J Vet Sci.
2013 Sep;14(3):299-305. 10.4142/jvs.2013.14.3.299.
Dissimilarity of ccrAB gene sequences between methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus among bovine isolates in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Microbiology, College of Veterinary Medicine and BK21 Program for Veterinary Science, Seoul National University, Seoul 151-742, Korea. yhp2738@korea.kr
- 2Departments of Veterinary Clinical Science and Animal Sciences, Washington State University, Pullman, WA 99164, USA.
- 3Animal and Plant Quarantine Agency, Anyang 430-757, Korea.
- KMID: 1705560
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2013.14.3.299
Abstract
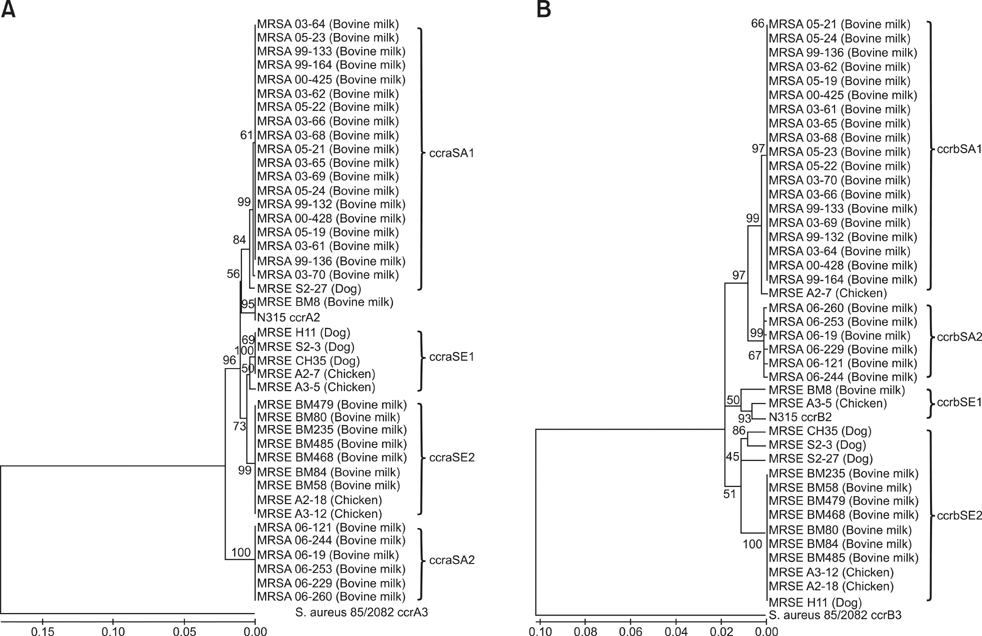
- The sequences of the ccrAB genes from bovine-, canine- and chicken-originating methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus (S.) epidermidis (MRSE) and bovine methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus (S.) aureus (MRSA) were compared to investigate the frequency of intra-species horizontal transfer of the staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec) complex. Nineteen MRSE strains were isolated from bovine milk, chickens, and dogs, and their genetic characteristics were investigated by multilocus sequence typing and SCCmec typing. Among the animal MRSE strains, the most frequent SCCmec type was type IV, which consisted of the type B mec complex and ccrAB type 2. The ccrA2 and ccrB2 genes were sequenced from the bovine, chicken and canine MRSE strains and compared with those of the bovine MRSA strains. The sequences generally clustered as MRSA and MRSE groups, regardless of the animal source. Additionally, no bovine MRSE sequence was associated with the bovine MRSA groups. Although most of the bovine MRSE and MRSA isolates possessed SCCmec type IV sequences, our results suggest that the intra-species gene transfer of the SCCmec complex between bovine S. aureus and bovine S. epidermidis strains is not a frequent event.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Anti-Bacterial Agents/*pharmacology
Bacterial Proteins/*genetics/metabolism
Bacterial Typing Techniques/veterinary
Cattle
Cattle Diseases/epidemiology/metabolism
Chickens
Dog Diseases/epidemiology/metabolism
Dogs
*Drug Resistance, Bacterial
*Gene Transfer, Horizontal
Methicillin/*pharmacology
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus/genetics/isolation & purification
Milk/microbiology
Multilocus Sequence Typing/veterinary
Poultry Diseases/epidemiology/metabolism
Prevalence
Republic of Korea/epidemiology
Staphylococcal Infections/epidemiology/microbiology/*veterinary
Staphylococcus epidermidis/genetics/isolation & purification
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Bacterial Proteins
Methicillin
Figure
Reference
-
1. Aires de Sousa M, de Lencastre H. Evolution of sporadic isolates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in hospitals and their similarities to isolates of community-acquired MRSA. J Clin Microbiol. 2003; 41:3806–3815.
