J Bacteriol Virol.
2007 Mar;37(1):23-30. 10.4167/jbv.2007.37.1.23.
Development of Neutralization Assay using Murine Leukemia Virus (MuLV) Pseudotyped with Japanese encephalitis Virus (JEV) env Gene
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Animal Biotechnology, College of Animal Bioscience & Technology, Konkuk University, Seoul, 143-701, Korea. kimera@konkuk.ac.kr
- 2Biological Diagnostic Products Team Biologics Headquarters #231 Jinheungno Eunpyung-Gu, Seoul,122-704, Korea.
- 3Department of Biotechnology, The Catholic University of Korea, 43-1 Yeokgok Dong, Wonmi-Ku, Bucheon, 420-743, Korea.
- KMID: 1513549
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4167/jbv.2007.37.1.23
Abstract
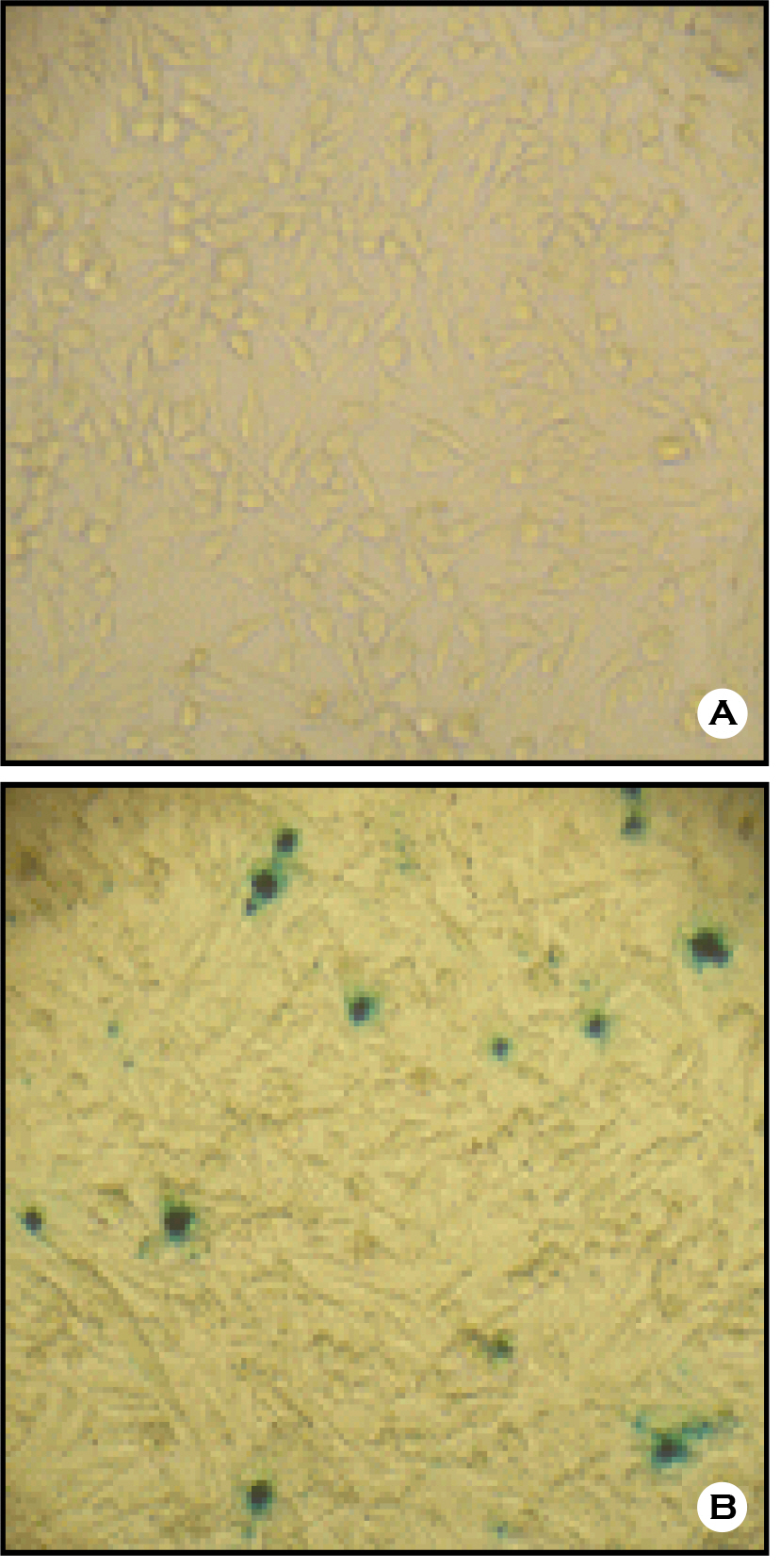
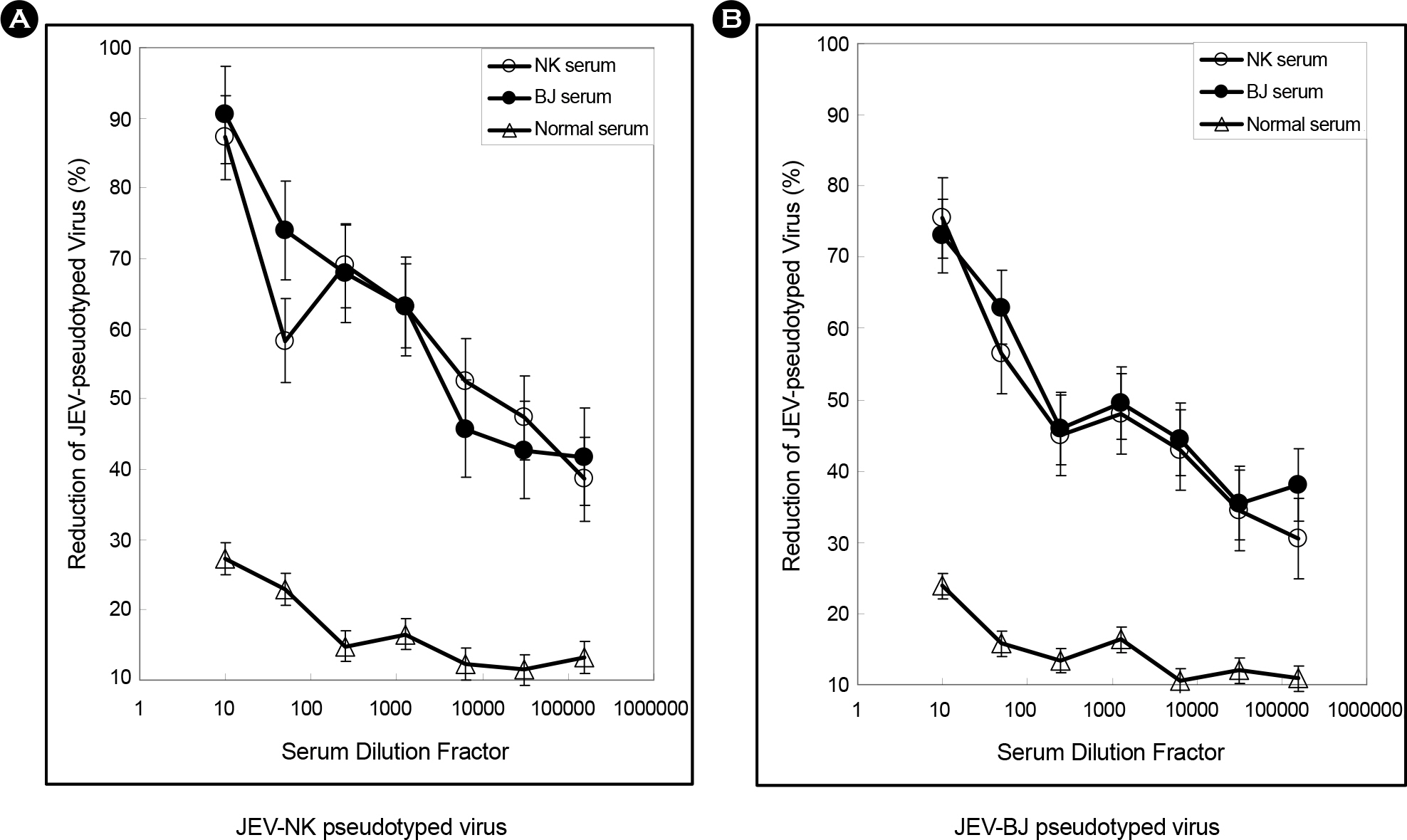
- The envelope (E) glycoprotein of JEV is the major antigen to elicit neutralizing antibody (NAb) against JEV infection. In order to develop a rapid and safe neutralization assay system for evaluation of the JEV vaccine strains, we constructed JEV-pseudotyped viruses with JEV env genes (Nakayama-NIH, Beijing-1). The titers of JEV-pseudotyped viruses with NK and BJ strains were 4.0x10(4) IFU/ml and 1.3x10(5) IFU/ml in Vero cell cultures, respectively. We have analyzed the neutralization activity of immunized mouse sera with JEV-NK and JEV-BJ pseudotyped viruses. The neutralizing antibody titers of NK and BJ (50% reduction of virus) were about 1:10,000 at each immunized sera. Compared with conventional plaque reduction neutralization test (PRNT), the method using JEV-pseudotyped virus has desirable advantages such as more rapid, easier, and non-biohazardous. This neutralization assay system might be useful to evaluate NAb activity against JEV vaccine strains or vaccine candidates.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1). 민경일, 김영민, 추미성, 백선영, 김재옥, 류승렬, 민복 순, 김연희, 박미경, 변우현, 허숙진. 낮은 복제수 플라스 미드를 활용한 일본뇌염바이러스 SA14-14–2주의 Full-Length cDNA 클론의 제작 및 안정적 유지. J Bacteriol Virol. 34:339–353. 2004.2). 박민수, 노혜옥, 손영모, Chandler L, Shope R, Tsai TF. SA14-14–2주 일본뇌염 약독화 생백신의 면역 반응에 대 한 연구. Korean J Pediatr. 43:351–359. 2000.3). Abe M, Kuzuhara S, Kino Y. Establishment of an analyzing method for a Japanese encephalitis virus neutralization test in Vero cells. Vaccine. 21:1989–1994. 2003.
Article4). Burns JC, Friedmann T, Driever W, Burrascano M, Yee JK. Vesicular stomatitis virus G glycoprotein pseudotyped retroviral vectors: concentration to very high titer and efficient gene transfer into mammalian and nonmammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 90:8033–8037. 1993.
Article5). Cosset FL, Takeuchi Y, Battini JL, Weiss RA, Collins MK. High-titer packaging cells producing recombinant retroviruses resistant to human serum. J Virol. 69:7430–7436. 1995.
Article6). Han DP, Kim HG, Kim YB, Poon LL, Cho MW. Development of a safe neutralization assay for SARS-CoV and characterization of S-glycoprotein. Virology. 326:140–149. 2004.
Article7). Kaur R, Vrati S. Development of a recombinant vaccine against Japanese encephalitis. J Neurovirol. 9:421–431. 2003.
Article8). Kim YB, Lee MK, Han DP, Cho MW. Development of a safe and rapid neutralization assay using murine leukemia virus pseudotyped with HIV type 1 envelope glycoprotein lacking the cytoplasmic domain. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 17:1715–1724. 2001.
Article9). Konishi E, Mason PW. Proper maturation of the Japanese encephalitis virus envelope glycoprotein requires cosynthesis with the premembrane protein. J Virol. 67:1672–1675. 1993.
Article10). Konishi E, Pincus S, Paoletti E, Shope RE, Wason PW. Avipox virus-vectored Japanese encephalitis virus vaccines: use as vaccine candidates in combination with purified subunit immunogens. Vaccine. 12:633–638. 1994.11). Kuno G, Chang GJ, Tsuchiya KR, Karabatsos N, Cropp CB. Phylogeny of the genus Flavivirus. J Virol. 72:73–83. 1998.12). Lee MK, Martin MA, Cho MW. Higher western blot immunoreactivity of glycoprotein 120 from R5 HIV type 1 isolates compared with X4 and X4R5 isolates. AIDS Res Hum Retro-viruses. 16:765–775. 2000.
Article13). Lee MK, Seo JK, Kim HK, Cho JH, Poo H, Kim KL. A vector system for introducing foreign HIV-1 env genes and pseudotyping of MuLV particles with the recombinant HIV-1 envelope proteins for anti-HIV-1 assay. Antiviral Res. 53:99–111. 2002.
Article14). Mauldin J, Carbone K, Hsu H, Yolken R, Rubin S. Mumps virus-specific antibody titers from pre-vaccine era sera: comparison of the plaque reduction neutralization assay and enzyme immunoassays. J Clin Microbiol. 43:4847–4851. 2005.
Article15). Mutoh E, Ishikawa T, Takamizawa A, Kurata T, Sata T, Kojima A. Japanese encephalitis subunit vaccine composed of virus-like envelope antigen particles purified from serum-free medium of a high-producer J12#26 cell clone. Vaccine. 22:2599–2608. 2004.
