J Korean Fract Soc.
2014 Apr;27(2):162-166. 10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.2.162.
Pulmonary Embolism Complication after Surgical Treatment of Patella Fracture: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Soonchunhyang University Hospital Seoul, Seoul, Korea. knee@schmc.ac.kr
- KMID: 1703116
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.2.162
Abstract
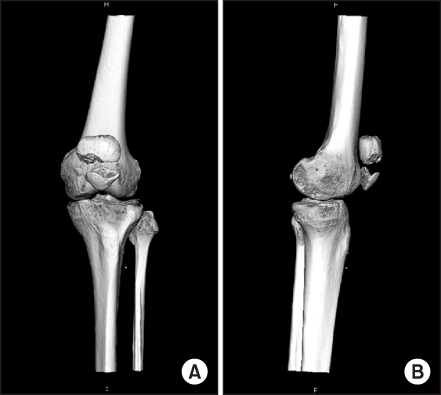
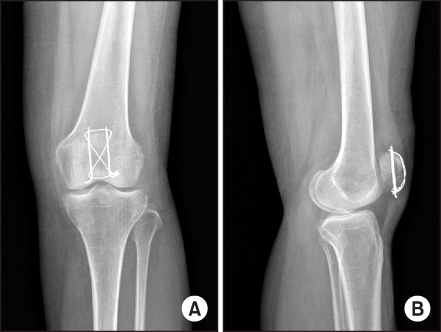
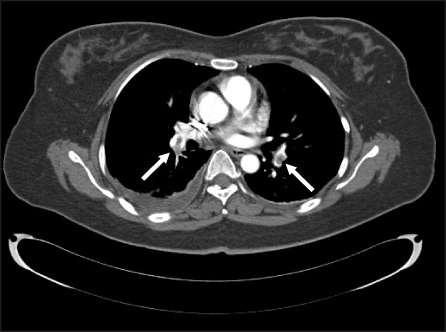
- Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism are serious and fatal complications in orthopedic surgery. Most cases of symptomatic pulmonary embolism in knee surgery have been reported after total knee arthroplasty, but rarely after patella fracture. We report on a case of symptomatic pulmonary embolism after surgical treatment of a patella fracture in a 42-year-old female patient.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Guyatt GH, Akl EA, Crowther M, Schünemann HJ, Gutterman DD, Zelman Lewis S. American College of Chest Physicians. Introduction to the ninth edition: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest. 2012; 141:48S–52S.2. Franco RF, Reitsma PH. Genetic risk factors of venous thrombosis. Hum Genet. 2001; 109:369–384.
Article3. Abelseth G, Buckley RE, Pineo GE, Hull R, Rose MS. Incidence of deep-vein thrombosis in patients with fractures of the lower extremity distal to the hip. J Orthop Trauma. 1996; 10:230–235.
Article4. Geerts WH, Code KI, Jay RM, Chen E, Szalai JP. A prospective study of venous thromboembolism after major trauma. N Engl J Med. 1994; 331:1601–1606.
Article5. Hak DJ. Prevention of venous thromboembolism in trauma and long bone fractures. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2001; 7:338–343.
Article6. Demers C, Marcoux S, Ginsberg JS, Laroche F, Cloutier R, Poulin J. Incidence of venographically proved deep vein thrombosis after knee arthroscopy. Arch Intern Med. 1998; 158:47–50.
Article7. Miyakis S, Lockshin MD, Atsumi T, et al. International consensus statement on an update of the classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). J Thromb Haemost. 2006; 4:295–306.
Article8. Kim YH, Yoo JH, Kim JS. Factors leading to decreased rates of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2007; 22:974–980.
Article9. Jang MJ, Bang SM, Oh D. Incidence of venous thromboembolism in Korea: from the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service database. J Thromb Haemost. 2011; 9:85–91.
Article10. Goel DP, Buckley R, deVries G, Abelseth G, Ni A, Gray R. Prophylaxis of deep-vein thrombosis in fractures below the knee: a prospective randomised controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009; 91:388–394.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment of Massive Pulmonary Embolism with Urokinase during Surgery for Femur Fracture
- Pulmonary and Renal Cement Embolisms During Balloon Kyphoplasty: A Case Report
- Pulmonary Embolism after Screw Fixation for a Greater Tubercle Fracture of Humerus
- Transverse Fracture through Screw Site after Cannulated Screw Fixation in Vertical Patella Fracture: A Case Report
- Untreated Sleeve Type Fracture of the Patella in Children: Report of a Case