J Korean Med Sci.
2007 Apr;22(2):380-382. 10.3346/jkms.2007.22.2.380.
Eikenella Corrodens Cervical Spinal Epidural Abscess Induced by a Fish Bone
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Gachon University of Medicine and Science, Gil Medical Center, 1198 Guwol-dong, Namdong-gu, Incheon, Korea. lyb@gilhospital.com
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Gil Medical Center, Gachon University of Medicine and Science, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 1713207
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2007.22.2.380
Abstract
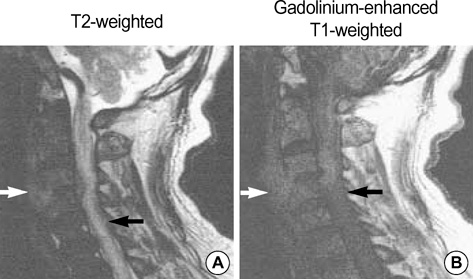
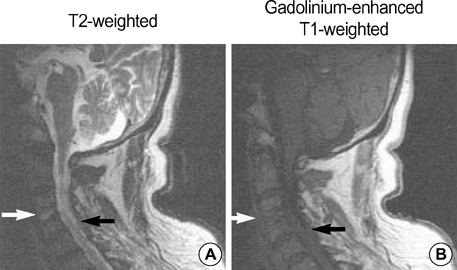
- Cervical spinal epidural abscess, caused by fish bone injury and a secondary infection by Eikenella corrodens which is part of the normal flora, has not been reported. A 72-yr-old man came to the hospital with pain in his posterior neck and both shoulders for 2 months. He also was experiencing weakness on his right side for 3 days. A fish bone had been stuck in his throat for about 2 months. Neurological examination revealed right hemiparesis, hypesthesia on the left extremities and neck stiffness. Laboratory findings showed an elevated ESR/CRP and leukocytosis, and magnetic resonance imaging revealed a retropharyngeal abscess and cervical myelitis. The patient was treated with emergency surgical decompression and antibiotics. A fish bone was removed from the C3-C4 intervertebral disc space. In the culture of chocolate blood agar and 5% sheep blood agar plate, E. corrodens was detected as a causative organism.
MeSH Terms
-
Male
Humans
Gram-Negative Bacterial Infections/diagnosis/*etiology/prevention & control
Foreign Bodies/*complications/*surgery
Food/*adverse effects
Fishes
Epidural Abscess/diagnosis/*etiology/*surgery
Eikenella corrodens/*isolation & purification
Decompression, Surgical
Bone and Bones
Anti-Bacterial Agents/administration & dosage
Animals
Aged
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Epidural Abscess Caused by Eikenella corrodens in a Previously Healthy Child
Ye Kyung Kim, Mi Seon Han, Song I Yang, Ki Wook Yun, Doo Hee Han, Jae Yoon Kim, Eun Hwa Choi
Pediatr Infect Vaccine. 2019;26(2):112-117. doi: 10.14776/piv.2019.26.e13.Oroesophageal Fish Bone Foreign Body
Heung Up Kim
Clin Endosc. 2016;49(4):318-326. doi: 10.5946/ce.2016.087.
Reference
-
1. Tsai YS, Lui CC. Retropharyngeal and epidural abscess from a swallowed fish bone. Am J Emerg Med. 1997. 15:381–382.
Article2. Curling OD, Gower DJ, McWhorter JM. Changing concepts in spinal epidural abscess: a report of 29 cases. Neurosurgery. 1990. 27:185–192.3. Heavy RJ, Vaccaro AR, Mesa JJ, Balderstone RA. Thoracolumbar infections in penetrating injuries to the spine. Orthop Clin North Am. 1996. 27:69–81.4. Durity F, Thompson GB. Localized cervical extradural abscess: case report. J Neurosurg. 1968. 28:387–390.5. Digby JM, Kersley JB. Pyogenic nontuberculous spine infection on analysis of 30 cases. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1979. 61:47–55.6. Berger S, Elidan J, Gay I. Retropharyngeal abscess caused by a traumatic perforation of the hypopharynx by a fish bone. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1990. 99:927–928.7. Har-El G, Aroesty JH, Shaha A, Lucente FE. Changing trends in deep neck abscess. A retrospective study of 110 patients. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1994. 77:446–450.8. Raab MG, Lutz RA, Stauffer ES. Eikenella corrodens vertebral osteomyelitis. A case report and literature review. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993. 293:144–147.
Article9. Nussbaum ES, Rigamonti D, Standiford H, Numagnchi Y, Wolf AL, Robinson WL. Spinal epidural abscess: a report 40 cases and review. Surg Neurol. 1992. 38:225–231.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Eikenella corrodens lsolated from Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy Wound
- Epidural Abscess Caused by Eikenella corrodens in a Previously Healthy Child
- A Case of Liver Abscess due to Eikenella corrodens Caused by Human Bites
- Infectious Keratitis Caused by Eikenella corrodens
- Chronic Spinal Epidural Abscess after Epidural Analgesia: Case Report