J Vet Sci.
2013 Jun;14(2):199-205. 10.4142/jvs.2013.14.2.199.
Clinical use of a ceramide-based moisturizer for treating dogs with atopic dermatitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Veterinary Medicine and Research Institute for Veterinary Science, Seoul National University, Seoul 151-742, Korea. cyhwang@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1705522
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2013.14.2.199
Abstract
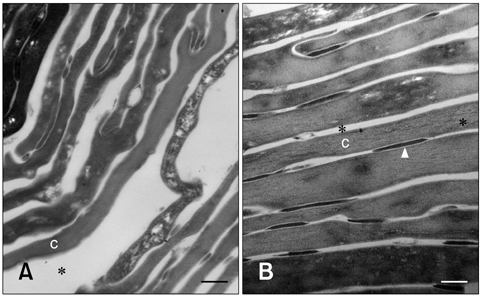
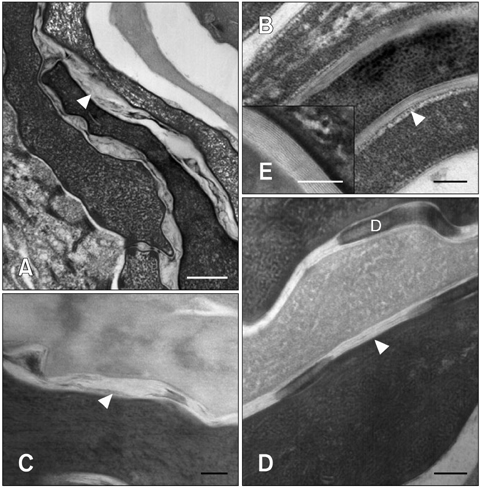
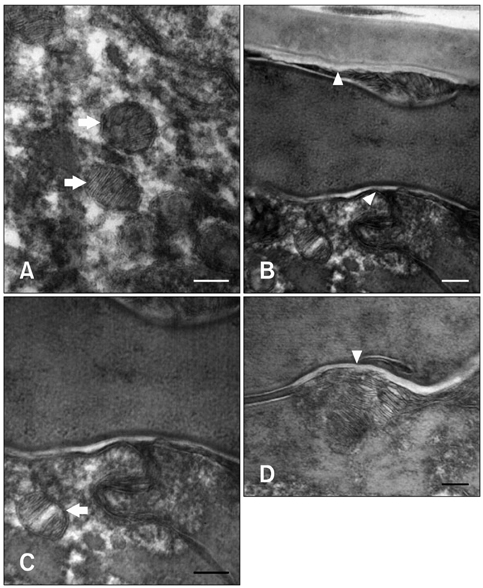
- In humans, skin barrier dysfunction is thought to be responsible for enhanced penetration of allergens. Similar to conditions seen in humans, canine atopic dermatitis (CAD) is characterized by derangement of corneocytes and disorganization of intercellular lipids in the stratum corenum (SC) with decreased ceramide levels. This study was designed to evaluate the effects of a moisturizer containing ceramide on dogs with CAD. Dogs (n = 20, 3~8 years old) with mild to moderate clinical signs were recruited and applied a moisturizer containing ceramide for 4 weeks. Transepidermal water loss (TEWL), skin hydration, pruritus index for canine atopic dermatitis (PICAD) scores, and canine atopic dermatitis extent and severity index (CADESI) scores of all dogs were evaluated. Skin samples from five dogs were also examined with transmission electron microscopy (TEM) using ruthenium tetroxide. TEWL, PICAD, and CADESI values decreased (p < 0.05) and skin hydration increased dramatically over time (p < 0.05). Electron micrographs showed that the skin barrier of all five dogs was partially restored (p < 0.05). In conclusion, these results demonstrated that moisturizer containing ceramide was effective for treating skin barrier dysfunction and CAD symptoms.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Ceramides/*therapeutic use
Cholesterol/*therapeutic use
Dermatitis, Atopic/complications/drug therapy/physiopathology/*veterinary
Dog Diseases/*drug therapy/etiology/physiopathology
Dogs
Emollients/*therapeutic use
Epidermis/drug effects/physiopathology/ultrastructure
Fatty Acids, Nonesterified/*therapeutic use
Female
Male
Microscopy, Electron, Transmission/veterinary
Pruritus/drug therapy/etiology/physiopathology/veterinary
Republic of Korea
Ruthenium Compounds/chemistry
Water Loss, Insensible/drug effects
Ceramides
Cholesterol
Emollients
Fatty Acids, Nonesterified
Ruthenium Compounds
Figure
Reference
-
1. Carlotti DN, Boulet M, Ducret J, Machicote G, Jasmin P, Rème CA, Albouy M. The use of recombinant omega interferon therapy in canine atopic dermatitis: a double-blind controlled study. Vet Dermatol. 2009; 20:405–411.
Article2. Chamlin SL, Kao J, Frieden IJ, Sheu MY, Fowler AJ, Fluhr JW, Williams ML, Elias PM. Ceramide-dominant barrier repair lipids alleviate childhood atopic dermatitis: changes in barrier function provide a sensitive indicator of disease activity. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002; 47:198–208.
