Lab Med Online.
2014 Jul;4(3):146-151. 10.3343/lmo.2014.4.3.146.
Seroprevalences of Mycoplasma pneumoniae IgM Antibodies among Children Living in Jeju Island, Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Cheju Halla General Hospital, Jeju, Korea. kyutaeg@daum.net
- 2Department of Clinical Pathology, Cheju Halla University, Jeju, Korea.
- KMID: 1706851
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/lmo.2014.4.3.146
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Mycoplasma pneumoniae (MP) is a major cause of community-acquired pneumonia in children. The particle agglutination (PA) assay is a clinical test routinely used to detect MP infection and to determine total MP antibody titers. Using this assay, however, it is difficult to differentiate between IgM and IgG antibodies. The aim of this study was to investigate the seroprevalence of MP IgM antibodies in children living in Jeju Island.
METHODS
We investigated the seroprevalence of mycoplasma IgM antibodies in 1,693 patients in the age of 0-10 yr who were ordered for mycoplasma IgM antibody testing in Cheju Halla Hospital between April 2011 and March 2013. Results were classified according to age, sex and the month and year during which the samples were obtained.
RESULTS
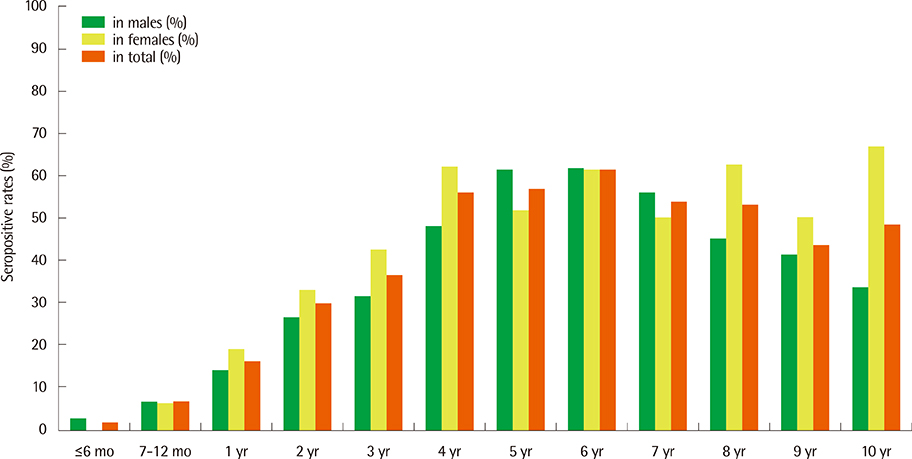
The overall positive rate for mycoplasma IgM antibody was 24.7% and was higher in females than in males (P=0.012). The positive rate was lowest in infants under 6 months of age, and gradually rose with increasing age until the age of 4 yr. A major increase in positive rates was observed between January-April of 2012 and minor cyclical increases were also observed at 2-4 month intervals during the study period.
CONCLUSIONS
The seroprevalence of mycoplasma IgM antibodies rises gradually with age until the age of 4 yr. A major peak in MP IgM antibody-positive cases was observed in early 2012, with minor cyclical increases at every 2-4 months. These results will be helpful in the interpretation and diagnosis of MP in children living in Jeju Island.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee HS, Choi KM. Recent trends in the prevalence of Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia according to age. Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis. 2008; 15:162–166.
Article2. Yun BY, Kim MR, Park JY, Choi EH, Lee HJ, Yun CK. Viral etiology and epidemiology of acute lower respiratory tract infections in Korean children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1995; 14:1054–1059.
Article3. Ahn KM, Chung SH, Chung EH, Koh YJ, Nam SY, Kim JH, et al. Clinical characteristics of acute viral lower respiratory tract infections in hospitalized children in Seoul, 1996-1998. J Korean Med Sci. 1999; 14:405–411.
Article4. Youn YS, Lee KY. Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children. Korean J Pediatr. 2012; 55:42–47.5. Kim S, Um TH, Cho CR. Evaluation of the Chorus Mycoplasma pneumoniae IgM assay for the serological diagnosis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. J Lab Med Qual Assur. 2012; 34:57–62.6. Lee K, Kim WJ, Kim DL, Kim JH, Chong MS. Frequency of Mycoplasma pneumoniae antibodies in children living on Jeju Island. Korean J Clin Microbiol. 2012; 15:32–36.
Article7. Moule JH, Caul EO, Wreghitt TG. The specific IgM response to Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection: interpretation and application to early diagnosis. Epidemiol Infect. 1987; 99:685–692.
Article8. Almasri M, Diza E, Papa A, Eboriadou M, Souliou E. Mycoplasma pneumoniae respiratory tract infections among Greek children. Hippokratia. 2011; 15:147–152.9. Hyun DS, Kwon WT. The study on the regional characteristics of climate change in Jeju Island. National institute of Meteorological Research, Korea meteorological administration;2009.10. Onozuka D, Hashizume M, Hagihara A. Impact of weather factors on Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. Thorax. 2009; 64:507–511.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Frequency of Mycoplasma pneumoniae Antibodies in Children Living on Jeju Island
- Prevalence of antibodies against chlamydia pneumoniae among blood donors and patients with tests of blood chemistry and mycoplasma pneumoniae antibody
- A clinical study of mycoplasma pneumonia in children during recent 5 years
- Bilateral Facial Nerve Palsy after Mycoplasma Pneumoniae Infection: A Variant of Guillain-Barre Syndrome?
- Clinical Characteristics of Macrolide-Resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae from Children in Jeju