Article2. Archer GL. Molecular epidemiology of multiresistant Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988; 21:Suppl C. 133–138.3. Baba T, Takeuchi F, Kuroda M, Yuzawa H, Aoki K, Oguchi A, Nagai Y, Iwama N, Asano K, Naimi T, Kuroda H, Cui L, Yamamoto K, Hiramatsu K. Genome and virulence determinants of high virulence community-acquired MRSA. Lancet. 2002; 359:1819–1827.
Article4. Bagcigil FA, Moodley A, Baptiste KE, Jensen VF, Guardabassi L. Occurrence, species distribution, antimicrobial resistance and clonality of methicillin- and erythromycin-resistant staphylococci in the nasal cavity of domestic animals. Vet Microbiol. 2007; 121:307–315.
Article5. Bochniarz M, Wawron W. Antibiotic susceptibility of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from bovine mastitis. Pol J Vet Sci. 2011; 14:405–410.
Article6. Boden-Albala B, Sacco RL, Lee HS, Grahame-Clarke C, Rundek T, Elkind MV, Wright C, Giardina EGV, DiTullio MR, Homma S, Paik MC. Metabolic syndrome and ischemic stroke risk Northern Manhattan study. Stroke. 2008; 39:30–35.7. Chongtrakool P, Ito T, Ma XX, Kondo Y, Trakulsomboon S, Tiensasitorn C, Jamklang M, Chavalit T, Song JH, Hiramatsu K. Staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec) typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated in 11 Asian countries: a proposal for a new nomenclature for SCCmec elements. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006; 50:1001–1012.
Article8. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; sixteenth informational supplement. Wayne: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2006. p. 44–51.9. Eady EA, Cove JH. Staphylococcal resistance revisited: community-acquired methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus-an emerging problem for the management of skin and soft tissue infections. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2003; 16:103–124.
Article10. Fey PD, Saïd-Salim B, Rupp ME, Hinrichs SH, Boxrud DJ, Davis CC, Kreiswirth BN, Schlievert PM. Comparative molecular analysis of community- or hospital-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003; 47:196–203.
Article11. Hanssen AM, Kjeldsen G, Sollid JUE. Local variants of Staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec in sporadic methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and methicillinresistant coagulase-negative Staphylococci: evidence of horizontal gene transfer? Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004; 48:285–296.
Article12. Hiramatsu K, Cui L, Kuroda M, Ito T. The emergence and evolution of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Trends Microbiol. 2001; 9:486–493.
Article13. Hisata K, Kuwahara-Arai K, Yamanoto M, Ito T, Nakatomi Y, Cui L, Baba T, Terasawa M, Sotozono C, Kinoshita S, Yamashiro Y, Hiramatsu K. Dissemination of methicillin-resistant staphylococci among healthy Japanese children. J Clin Microbiol. 2005; 43:3364–3372.
Article14. Ito T, Katayama Y, Asada K, Mori N, Tsutsumimoto K, Tiensasitorn C, Hiramatsu K. Structural comparison of three types of staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec integrated in the chromosome in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001; 45:1323–1336.
Article15. Ito T, Katayama Y, Hiramatsu K. Cloning and nucleotide sequence determination of the entire mec DNA of pre-methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus N315. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1999; 43:1449–1458.
Article16. Jeon BY, Kim HJ, Kim SC, Jo EK, Park JK, Paik TH, Kim SJ, Cho SN. Protection of mice against Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection by immunization with aqueous fraction of Triton X-100-soluble cell wall proteins. Scand J Immunol. 2008; 67:18–23.
Article17. Katayama Y, Ito T, Hiramatsu K. A new class of genetic element, staphylococcus cassette chromosome mec, encodes methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2000; 44:1549–1555.
Article18. Kondo Y, Ito T, Ma XX, Watanabe S, Kreiswirth BN, Etienne J, Hiramatsu K. Combination of multiplex PCRs for staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec type assignment: rapid identification system for mec, ccr, and major differences in junkyard regions. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007; 51:264–274.
