J Korean Acad Nurs.
2013 Aug;43(4):536-546. 10.4040/jkan.2013.43.4.536.
A Meta-analysis of the Effect of Walking Exercise on Lower Limb Muscle Endurance, Whole Body Endurance and Upper Body Flexibility in Elders
- Affiliations
-
- 1Nursing Informatics and Statistics Laboratory, College of Nursing, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- 2College of Nursing, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea. hapark@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1707155
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.4.536
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to determine whether walking exercise improved physical function in elderly people using meta-analysis.
METHODS
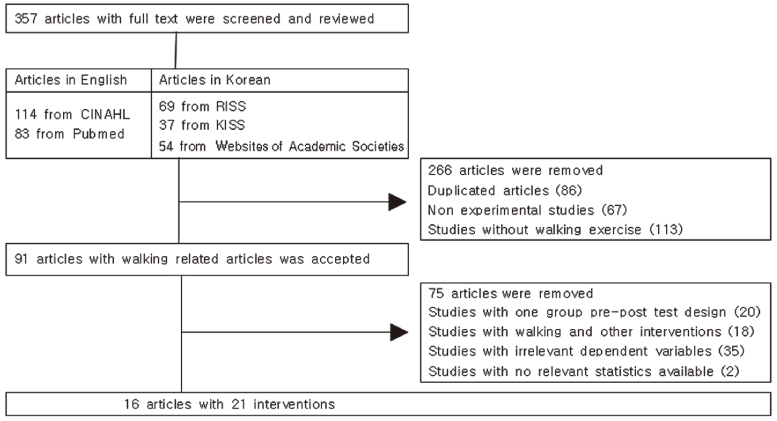
Medical and nursing literature databases were searched to identify the studies on the effectiveness of walking exercise on physical function. In the databases, there were 16 articles reporting 21 interventions. Overall effect sizes for three outcome variables, elders' physical function in lower limb muscle endurance, whole body endurance and upper body flexibility, were calculated. Effects of study characteristics on outcome variables were analyzed.
RESULTS
The meta-analysis showed that walking exercise generally had positive effects on CST (chair stand test), 6MW (6 min walking), and SRT (standing or sitting reach test) with overall weighted effect sizes of 1.06, 0.41 and 0.29 respectively. This study also showed that the chronic disease status of the elders, intervention methods, and type of residence had different effects on CST, 6MW and SRT.
CONCLUSION
The results indicate that walking exercise improves physical function in elders. Walking exercise which can be done at any time and any location is indeed a very effective exercise for elderly people.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Literature Review for the Effects of Physical Activity on Musculoskeletal Outcomes in Community-dwelling Older Adults
Kyung Choon Lim, Jeung-Im Kim, Young Ran Chae
Korean J Women Health Nurs. 2014;20(4):297-308. doi: 10.4069/kjwhn.2014.20.4.297.
