Hanyang Med Rev.
2009 Aug;29(3):210-219. 10.7599/hmr.2009.29.3.210.
Transoral Laser Surgery for Laryngeal Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. kdlee@ns.kosinmed.or.kr
- KMID: 1505097
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7599/hmr.2009.29.3.210
Abstract
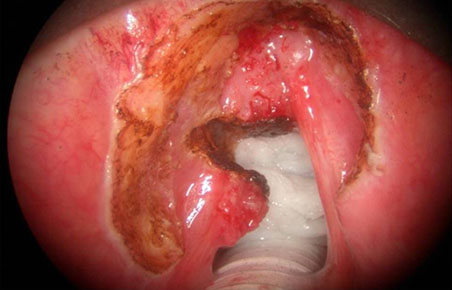
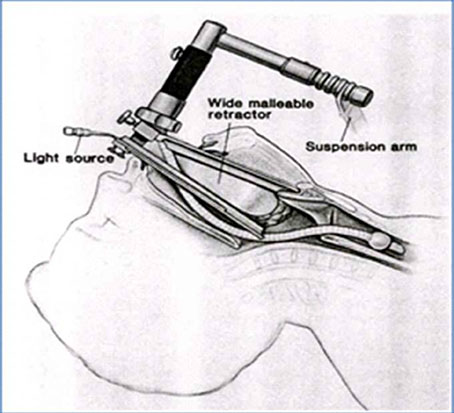
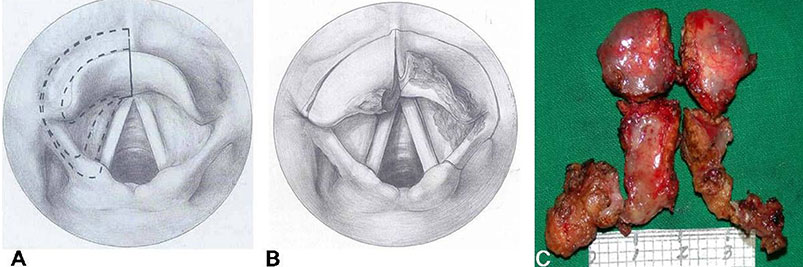
- The quality of life after surgery for laryngeal cancer may be as important as complete resection of the tumor. Transoral CO2 laser partial laryngectomy for the management of early laryngeal cancer has advangtages with regard to oncological results, preservation of laryngeal functions, complications and cost in comparison to those of open surgery or radiation therapy (RT). Moreover, transoral laser surgery could be a good choice as a salvage surgery in RT-failured early laryngeal cancer. Accumulation of more clinical experiences may lead to consensus for laser surgery as an alternative surgical method to open conserative laryngeal surgery, as it has been with the shift from total laryngectomy to conservative laryngectomy.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Strong MS, Jako GJ. Laser surgery in the larynx. Early clinical experience with continuous CO2 laser. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1972; 81:791–798.
Article2. Vaughan CW. Transoral laryngeal surgery using the CO2 laser: laboratory experiments and clinical experience. Laryngoscope. 1978; 88:1399–1420.
Article3. Zeitels SM, Vaughan CW, Domanowski GF, Fuleihan NS, Simpson GT 2nd. Laser epiglottectomy: endoscopic technique and indications. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1990; 103:337.
Article4. Davis RK, Kelly SM, Hayes J. Endoscopic CO2 laser excisional biopsy of early supraglottic cancer. Laryngoscope. 1991; 101:680–683.5. Zeitels SM, Davis RK. Endoscopic laser management of supraglottic cancer. Am J Otolaryngol. 1995; 16:2–11.
Article6. Ambrosch P, Kron M, Steiner W. Carbon dioxide laser microsurgery for early supraglottic carcinoma. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1998; 107:680–688.
Article7. Eckel HE, Thumfart WF. Laser surgery for the treatment of larynx carcinomas: indications, techniques, and preliminary results. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1992; 101:113–118.
