Korean J Radiol.
2014 Feb;15(1):134-139. 10.3348/kjr.2014.15.1.134.
Calcifying Aponeurotic Fibroma: Case Report with Radiographic and MR Features
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Inje University College of Medicine, Haeundae Paik Hospital, Busan 612-896, Korea. okkimmd@hanafos.com
- 2Department of Pathology, Inje University College of Medicine, Haeundae Paik Hospital, Busan 612-896, Korea.
- KMID: 1711488
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.1.134
Abstract
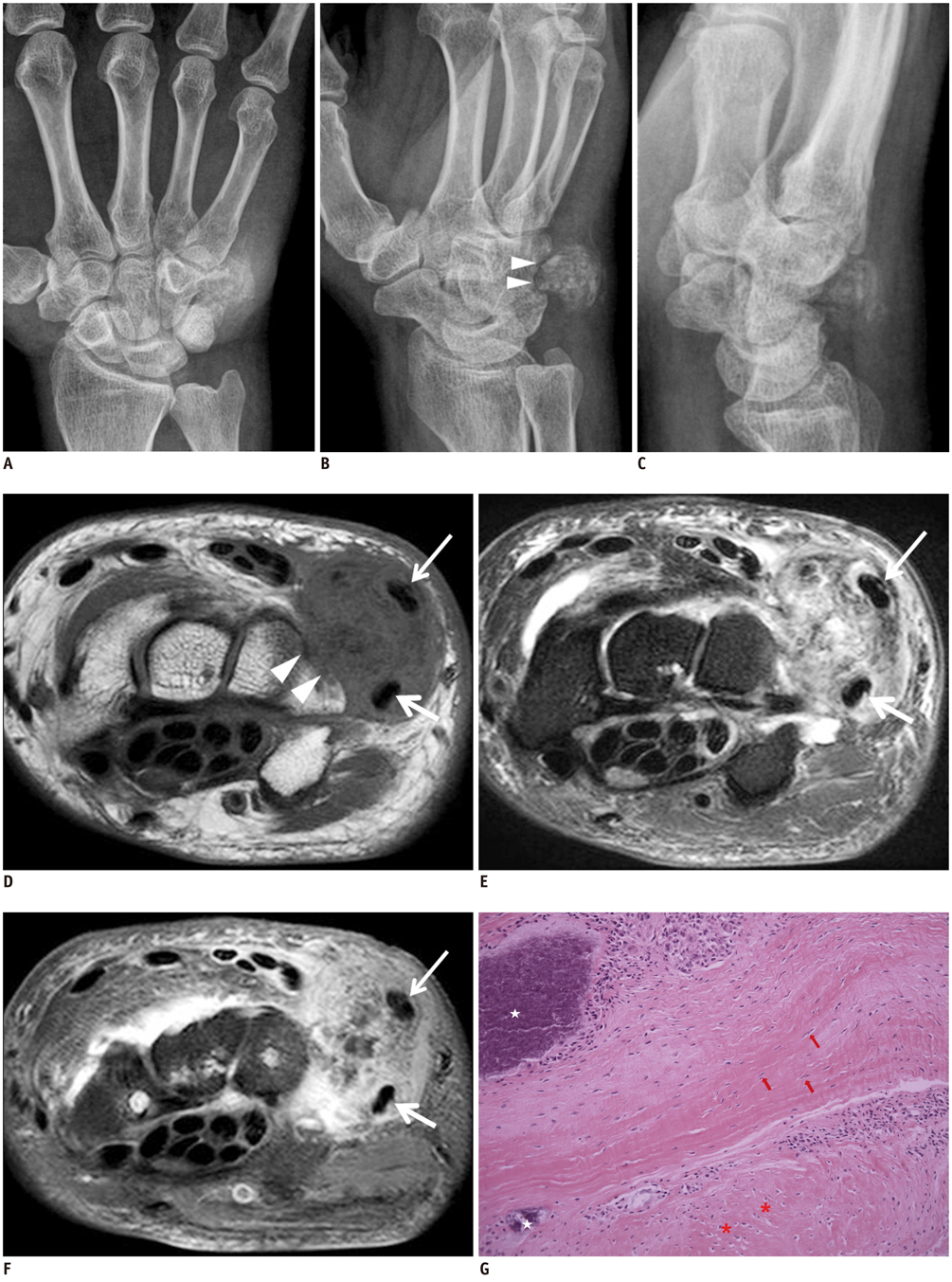
- Calcifying aponeurotic fibroma is a rare, benign fibroblastic tumor. The lesion has a propensity for local invasion and a high recurrent rate. Therefore, accurate preoperative diagnosis and complete excision are important to prevent the recurrence of the tumor after surgical removal. However, radiographic and magnetic resonance imaging findings of calcifying aponeurotic fibroma have been extremely rarely described in the radiology literature. Thus, we report a rare case of calcifying aponeurotic fibroma affecting the dorsal wrist in a 67-year-old man, describe radiographic and MR findings, and discuss the differential diagnosis of the tumor.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Calcifying Aponeurotic Fibroma of the Knee: a Case Report with Radiographic and MRI Finding
Seung Hyun Lee, In Sook Lee, You Seon Song, Kyung Un Choi, Jeung Il Kim, Jong Woon Song
Investig Magn Reson Imaging. 2017;21(4):259-263. doi: 10.13104/imri.2017.21.4.259.
Reference
-
1. Keasbey LE. Juvenile aponeurotic fibroma (calcifying fibroma); a distinctive tumor arising in the palms and soles of young children. Cancer. 1953; 6:338–346.2. Goldman RL. The cartilage analogue of fibromatosis (aponeurotic fibroma). Further observations based on 7 new cases. Cancer. 1970; 26:1325–1331.3. Murphey MD, Ruble CM, Tyszko SM, Zbojniewicz AM, Potter BK, Miettinen M. From the archives of the AFIP: musculoskeletal fibromatoses: radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics. 2009; 29:2143–2173.4. Kwak HS, Lee SY, Kim JR, Lee KB. MR imaging of calcifying aponeurotic fibroma of the thigh. Pediatr Radiol. 2004; 34:438–440.5. Lafferty KA, Nelson EL, Demuth RJ, Miller SH, Harrison MW. Juvenile aponeurotic fibroma with disseminated fibrosarcoma. J Hand Surg Am. 1986; 11:737–740.6. Enzinger FM, Weiss SW. Fibrous tumors of infancy andchildhood. In : Enzinger FM, Weiss SW, editors. Soft tissue tumors. 3rd ed. St. Louis: Mosby;1995. p. 231–268.7. Fetsch JF, Miettinen M. Calcifying aponeurotic fibroma: a clinicopathologic study of 22 cases arising in uncommon sites. Hum Pathol. 1998; 29:1504–1510.8. Drape JL, Le Viet D. MR imaging of the fingers. In : Stoller DW, Li AE, Bredella MA, Potter HG, Rosenberg ZS, Bencardino JT, editors. Magnetic resonance imaging in orthopedics and sports medicine. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: LW & W;2007. p. 1847–1932.9. Sookur PA, Saifuddin A. Indeterminate soft-tissue tumors of the hand and wrist: a review based on a clinical series of 39 cases. Skeletal Radiol. 2011; 40:977–989.10. van Vliet M, Kliffen M, Krestin GP, van Dijke CF. Soft tissue sarcomas at a glance: clinical, histological, and MR imaging features of malignant extremity soft tissue tumors. Eur Radiol. 2009; 19:1499–1511.