Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab.
2014 Mar;19(1):49-52. 10.6065/apem.2014.19.1.49.
Glycogenic hepatopathy in a Korean girl with poorly controlled type 1 diabetes mellitus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. pedhwang@ajou.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- KMID: 1702665
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.6065/apem.2014.19.1.49
Abstract
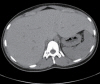
- Glycogenic hepatopathy (GH) is a rare complication of type 1 diabetes mellitus. We report the case of a 13-year-old diabetic female with poorly controlled blood sugar levels who presented with abdominal pain and distention 1 month in duration. She exhibited tender hepatomegaly, an elevated lipid profile, and elevated serum transaminase levels. Her liver histology was consistent with GH. The pathophysiology and/or underlying genetic background of GH remains unclear. The optimum treatment for GH is optimal glycemic control, and the prognosis is favorable. Clinicians should be aware of the possibility of GH and observe the clinical response to optimal glycemic control prior to invasive investigation.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sperling M. Pediatric endocrinology. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders;2008. p. 376.3. El-Karaksy HM, Anwar G, Esmat G, Mansour S, Sabry M, Helmy H, et al. Prevalence of hepatic abnormalities in a cohort of Egyptian children with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Pediatr Diabetes. 2010; 11:462–470. PMID: 20042012.
Article4. Al-Hussaini AA, Sulaiman NM, Alzahrani MD, Alenizi AS, Khan M. Prevalence of hepatopathy in type 1 diabetic children. BMC Pediatr. 2012; 12:160. PMID: 23039762.
Article5. Cha JH, Ra SH, Park YM, Ji YK, Lee JH, Park SY, et al. Three cases of glycogenic hepatopathy mimicking acute and relapsing hepatitis in type I diabetes mellitus. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2013; 19:421–425. PMID: 24459648.
Article6. Chung IH, Jeong SJ, Cho YA, Kim GI, Yoo EG. Liver dysfunction due to hepatic glycogenosis in a girl with type 1 diabetes. J Korean Soc Pediatr Endocrinol. 2009; 14:174–178.7. Jin HY, Kang DY, Choi JH. Hepatic glycogenosis in a patient with poorly controlled type 1 diabetes mellitus. Korean J Pediatr. 2009; 52:1279–1282.
Article8. Lee SH, Kwon HS, Shin JA, Kim WC, Kim JH, Choi YH, et al. A case of hepatic glycogenosis in a patient with uncontrolled type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Korean Diabetes Assoc. 2006; 30:82–86.
Article9. Park J, Song DH, Park JS, Nam JY, Kim CS, Kim DM, et al. A case of hepatomegaly due to diabetic glycogenosis reversed by glycemic control. J Korean Soc Endocrinol. 2004; 19:223–228.10. Mauriac P. Gros ventre, hepatomegalie, troubles de las croissance chez les enfants diabetiques traits depuis plusieurs annes parl'insuline. Gaz Hebd Med Bordeaux. 1930; 26:402–410.11. Abaci A, Bekem O, Unuvar T, Ozer E, Bober E, Arslan N, et al. Hepatic glycogenosis: a rare cause of hepatomegaly in Type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Complications. 2008; 22:325–328. PMID: 18413182.
Article12. Hudacko RM, Manoukian AV, Schneider SH, Fyfe B. Clinical resolution of glycogenic hepatopathy following improved glycemic control. J Diabetes Complications. 2008; 22:329–330. PMID: 18413180.
Article13. Munns CF, McCrossin RB, Thomsett MJ, Batch J. Hepatic glycogenosis: reversible hepatomegaly in type 1 diabetes. J Paediatr Child Health. 2000; 36:449–452. PMID: 11036799.
Article15. Tomihira M, Kawasaki E, Nakajima H, Imamura Y, Sato Y, Sata M, et al. Intermittent and recurrent hepatomegaly due to glycogen storage in a patient with type 1 diabetes: genetic analysis of the liver glycogen phosphorylase gene (PYGL). Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2004; 65:175–182. PMID: 15223230.
Article16. Chatila R, West AB. Hepatomegaly and abnormal liver tests due to glycogenosis in adults with diabetes. Medicine (Baltimore). 1996; 75:327–333. PMID: 8982149.
Article17. Sheth SG, Gordon FD, Chopra S. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Ann Intern Med. 1997; 126:137–145. PMID: 9005748.
Article18. Sweetser S, Kraichely RE. The bright liver of glycogenic hepatopathy. Hepatology. 2010; 51:711–712. PMID: 19957373.
Article19. Murata F, Horie I, Ando T, Isomoto E, Hayashi H, Akazawa S, et al. A case of glycogenic hepatopathy developed in a patient with new-onset fulminant type 1 diabetes: the role of image modalities in diagnosing hepatic glycogen deposition including gradient-dual-echo MRI. Endocr J. 2012; 59:669–676. PMID: 22673296.
Article20. van den Brand M, Elving LD, Drenth JP, van Krieken JH. Glycogenic hepatopathy: a rare cause of elevated serum transaminases in diabetes mellitus. Neth J Med. 2009; 67:394–396. PMID: 20009116.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Three cases of glycogenic hepatopathy mimicking acute and relapsing hepatitis in type I diabetes mellitus
- Self-Management and Its Predictors for Patients with Poorly Controlled Type 2 Diabetes
- Low Serum Testosterone Concentrations in Hospitalized Men with Poorly Controlled Type 2 Diabetes
- A case of diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state complicated with iatrogenic left femoral arterial thrombosis in a 14-year-old girl with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Blood Pressure Target in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus