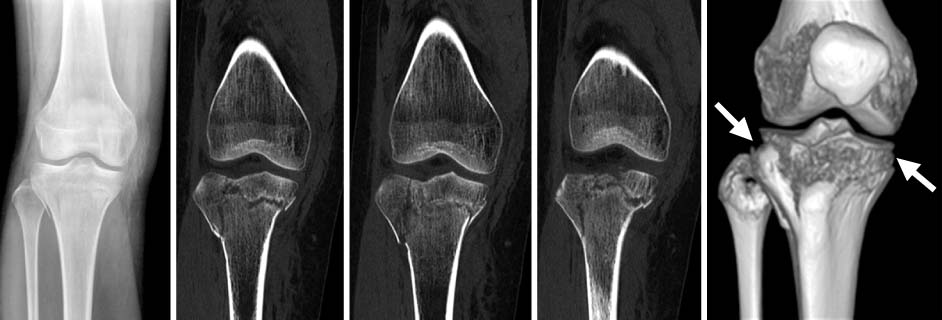
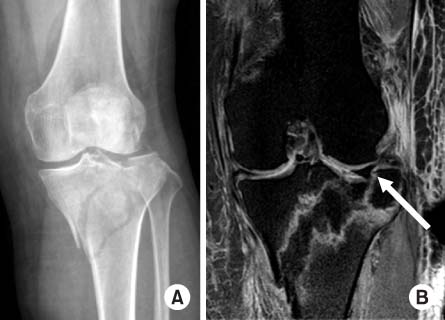
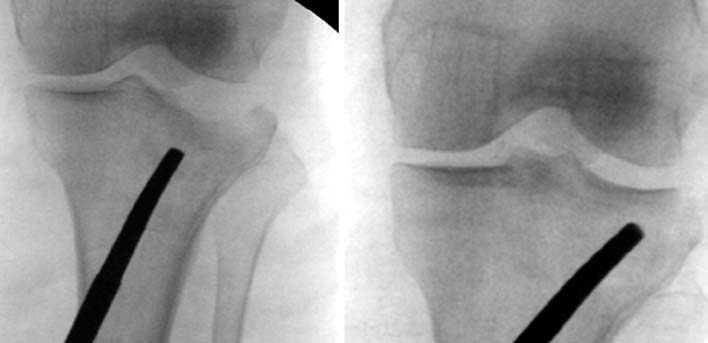
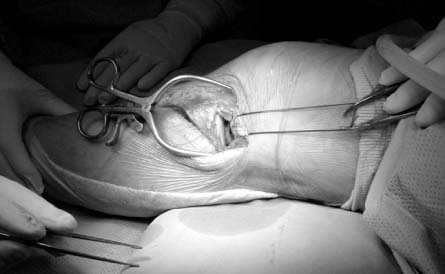
J Korean Fract Soc.
2014 Jul;27(3):245-260. 10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.3.245.
Current Concepts in Management of Tibia Plateau Fracture
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Center for Joint Diseases and Rheumatism, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. drkim@khu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1708719
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.3.245
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lin S, Mauffrey C, Hammerberg EM, Stahel PF, Hak DJ. Surgical site infection after open reduction and internal fixation of tibial plateau fractures. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014; 24:797–803.
Article2. Moore TM, Patzakis MJ, Harvey JP. Tibial plateau fractures: definition, demographics, treatment rationale, and long-term results of closed traction management or operative reduction. J Orthop Trauma. 1987; 1:97–119.3. Scott WN. Insall & scott surgery of the knee. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone;2006. p. 1133–1146.4. Young MJ, Barrack RL. Complications of internal fixation of tibial plateau fractures. Orthop Rev. 1994; 23:149–154.5. Brunner A, Horisberger M, Ulmar B, Hoffmann A, Babst R. Classification systems for tibial plateau fractures; does computed tomography scanning improve their reliability? Injury. 2010; 41:173–178.
Article6. Doornberg JN, Rademakers MV, van den Bekerom MP, et al. Two-dimensional and three-dimensional computed tomography for the classification and characterisation of tibial plateau fractures. Injury. 2011; 42:1416–1425.
Article7. Macarini L, Murrone M, Marini S, Calbi R, Solarino M, Moretti B. Tibial plateau fractures: evaluation with multidetector-CT. Radiol Med. 2004; 108:503–514.8. Markhardt BK, Gross JM, Monu JU. Schatzker classification of tibial plateau fractures: use of CT and MR imaging improves assessment. Radiographics. 2009; 29:585–597.
Article9. Barei DP, Nork SE, Mills WJ, Coles CP, Henley MB, Benirschke SK. Functional outcomes of severe bicondylar tibial plateau fractures treated with dual incisions and medial and lateral plates. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006; 88:1713–1721.
Article10. Lobenhoffer P. Posterolateral transfibular approach to tibial plateau fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2011; 25:e31. author reply e31.
Article11. Cannada LK, Anglen JO, Archdeacon MT, Herscovici D Jr, Ostrum RF. Avoiding complications in the care of fractures of the tibia. Instr Course Lect. 2009; 58:27–36.12. Chang YH, Tu YK, Yeh WL, Hsu RW. Tibial plateau fracture with compartment syndrome: a complication of higher incidence in Taiwan. Chang Gung Med J. 2000; 23:149–155.13. Gardner MJ, Yacoubian S, Geller D, et al. The incidence of soft tissue injury in operative tibial plateau fractures: a magnetic resonance imaging analysis of 103 patients. J Orthop Trauma. 2005; 19:79–84.
Article14. Mui LW, Engelsohn E, Umans H. Comparison of CT and MRI in patients with tibial plateau fracture: can CT findings predict ligament tear or meniscal injury? Skeletal Radiol. 2007; 36:145–151.
Article15. Shepherd L, Abdollahi K, Lee J, Vangsness CT Jr. The prevalence of soft tissue injuries in nonoperative tibial plateau fractures as determined by magnetic resonance imaging. J Orthop Trauma. 2002; 16:628–631.
Article16. Marsh JL, Slongo TF, Agel J, et al. Fracture and dislocation classification compendium - 2007: Orthopaedic Trauma Association classification, database and outcomes committee. J Orthop Trauma. 2007; 21:S1–S133.17. Tejwani NC, Hak DJ, Finkemeier CG, Wolinsky PR. High-energy proximal tibial fractures: treatment options and decision making. Instr Course Lect. 2006; 55:367–379.18. Biggi F, Di Fabio S, D'Antimo C, Trevisani S. Tibial plateau fractures: internal fixation with locking plates and the MIPO technique. Injury. 2010; 41:1178–1182.
Article19. Koval KJ, Sanders R, Borrelli J, Helfet D, DiPasquale T, Mast JW. Indirect reduction and percutaneous screw fixation of displaced tibial plateau fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 1992; 6:340–346.
Article20. Lowe JA, Tejwani N, Yoo BJ, Wolinsky PR. Surgical techniques for complex proximal tibial fractures. Instr Course Lect. 2012; 61:39–51.21. Abdel-Hamid MZ, Chang CH, Chan YS, et al. Arthroscopic evaluation of soft tissue injuries in tibial plateau fractures: retrospective analysis of 98 cases. Arthroscopy. 2006; 22:669–675.
Article22. Burdin G. Arthroscopic management of tibial plateau fractures: surgical technique. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2013; 99:S208–S218.
Article23. Chiu CH, Cheng CY, Tsai MC, et al. Arthroscopy-assisted reduction of posteromedial tibial plateau fractures with buttress plate and cannulated screw construct. Arthroscopy. 2013; 29:1346–1354.
Article24. Fowble CD, Zimmer JW, Schepsis AA. The role of arthroscopy in the assessment and treatment of tibial plateau fractures. Arthroscopy. 1993; 9:584–590.
Article25. Kim DH, Lee GC, Choi KY, Cho SW, Ha SH. Arthroscopic assisted intra-articular reduction and internal fixation of tibia plateau fracture. J Korean Fract Soc. 2013; 26:191–198.
Article26. Chang SM, Wang X, Zhou JQ, Huang YG, Zhu XZ. Posterior coronal plating of bicondylar tibial plateau fractures through posteromedial and anterolateral approaches in a healthy floating supine position. Orthopedics. 2012; 35:583–588.
Article27. Cherney S, Gardner MJ. Bicondylar tibial plateau fractures: assessing and treating the medial fragment. J Knee Surg. 2014; 27:39–45.
Article28. Luo CF, Sun H, Zhang B, Zeng BF. Three-column fixation for complex tibial plateau fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2010; 24:683–692.
Article29. He X, Ye P, Hu Y, et al. A posterior inverted L-shaped approach for the treatment of posterior bicondylar tibial plateau fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013; 133:23–28.
Article30. Oh JK, Oh CW, Hahn SB, Roh KJ, Lee KH. Treatment of complex tibial plateau fractures: a modified patient positioning for the combined anterior and posterior approaches. J Korean Fract Soc. 2006; 19:396–400.
Article31. Partenheimer A, Gösling T, Müller M, et al. Management of bicondylar fractures of the tibial plateau with unilateral fixed-angle plate fixation. Unfallchirurg. 2007; 110:675–683.32. Solomon LB, Stevenson AW, Baird RP, Pohl AP. Posterolateral transfibular approach to tibial plateau fractures: technique, results, and rationale. J Orthop Trauma. 2010; 24:505–514.
Article33. Tao J, Hang DH, Wang QG, et al. The posterolateral shearing tibial plateau fracture: treatment and results via a modified posterolateral approach. Knee. 2008; 15:473–479.
Article34. Zhang W, Luo CF, Putnis S, Sun H, Zeng ZM, Zeng BF. Biomechanical analysis of four different fixations for the posterolateral shearing tibial plateau fracture. Knee. 2012; 19:94–98.
Article35. Chen WT, Zhang YQ, Chang SM. Posterolateral approach for plating of tibial plateau fractures and the risk of injury to the anterior tibial vessels. J Orthop Trauma. 2013; 27:e228–e229.
Article36. Huang YG, Chang SM. The posterolateral approach for plating tibial plateau fractures: problems in secondary hardware removal. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012; 132:733–734.
Article37. Apley AG. Fractures of the tibial plateau. Orthop Clin North Am. 1979; 10:61–74.
Article38. DeCoster TA, Nepola JV, el-Khoury GY. Cast brace treatment of proximal tibia fractures. A ten-year follow-up study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988; (231):196–204.39. Drennan DB, Locher FG, Maylahn DJ. Fractures of the tibial plateau. Treatment by closed reduction and spica cast. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1979; 61:989–995.
Article40. Bozkurt M, Turanli S, Doral MN, et al. The impact of proximal fibula fractures in the prognosis of tibial plateau fractures: a novel classification. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2005; 13:323–328.
Article41. Choi JY, Shin YW, Lee BJ. Analysis of risk factors for the posterolateral articular depression and status of posterolateral fragment in lateral condylar and bicondylar tibial plateau fractures with joint depression. J Korean Fract Soc. 2013; 26:241–247.
Article42. Cho KY, Oh HS, Yoo JH, Kim DH, Cho YJ, Kim KI. Treatment of schatzker type V and VI tibial plateau fractures using a midline longitudinal incision and dual plating. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2013; 25:77–83.
Article43. Cift H, Cetik O, Kalaycioglu B, Dirikoglu MH, Ozkan K, Eksioglu F. Biomechanical comparison of plate-screw and screw fixation in medial tibial plateau fractures (Schatzker 4). A model study. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2010; 96:263–267.
Article44. Gosling T, Schandelmaier P, Muller M, Hankemeier S, Wagner M, Krettek C. Single lateral locked screw plating of bicondylar tibial plateau fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005; 439:207–214.
Article45. Hasan S, Ayalon OB, Yoon RS, et al. A biomechanical comparison between locked 3.5-mm plates and 4.5-mm plates for the treatment of simple bicondylar tibial plateau fractures: is bigger necessarily better? J Orthop Traumatol. 2014; 15:123–129.
Article46. Jiang R, Luo CF, Wang MC, Yang TY, Zeng BF. A comparative study of Less Invasive Stabilization System (LISS) fixation and two-incision double plating for the treatment of bicondylar tibial plateau fractures. Knee. 2008; 15:139–143.
Article47. Kraus TM, Martetschläger F, Müller D, et al. Return to sports activity after tibial plateau fractures: 89 cases with minimum 24-month follow-up. Am J Sports Med. 2012; 40:2845–2852.
Article48. Weaver MJ, Harris MB, Strom AC, et al. Fracture pattern and fixation type related to loss of reduction in bicondylar tibial plateau fractures. Injury. 2012; 43:864–869.
Article49. Chae IJ, Park SW, Lee SH, Noh W, Kim HJ, Hahn SB. Treatment of Shatzker type VI tibia plateau fracture using lateral and posteromedial dual incision approach and dual plating. J Korean Fract Soc. 2009; 22:252–258.
Article50. Musahl V, Tarkin I, Kobbe P, Tzioupis C, Siska PA, Pape HC. New trends and techniques in open reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the tibial plateau. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009; 91:426–433.
Article51. Zhang Y, Fan DG, Ma BA, Sun SG. Treatment of complicated tibial plateau fractures with dual plating via a 2-incision technique. Orthopedics. 2012; 35:e359–e364.
Article52. Liu YP, Yu GR. Posterolateral approaches for the treatment of tibial plateau fractures and total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Trauma. 2011; 25:e83–e84. author reply e84-85.53. Muhm M, Schneider P, Ruffing T, Winkler H. Posterocentral approach to the posterior tibial plateau: Reconstruction of tibial plateau fractures and avulsions of the posterior cruciate ligament. Unfallchirurg. 2013; [Epub].54. Anglen JO, Aleto T. Temporary transarticular external fixation of the knee and ankle. J Orthop Trauma. 1998; 12:431–434.
Article55. Egol KA, Tejwani NC, Capla EL, Wolinsky PL, Koval KJ. Staged management of high-energy proximal tibia fractures (OTA types 41): the results of a prospective, standardized protocol. J Orthop Trauma. 2005; 19:448–455. discussion 456.56. Haidukewych GJ. Temporary external fixation for the management of complex intra- and periarticular fractures of the lower extremity. J Orthop Trauma. 2002; 16:678–685.
Article57. Oh JK. Treatment of complex tibial plateau fractures. J Korean Fract Soc. 2005; 18:349–358.
Article58. Westmoreland GL, McLaurin TM, Hutton WC. Screw pullout strength: a biomechanical comparison of large-fragment and small-fragment fixation in the tibial plateau. J Orthop Trauma. 2002; 16:178–181.
Article59. Karunakar MA, Egol KA, Peindl R, Harrow ME, Bosse MJ, Kellam JF. Split depression tibial plateau fractures: a biomechanical study. J Orthop Trauma. 2002; 16:172–177.
Article60. Koval KJ, Polatsch D, Kummer FJ, Cheng D, Zuckerman JD. Split fractures of the lateral tibial plateau: evaluation of three fixation methods. J Orthop Trauma. 1996; 10:304–308.
Article61. Schatzker J. Compression in the surgical treatment of fractures of the tibia. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1974; (105):220–239.
Article62. Schatzker J, McBroom R, Bruce D. The tibial plateau fracture. The Toronto experience 1968--1975. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979; (138):94–104.63. Ruiz-Ibán MÁ, Diaz-Heredia J, Elías-Martín E, Moros-Marco S, Cebreiro Martinez Del Val I. Repair of meniscal tears associated with tibial plateau fractures: a review of 15 cases. Am J Sports Med. 2012; 40:2289–2295.
Article64. Mauffrey C, Seligson D, Lichte P, Pape HC, Al-Rayyan M. Bone graft substitutes for articular support and metaphyseal comminution: what are the options? Injury. 2011; 42:Suppl 2. S35–S39.
Article65. Chan KK, Resnick D, Goodwin D, Seeger LL. Posteromedial tibial plateau injury including avulsion fracture of the semimembranous tendon insertion site: ancillary sign of anterior cruciate ligament tear at MR imaging. Radiology. 1999; 211:754–758.
Article66. Weil YA, Gardner MJ, Boraiah S, Helfet DL, Lorich DG. Posteromedial supine approach for reduction and fixation of medial and bicondylar tibial plateau fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2008; 22:357–362.
Article67. Bucholz RW, Court-Brown CM, Heckman JD, Tornetta P. Rockwood and Green's fractures in adults. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott;2010. p. 1780–1831.68. Tejwani NC, Achan P. Staged management of high-energy proximal tibia fractures. Bull Hosp Jt Dis. 2004; 62:62–66.69. Mahadeva D, Costa ML, Gaffey A. Open reduction and internal fixation versus hybrid fixation for bicondylar/severe tibial plateau fractures: a systematic review of the literature. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2008; 128:1169–1175.
Article70. Maroto MD, Scolaro JA, Henley MB, Dunbar RP. Management and incidence of tibial tubercle fractures in bicondylar fractures of the tibial plateau. Bone Joint J. 2013; 95:1697–1702.
Article71. Yoon YC, Oh JK, Oh CW, Sahu D, Hwang JH, Cho JW. Inside out rafting K-wire technique for tibial plateau fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012; 132:233–237.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Clinical analysis of the Tibial Piateau Fracture
- Injury of Lateral Meniscus Associated with Tibia Plateau Fracture
- A Clinical study of the Tibial Plateau Fracture
- A Clinical Study of the Tibia Plateau Fracture
- Treatment of Shatzker Type VI Tibia Plateau Fracture Using Lateral and Posteromedial Dual Incision Approach and Dual Plating