Reference
-
1. Cohen J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. New York, NY: Academic Press;1977.2. Daley MJ, Spinks WL. Exercise, mobility and aging. Sports Med. 2000; 29(1):1–12.3. Bastone Ade C, Jacob Filho W. Effect of an exercise program on functional performance of institutionalized elderly. J Rehabil Res Dev. 2004; 41(5):659–668. http://dx.doi.org/10.1682/JRRD.2003.01.0014.4. Gregg EW, Cauley JA, Stone K, Thompson TJ, Bauer DC, Cummings SR, et al. Relationship of changes in physical activity and mortality among older women. JAMA. 2003; 289(18):2379–2386. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jama.289.18.2379.5. Gu MO, Conn VS. Meta-analysis of the effects of exercise interventions on functional status in older adults. Res Nurs Health. 2008; 31(6):594–603. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/nur.20290.6. Ha MS, Kwak YS, Ji JG. The effects of aerobic exercise on flexibility, MDA and SOD in musculoskeletal disease patients. Exerc Sci. 2012; 21(3):365–372.7. Hedges LV, Olkin I. Statistical methods for meta-analysis. Orlando, FL: Academic Press;1985.8. Heyn P, Abreu BC, Ottenbacher KJ. The effects of exercise training on elderly persons with cognitive impairment and dementia: A meta-analysis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2004; 85(10):1694–1704.9. Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJ, Gavaghan DJ, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: Is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials. 1996; 17(1):1–12.10. Jung YS. A meta analysis of the effects of exercise programs in the elderly. Seoul: Ewha Womans University;2006. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.11. Kang JS. Effects of a regular walking exercise on functional improvement in the Korean elderly. Seoul: Yonsei University;2007. Unpublished master's thesis.12. Kim BY. The effects of walking exercise during 12 weeks on the cardiorespiratory function and physical fitness in elderly women. J Sport Leis Stud. 2008; 33(2):851–862.13. Kim SH. Effects of intermittent walking for health related physical fitness and metabolic syndrome risk factors in elderly women. J Korean Gerontol Soc. 2009; 29(4):1397–1411.14. Kim SY, Park JE, Seo HJ, Lee YJ, Jang BH, Son HJ, et al. NECA's guidance for undertaking systematic reviews and meta-analyses for intervention. Seoul: National Evidence-based Healthcare Collaborating Agency;2011.15. Korea Institute of Sport Science. Exercise prescription. Seoul: 21st Publishing;2000.16. Lee EO, Song HH, Lee BS, Kim JH, Lee EH, Lee EJ, et al. Effects nursing interventions on anxiety and / or stress: A meta-analysis. J Nurs Acad Soc. 1992; 22(4):526–551.17. Lim HJ, Kim YS, Cho HS, Kim CH, Lim HJ, Jeong HS, et al. Effects of regular walking exercise on health-related parameters in persons with chronic diseases. J Life Sci. 2009; 19(12):1750–1757.18. Lipsey MW, Wilson DB. Practical meta-analysis. California: Sage Publications;2001.19. National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Methods for development of NICE public health guidance. London, UK: Author;2006.20. Roh KH, Park HA. A meta-analysis on the effectiveness of computer-based education in nursing. Healthc Inform Res. 2010; 16(3):149–157. http://dx.doi.org/10.4258/hir.2010.16.3.149.21. Rolland Y, Pillard F, Klapouszczak A, Reynish E, Thomas D, Andrieu S, et al. Exercise program for nursing home residents with Alzheimer's disease: A 1-year randomized, controlled trial. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2007; 55(2):158–165. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1532-5415.2007.01035.x.22. Schoenfelder DP, Rubenstein LM. An exercise program to improve fall-related outcomes in elderly nursing home residents. Appl Nurs Res. 2004; 17(1):21–31.23. Shin YH. The effect of walking exercise program on physical function and emotional state in elderly women. Seoul: Ewha Womans University;1997. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.24. Son JU, Lee JH. The effect of the walking exercise on physiological index, physical fitness, self esteem, depression and life satisfaction in the institutionalized elderly women. J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs. 2006; 17(1):5–16.25. Song HH. Meta-analysis. Paju: Cheong Moon Gak Publisher;1998.26. Statistics Korea. Government statistics of elderly in 2010. Daejeon: Author;2010.27. Sung KW. Content analysis of exercise programs for the elderly in Korean and foreign articles. J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs. 2007; 18(1):156–168.28. Tappen RM, Roach KE, Applegate EB, Stowell P. Effect of a combined walking and conversation intervention on functional mobility of nursing home residents with Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 2000; 14(4):196–201.29. Venturelli M, Scarsini R, Schena F. Six-month walking program changes cognitive and ADL performance in patients with Alzheimer. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2011; 26(5):381–388. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/1533317511418956.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effect of an Exercise Program on Body Composition and Physical Fitness in Obese Female College Students
- Exercise Testing and Prescription
- Effects of Short-Term Cardiovascular Endurance Exercise on Body Composition and Blood Pressure
- Skeletal Muscle Glycogen Breakdown According to Duration of Endurance Training
- Rehabilitative Exercise for Osteoarthritis Patients