Article3. Cork MJ, Robinson DA, Vasilopoulos Y, Ferguson A, Moustafa M, MacGowan A, Duff GW, Ward SJ, Tazi-Ahnini R. New perspectives on epidermal barrier dysfunction in atopic dermatitis: gene-environment interactions. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006; 118:3–21.
Article4. DeBoer DJ, Hillier A. The ACVD task force on canine atopic dermatitis (XV): fundamental concepts in clinical diagnosis. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2001; 81:271–276.
Article5. Downing DT. Lipid and protein structures in the permeability barrier of mammalian epidermis. J Lipid Res. 1992; 33:301–313.
Article6. Fartasch M. The nature of the epidermal barrier: structural aspects. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 1996; 18:273–282.
Article7. Han SH, Lee JS, Kim YJ, Kim J, Chang IS, Chung DJ, Suh KD, Kim JW. Quantitative characterization of degradation behaviors of antioxidants stabilized in lipid particles. Talanta. 2007; 71:2129–2133.
Article8. Hillier A, Griffin CE. The ACVD task force on canine atopic dermatitis (I): incidence and prevalence. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2001; 81:147–151.
Article9. Inman AO, Olivry T, Dunston SM, Monteiro-Riviere NA, Gatto H. Electron microscopic observations of stratum corneum intercellular lipids in normal and atopic dogs. Vet Pathol. 2001; 38:720–723.
Article10. Leung DYM, Boguniewicz M, Howell MD, Nomura I, Hamid QA. New insights into atopic dermatitis. J Clin Invest. 2004; 113:651–657.
Article11. Madison KC, Swartzendruber DC, Wertz PW, Downing DT. Presence of intact intercellular lipid lamellae in the upper layers of the stratum corneum. J Invest Dermatol. 1987; 88:714–718.
Article12. Marsella R, Olivry T, Carlotti DN. Current evidence of skin barrier dysfunction in human and canine atopic dermatitis. Vet Dermatol. 2011; 22:239–248.
Article13. Marsella R, Samuelson D. Unravelling the skin barrier: a new paradigm for atopic dermatitis and house dust mites. Vet Dermatol. 2009; 20:533–540.
Article14. Marsella R, Samuelson D, Doerr K. Transmission electron microscopy studies in an experimental model of canine atopic dermatitis. Vet Dermatol. 2010; 21:81–88.
Article15. Van der Meulen J, van den Bergh BAI, Mulder AA, Mommaas AM, Bouwstra JA, Koerten HK. The use of vibratome sections for the ruthenium tetroxide protocol: a key for optimal visualization of epidermal lipid bilayers of the entire human stratum corneum in transmission electron microscopy. J Microsc. 1996; 184:67–70.
Article16. Na JI, Hwang JS, Park HJ, Kim DH, Park WS, Youn SW, Huh CH, Park KC. A new moisturizer containing physiologic lipid granules alleviates atopic dermatitis. J Dermatolog Treat. 2010; 21:23–27.
Article17. Olivry T, Mueller R, Nuttall T, Favrot C, Prélaud C. Determination of CADESI-03 thresholds for increasing severity levels of canine atopic dermatitis. Vet Dermatol. 2008; 19:115–119.
Article18. Olivry T, Wofford J, Paps JS, Dunston SM. Stratum corneum removal facilitates experimental sensitization to mite allergens in atopic dogs. Vet Dermatol. 2011; 22:188–196.
Article19. Park KY, Kim DH, Jeong MS, Li K, Seo SJ. Changes of antimicrobial peptides and transepidermal water loss after topical application of tacrolimus and ceramide-dominant emollient in patients with atopic dermatitis. J Korean Med Sci. 2010; 25:766–771.
Article20. Piekutowska A, Pin D, Rème D, Gatto H, Haftek M. Effects of a topically applied preparation of epidermal lipids on the Stratum Corneum barrier of atopic dogs. J Comp Pathol. 2008; 138:197–203.
Article21. Pinnagoda J, Tupker RA, Agner T, Serup J. Guidelines for transepidermal water loss (TEWL) measurement. A report from the standardization group of the European society of contact dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. 1990; 22:164–178.22. Popa I, Thuy LH, Colsch B, Pin D, Gatto H, Haftek M, Portoukalian J. Analysis of free and protein-bound ceramides by tape stripping of stratum corneum from dogs. Arch Dermatol Res. 2010; 302:639–644.
Article23. Reiter LV, Torres SMF, Wertz PW. Characterization and quantification of ceramides in the nonlesional skin of canine patients with atopic dermatitis compared with controls. Vet Dermatol. 2009; 20:260–266.
Article24. Willemse T. Atopic dermatitis in dogs: current diagnostic criteria. Tijdschr Diergeneeskd. 1988; 113:74–79.25. Yilmaz E, Borchert HH. Effect of lipid-containing, positively charged nanoemulsions on skin hydration, elasticity and erythema an-in vivo study. Int J Pharm. 2006; 307:232–238.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Steroid-sparing Effect of an Emollient APDDR-0801 in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis
- Measurement of Atopic Dermatitis Disability
- Evaluation of the Anti-inflammatory Effect of a Moisturizer Containing Green-Tea Extracts
- The Effects of Physiogel(R) Cream on the Allergic Contact Dermatitis
- The Therapeutic Efficacy of the Moisturizer APDDR-0801 for Patients with Atopic Dermatitis