Cut-off Values of Visceral Fat Area and Waist Circumference: Diagnostic Criteria for Abdominal Obesity in a Korean Population
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Family Medicine, Uijeongbu St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, School of Medicine, 65-1 Kumoh-dong, Uijeongbu, Korea. yks6303@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 1713117
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2006.21.6.1048
Abstract
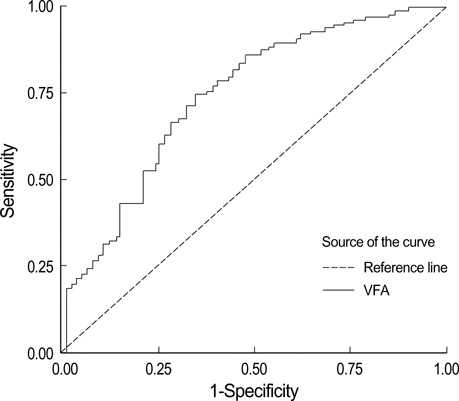
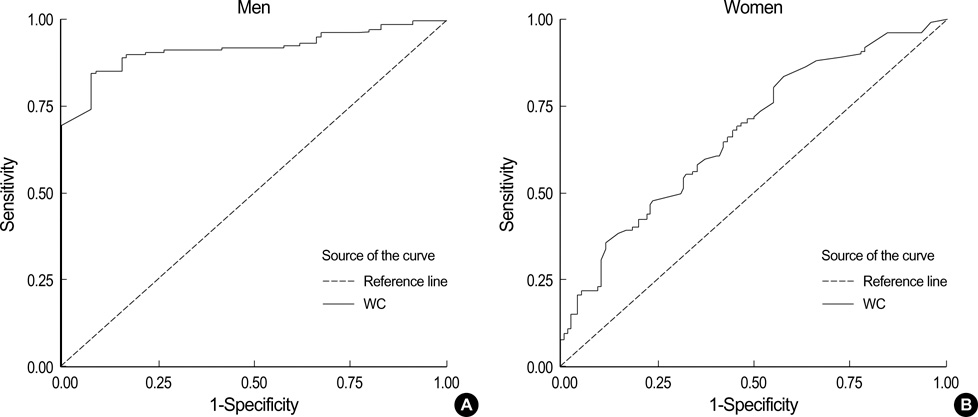
- The aim of this study was to determine the appropriate cut-off values for visceral fat area and waist circumference (WC) associated with an increase in risk for obesity-related disorder, and to validate diagnostic criteria for abdominal obesity and the metabolic syndrome in a Korean adult population. We included 413 subjects (174 men and 239 women) for this study. Subjects were selected among Korean adults who visited the obesity clinic at St. Mary's Hospital and Kangnam St. Mary's Hospital from January 1999 to August 2005. All patients had computed tomography performed. The cut-off value, of visceral fat area associated with an increase risk of obesity-related disorder, according to the receiver operating characteristics curve, was 103.8 cm2 (sensitivity 74.5%, specificity 64.7%, p<0.001). The cut-off value for the WC was 89.8 cm in men (sensitivity 84.7%, specificity 91.7%, p<0.005) and 86.1 cm in women (sensitivity 83.9%, specificity 62.9%, p<0.001). Based on the results of this study, the visceral fat area associated with an increased risk of obesity-related disorder in Korea was 103.8 cm2 and the WC was 89.8 cm in men and 86.1 cm in women.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Optimal Waist Circumference Cutoff Values for Metabolic Syndrome Diagnostic Criteria in a Korean Rural Population
Jang Hyun Koh, Sang Baek Koh, Mi Young Lee, Pil Moon Jung, Bo Hwan Kim, Jang Yel Shin, Young Goo Shin, So Yeon Ryu, Tae Yong Lee, Jong Ku Park, Choon Hee Chung
J Korean Med Sci. 2010;25(5):734-737. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.5.734.Cut-Off Values of Visceral Fat Area and Waist-to-Height Ratio: Diagnostic Criteria for Obesity-Related Disorders in Korean Children and Adolescents
Kang-Kon Lee, Hye-Soon Park, Keun-Sang Yum
Yonsei Med J. 2012;53(1):99-105. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2012.53.1.99.Visceral-to-Subcutaneous Abdominal Fat Ratio Is Associated with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Liver Fibrosis
Chan-Hee Jung, Eun-Jung Rhee, Hyemi Kwon, Yoosoo Chang, Seungho Ryu, Won-Young Lee
Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(1):165-176. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2020.35.1.165.Sex Differences of Visceral Fat Area and Visceral-to-Subcutaneous Fat Ratio for the Risk of Incident Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Eun Hee Kim, Hong-Kyu Kim, Min Jung Lee, Sung-Jin Bae, Jaewon Choe, Chang Hee Jung, Chul-Hee Kim, Joong-Yeol Park, Woo Je Lee
Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):486-498. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2021.0095.
Reference
-
1. Steering Committee of the WHO Western Pacific Region, IASO & IOTF. The Asia-Pacific perspective: Redefining obesity and its treatment. 2000. Australia:2. Kobayashi H, Nakamura T, Miyaoka K, Nishida M, Funahashi T, Yamashita S, Matsuzawa Y. Visceral fat accumulation contributes to insulin resistance, small-sized low-density lipoprotein, and progression of coronary artery disease in middle-aged non-obese Japanese men. Jpn Circ J. 2001. 65:193–199.
Article3. Fujimoto WY, Newell-Morris LL, Grote M, Bergstrom RW, Shuman WP. Visceral fat obesity and morbidity: NIDDM and atherogenic risk in Japanese-American men and women. Int J Obes. 1991. 15:Suppl 2. 41–44.4. Pouliot MC, Despres JP, Lemieux S, Moorjari S, Bouchard C, Tremblay A, Nadeau A, Lupien PJ. Waist circumference and abdominal sagittal diameter: best simple anthropometric indexes of abdominal visceral adipose tissue accumulation and related cardiovascular risk in men and women. Am J Cardiol. 1994. 73:460–468.
Article5. Han TS, Van Leer EM, Seidell JC, Lean ME. Waist circumference action levels in the identification of cardiovascular risk factors: prevalence study in a random sample. BMJ. 1995. 311:1401–1405.
Article6. NHLBI. Executive Summary of The Third Report of The National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol In Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA. 2001. 285:2486–2497.7. Ferland M, Despres JP, Tremblay A, Pinault S, Nadeau A, Moorjani S, Lupien PJ, Theriault G, Bouchard C. Assessment of adipose tissue distribution by computed axial tomography in obese women: association with body density and anthropometric measurements. Br J Nutr. 1989. 61:139–148.
Article8. American Society of Hypertension. Recommendations for routine blood pressure measurement by indirect cuff sphygmomanometry. Am J Hypertens. 1992. 5:207–209.9. The Examination Committee of Criteria for 'Obesity Disease' in Japan, Japan Society for the Study of Obesity. New criteria for 'obesity disease' in Japan. Circ J. 2002. 66:987–992.10. Tokunaga K, Matsuzawa Y, Ishikawa K, Tarui S. A novel technique for the determination of body fat by computed tomography. Int J Obes. 1983. 7:437–445.11. Seidell JC, Bakker CJ, van der Kooy K. Imaging techniques for measuring adipose-tissue distribution: A comparison between computed tomography and 1.5T magnetic resonance. Am J Clin Nutr. 1990. 51:953–957.12. Perry AC, Applegate EB, Allison ML, Miller PC, Siganorile JF. Relation between anthropometric measures of fat distribution and cardiovascular risk factors in overweight pre- and postmenopausal women. Am J Clin Nutr. 1997. 66:829–836.
Article13. Kim SM, Kim SS, Yoon SJ, Shim KW, Choi HJ, Kim KM, Lee DJ. What is the best simple anthropometric indexes of abdominal visceral fat in obese patients? Korean J Obes. 1998. 7:157–168.14. Alberti KG, Zimmet PZ. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabet Med. 1998. 15:539–553.
Article15. Lear SA, Chen MM, Frohlich JJ, Birmingham CL. The relationship between waist circumference and metabolic risk factors: cohorts of European and Chinese descent. Metabolism. 2002. 51:1427–1432.
Article16. Li G, Chen X, Jang Y, Wang J, Xing X, Yang W, Hu Y. Obesity, coronary heart disease risk factors and diabetes in Chinese: an approach to the criteria of obesity in the Chinese population. Obes Rev. 2002. 3:167–172.
Article17. Araneta MR, Wingard DL, Barrett-Connor E. Type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome in Filipina-American women: A high-risk non-obese population. Diabetes Care. 2002. 25:494–499.18. Fujimoto WY, Bergstrom RW, Boyko EJ, Chen K, Kahn SE, Leonetti DL, McNeely MJ, Newell LL, Shofer JB, Wahl PW. Type 2 diabetes and the metabolic syndrome in Japanese Americans. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2000. 50:Suppl 2. S73–S76.
Article19. McKeigue PM, Shah B, Marmot MG. Relation of central obesity and insulin resistance with high diabetes prevalence and cardiovascular risk in South Asians. Lancet. 1991. 337:382–386.
Article20. Deurenberg-Yap M, Chew SK, Deurenberg P. Elevated body fat percentage and cardiovascular risks at low body mass index levels among Singaporean Chinese, Malays and Indians. Obes Rev. 2002. 3:209–215.
Article21. Gurrici S, Hartriyanti Y, Hautvast JG, Deurenberg P. Relationship between body fat and body mass index: differences between Indonesians and Dutch Caucasians. Eur J Clin Nutr. 1998. 52:779–783.
Article22. Park YW, Allison DB, Heymsfield SB, Gallagher D. Larger amounts of visceral adipose tissue in Asian Americans. Obes Res. 2001. 9:381–387.
Article23. Grundy SM. Hypertriglyceridemia, insulin resistance, and the metabolic syndrome. Am J Cardiol. 1999. 83:25F–29F.
Article24. Unwin N, Harland J, White M, Bhopal R, Winocour P, Stephenson P, Watson W, Tuner C, Alberti KG. Body mass index, waist circumference, waist-hip ratio, and glucose intolerance in Chinese and Europid adults in Newcastle, UK. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1997. 51:160–166.
Article25. Kwon HS, Park YM, Lee HJ, Lee JH, Choi YH, Ko SH, Lee JM, Kim SR, Kang SY, Lee WC, Ahn MS, Noh JH, Kang JM, Kim DS, Yoon KH, Cha BY, Lee KW, Kang SK, Son HY. The prevalence and clinical characteristics of the metabolic syndrome in middle-aged Korean adults. Korean J Intern Med. 2005. 20:310–316.26. Choi SH, Kim DJ, Lee KE, Kim YM, Song YD, Kim HD, Ahn CW, Cha BS, Huh KB, Lee HC. Cut-off value of waist circumference for metabolic syndrome patients in Korean adult population. Korean J Obes. 2004. 13:53–60.27. Park HS, Yun YS, Park JY, Kim YS, Choi JM. Obesity, abdominal obesity, and clustering of cardiovascular risk factors in South Korea. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2003. 12:411–418.28. Lee HJ, Kwon HS, Park YM, Chun HN, Choi YH, Ko SH, Lee JM, Yoon KH, Cha BY, Lee WC, Lee KW, Son HY, Kang SK, Ahn MS, Kang JM, Kim DS. Waist circumference as a risk factor for metabolic syndrome in Korean adult; evaluation from 5 different criteria of metabolic syndrome. J Korean Diaetes Assoc. 2005. 29:48–56.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cut-off Value of Visceral Fat Area at Risk of Obesity-related Disorders in Korean Adult Population
- The Association of Visceral Fat Area with Anthropometric Variables and its Risk for Metabolic Syndrome
- The Accuracy of the Assessment of Visceral Obesity by InBody 4.0 and Waist Circumference
- The correlation between simple anthropometric indices and abdominal visceral fat accumulation by computed tomography
- Cut-Off Values for Visceral Fat Area Identifying Korean Adults at Risk for Metabolic Syndrome