Article8. Rudert H. Technique and results of transoral laser surgery of supraglottic carcinomas. Adv Otorhinolaryngol. 1995; 49:227–230.
Article9. Rudert HH, Werner JA. Endoscopic resections of glottic and supraglottic carcinomas with the CO2 laser. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 1995; 146–148.10. Steiner W. Results of curative laser microsurgery of laryngeal carcinomas. Am J Otolaryngol. 1993; 14:116–121.
Article11. Pearson BW, Salassa JR. Transoral laser microresection for cancer of the larynx involving the anterior commissure. Laryngoscope. 2003; 113:1104–1112.
Article12. Solares CA, Strome M. Transoral robot-assisted CO2 laser supraglottic laryngectomy: experimental and clinical data. Laryngoscope. 2007; 117:817–820.
Article13. Desai SC, Sung CK, Jang DW, Genden EM. Transoral Robotic Surgery Using a Carbon Dioxide Flexible Laser for Tumors of the Upper Aerodigestive Tract. Laryngoscope. 2008; 118:2187–2189.
Article14. Steiner W. Experience in endoscopic laser surgery of malignant tumours of the upper aero-digestive tract. Adv Otorhinolaryngol. 1988; 39:135–144.
Article15. Zeitels SM, Vaughan CW. The adjustable supraglottiscope. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1990; 103:487–492.
Article16. Ansarin M, Planicka M, Rotundo S, Santoro L, Zurlo V, Maffini F, Alterio D, Cattaneo A, Chiesa F. Endoscopic carbon dioxide laser surgery for glottic cancer recurrence after radiotherapy: oncological results. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007; 133:1193–1197.
Article17. Grant DG, Salassa JR, Hinni ML, Pearson BW, Hayden RE, Perry WC. Transoral laser microsurgery for recurrent laryngeal and pharyngeal cancer. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008; 138:606–613.
Article18. Virtaniemi JA, Hirvikoski PP, Kumpulainen EJ, Johansson RT, Kosma VM. Surgical management of irradiation failures in T1-T2 squamous cell carcinoma of the glottic larynx. Anticancer Research. 2001; 21:4185–4188.19. Kremer B, Schlondorff G. Late lethal secondary hemorrhage after laser supraglottic laryngectomy. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2001; 127:203–205.
Article20. Puxeddu R, Piazza C, Mensi MC, Ledda GP, Argiolas F, Peretti G. Carbon dioxide laser salvage surgery after radiotherapy failure in T1 and T2 glottic carcinoma. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2004; 130:84–88.
Article21. Piazza C, Peretti G, Cattaneo A, Garrubba F, De Zinis LOR, Nicolai P. Salvage surgery after radiotherapy for laryngeal cancer: from endoscopic resections to open-neck partial and total laryngectomies. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007; 133:1037–1043.
Article22. Quer M, Leon X, Orus C, Venegas P, Lopez M, Burgues J. Endoscopic laser surgery in the treatment of radiation failure of early laryngeal carcinoma. Head Neck. 2000; 22:520–523.
Article23. Sewnaik A, Meeuwis CA, van der Kwast TH, Kerrebijn JD. Partial laryngectomy for recurrent glottic carcinoma after radiotherapy. Head Neck. 2005; 27:101–107.
Article24. Steiner W, Vogt P, Ambrosch P, Kron M. Transoral carbon dioxide laser microsurgery for recurrent glottic carcinoma after radiotherapy. Head Neck. 2004; 26:477–484.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Recent Advances in Management of Laryngeal Cancer
- Clinical Outcome of Supraglottic Laryngectomy in Supraglottic Cancer : Open vs Transoral Laser Supraglottic Laryngectomy
- Comparative Study between Transoral Laser Microsurgery and Transoral Videolaryngoscopic Surgery in Benign Laryngeal Tumors
- Transoral CO2 Laser Resection for Post-Radiation Arytenoid Edema
- Transoral CO2 Laser Surgery of Supraglottic Cancer