Article16). Schnierle BS, Stitz J, Bosch V, Nocken F, Merget-Millitzer H, Engelstadter M, Kurth R, Groner B, Cichutek B. Pseudotyping of murine leukemia virus with the envelope glycoproteins of HIV generates a retroviral vector with specificity of infection for CD4-expressing cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 94:8640–8645. 1997.
Article17). Shibata R, Igarashi T, Haigwood N, Buckler-White A, Ogert R, Ross W, Willey R, Cho MW, Martin MA. Neutralizing antibody directed against the HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein can completely block HIV-1/SIV chimeric virus infections of macaque monkeys. Nat Med. 5:204–210. 1999.
Article18). Ting SH, See E, Tan HC, Lee MA, Ooi EE. Development of a simplified assay for the detection of neutralizing antibodies to Japanese encephalitis virus. J Virol Methods. 93:43–47. 2001.
Article19). Vazquez S, Valdes O, Pupo M, Delgado I, Alvarez M, Pelegrino JL, Guzman MG. MAC-ELISA and ELISA inhibition methods for detection of antibodies after yellow fever vaccination. J Virol Methods. 110:179–184. 2003.20). Venugopal K, Gould EA. Towards a new generation of flavivirus vaccines. Vaccine. 12:966–975. 1994.
Article21). Vorndam V, Beltran M. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay-format microneutralization test for dengue viruses. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 66:208–212. 2002.
Article22). Wengler G. Cell-associated West Nile flavivirus is covered with E+pre-M protein heterodimers which are destroyed and reorganized by proteolytic cleavage during virus release. J Virol. 63:2521–2526. 1989.
Article23). Wu HH, Chen CT, Lin YL, Lee ST. Sub-fragments of the envelope gene are highly protective against the Japanese encephalitis virus lethal infection in DNA priming-protein boosting immunization strategies. Vaccine. 22:793–800. 2004.
Article24). Wu SC, Lian WC, Hsu LC, Liau MY. Japanese encephalitis virus antigenic variants with characteristic differences in neutralization resistance and mouse virulence. Virus Res. 51:173–181. 1997.25). Wu SC, Lin CW. Neutralizing peptide ligands selected from phage-displayed libraries mimic the conformational epitope on domain III of the Japanese encephalitis virus envelope protein. Virus Res. 76:59–69. 2001.
Article26). Yang DK, Kweon CH, Kim BH, Lim SI, Kwon JH, Kim SH, Song JY, Han HR. Immunogenicity of baculovirus expressed recombinant proteins of Japanese encephalitis virus in mice. J Vet Sci. 6:125–133. 2005.
Article27). Yang KD, Yeh WT, Chen RF, Chuon HL, Tsai HP, Yao CW, Shaio MF. A model to study neurotropism and persistency of Japanese encephalitis virus infection in human neuroblastoma cells and leukocytes. J Gen Virol. 85:635–642. 2004.
Article28). Yasuda A, Kimura-Kuroda J, Ogimoto M, Miyamoto M, Sata T, Sato T, Takamura C, Kurata T, Kojima A, Yasui K. Induction of protective immunity in animals vaccinated with recombinant vaccinia viruses that express PreM and E glycoproteins of Japanese encephalitis virus. J Virol. 64:2788–2795. 1990.
Article29). Yee JK, Miyanohara A, LaPorte P, Bouic K, Burns JC, Friedmann T. A general method for the generation of high-titer, pantropic retroviral vectors: highly efficient infection of primary hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 91:9564–9568. 1994.
Article30). Yun SI, Kim SY, Rice CM, Lee YM. Development and application of a reverse genetics system for Japanese encephalitis virus. J Virol. 77:6450–6465. 2003.
Article31). Zielinska E, Liu D, Wu HY, Quiroz J, Rappaport R, Yang DP. Development of an improved microneutralization assay for respiratory syncytial virus by automated plaque counting using imaging analysis. Virol J. 2:84. 2005.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Serosurveillance for Japanese encephalitis virus infection among equines in India
- Detection of Neutralizing Antibody Against Japanese Encephalitis Virus in Wild Boars of Korea
- Establishment of a Multiplex RT-PCR for the Sensitive and Differential Detection of Japanese Encephalitis Virus Genotype 1 and 3
- Intracellular Localization of the Japanese Encephalitis Virus Capsid Protein
- Improvement of indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of Japanese encephalitis virus antibodies in swine sera