Article19. Koneman EW, Allen SD, Janda WM, Schreckenberger PC, Winn WC. Color Atlas and Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;1997. p. 547–559.20. Kozitskaya S, Cho SH, Dietrich K, Marre R, Naber K, Ziebuhr W. The bacterial insertion sequence element IS256 occurs preferentially in nosocomial Staphylococcus epidermidis isolates: association with biofilm formation and resistance to aminoglycosides. Infect Immun. 2004; 72:1210–1215.
Article21. Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M. MEGA3: Integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinform. 2004; 5:150–163.
Article22. Kwon NH, Park KT, Jung WK, Youn HY, Lee Y, Kim SH, Bae W, Lim JY, Kim JY, Kim JM, Hong SK, Park YH. Characteristics of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from chicken meat and hospitalized dogs in Korea and their epidemiological relatedness. Vet Microbiol. 2006; 117:304–312.
Article23. Kwon NH, Park KT, Moon JS, Jung WK, Kim SH, Kim JM, Hong SK, Koo HC, Joo YS, Park YH. Staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec) characterization and molecular analysis for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and novel SCCmec subtype IVg isolated from bovine milk in Korea. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005; 56:624–632.
Article24. Liu D, Swiatlo E, Austin FW, Lawrence ML. Use of a putative transcriptional regulator gene as target for specific identification of Staphylococcus epidermidis. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2006; 43:325–330.
Article25. Malik S, Coombs GW, O'Brien FG, Peng H, Barton MD. Molecular typing of methicillin-resistant staphylococci isolated from cats and dogs. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2006; 58:428–431.
Article26. Mongkolrattanothai K, Boyle S, Murphy TV, Daum RS. Novel non-mecA-containing staphylococcal chromosomal cassette composite island containing pbp4 and tagF genes in a commensal staphylococcal species: a possible reservoir for antibiotic resistance islands in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004; 48:1823–1836.
Article27. Moon JS, Lee AR, Kang HM, Lee ES, Kim MN, Paik YH, Park YH, Joo YS, Koo HC. Phenotypic and genetic antibiogram of methicillin-resistant staphylococci isolated from bovine mastitis in Korea. J Dairy Sci. 2007; 90:1176–1185.
Article28. Nam HM, Lee AL, Jung SC, Kim MN, Jang GC, Wee SH, Lim SK. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus and characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bovine mastitis in Korea. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2011; 8:231–238.
Article29. Okuma K, Iwakawa K, Turnidge JD, Grubb WB, Bell JM, O'Brien FG, Coombs GW, Pearman JW, Tenover FC, Kapi M, Tiensasitorn C, Ito T, Hiramatsu K. Dissemination of new methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clones in the community. J Clin Microbiol. 2002; 40:4289–4294.
Article30. Rabaud C, Mauuary G. Infection and/or colonization by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis (MRSE). Pathol Biol (Paris). 2001; 49:812–814.
Article31. Strommenger B, Kehrenberg C, Kettlitz C, Cuny C, Verspohl J, Witte W, Schwarz S. Molecular characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains from pet animals and their relationship to humans isolates. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2006; 57:461–465.
Article32. Thomas JC, Vargas MR, Miragaia M, Peacock SJ, Archer GL, Enright MC. Improved multilocus sequence typing scheme for Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Clin Microbiol. 2007; 45:616–619.
Article33. Wielders CLC, Vriens MR, Brisse S, de Graaf-Miltenburg LAM, Troelstra A, Fleer A, Schmitz FJ, Verhoef J, Fluit AC. In-vivo transfer of mecA DNA to Staphylococcus aureus [corrected]. Lancet. 2001; 357:1674–1675.34. Yasuda R, Kawano J, Onda H, Takagi M, Shimizu A, Anzai T. Methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from healthy horses in Japan. Am J Vet Res. 2000; 61:1451–1455.
Article35. Zhang Y, Agidi S, LeJeune JT. Diversity of staphylococcal cassette chromosome in coagulase-negative staphylococci from animal sources. J Appl Microbiol. 2009; 107:1375–1383.
Article36. Ziebuhr W, Hennig S, Eckart M, Kränzler H, Batzilla C, Kozitskaya S. Nosocomial infections by Staphylococcus epidermidis: how a commensal bacterium turns into a pathogen. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2006; 28:Suppl 1. S14–S20.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Detection of Multidrug Resistant Patterns and Associated - genes of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus ( MRSA ) Isolated from Clinical Specimens
- A statistical analysis of methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus
- A case of multiple furunculosis caused by methicillin-resistant staphylococcs aureus
- Characteristics of methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus isolates from various clinical materials
- A Survey for Methicillin - Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus