occupational Asthma and Rhinitis Induced by a Herbal Medicine, Wonji (Polygala tenuifolia)
- Occupational asthma caused by several kinds of herb materials
- A Case of Occupational Rhinitis Induced by Maize Pollen Exposure in a Farmer: Detection of IgE-Binding Components