Korean J Urogenit Tract Infect Inflamm.
2013 Oct;8(2):121-124. 10.14777/kjutii.2013.8.2.121.
Renal Papillary Necrosis with Calyceal Rupture: Caused by Acute Pyelonephritis and Analgesic Abuse
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea. kurology@jejunuh.co.kr
- KMID: 1502118
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14777/kjutii.2013.8.2.121
Abstract
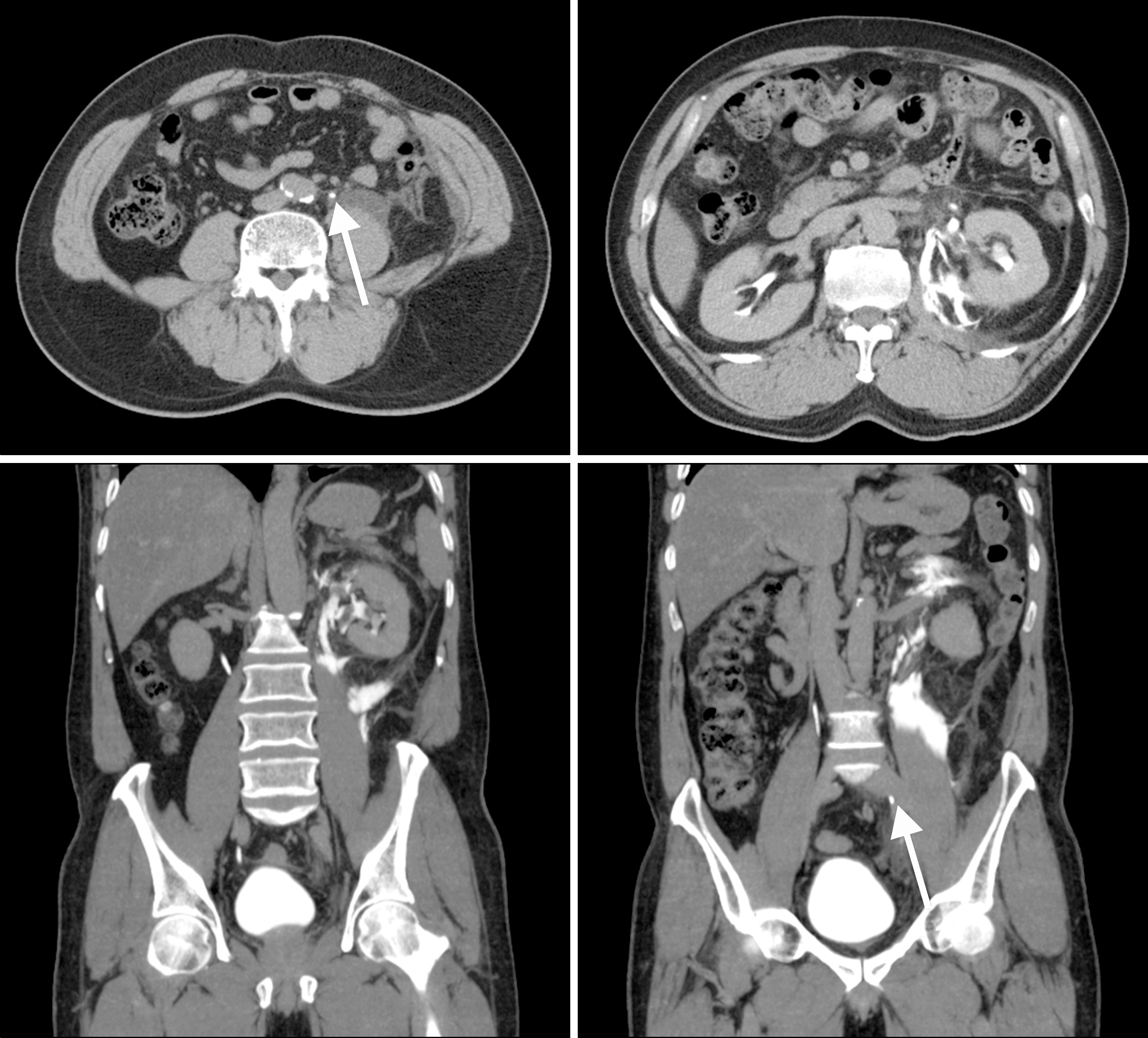
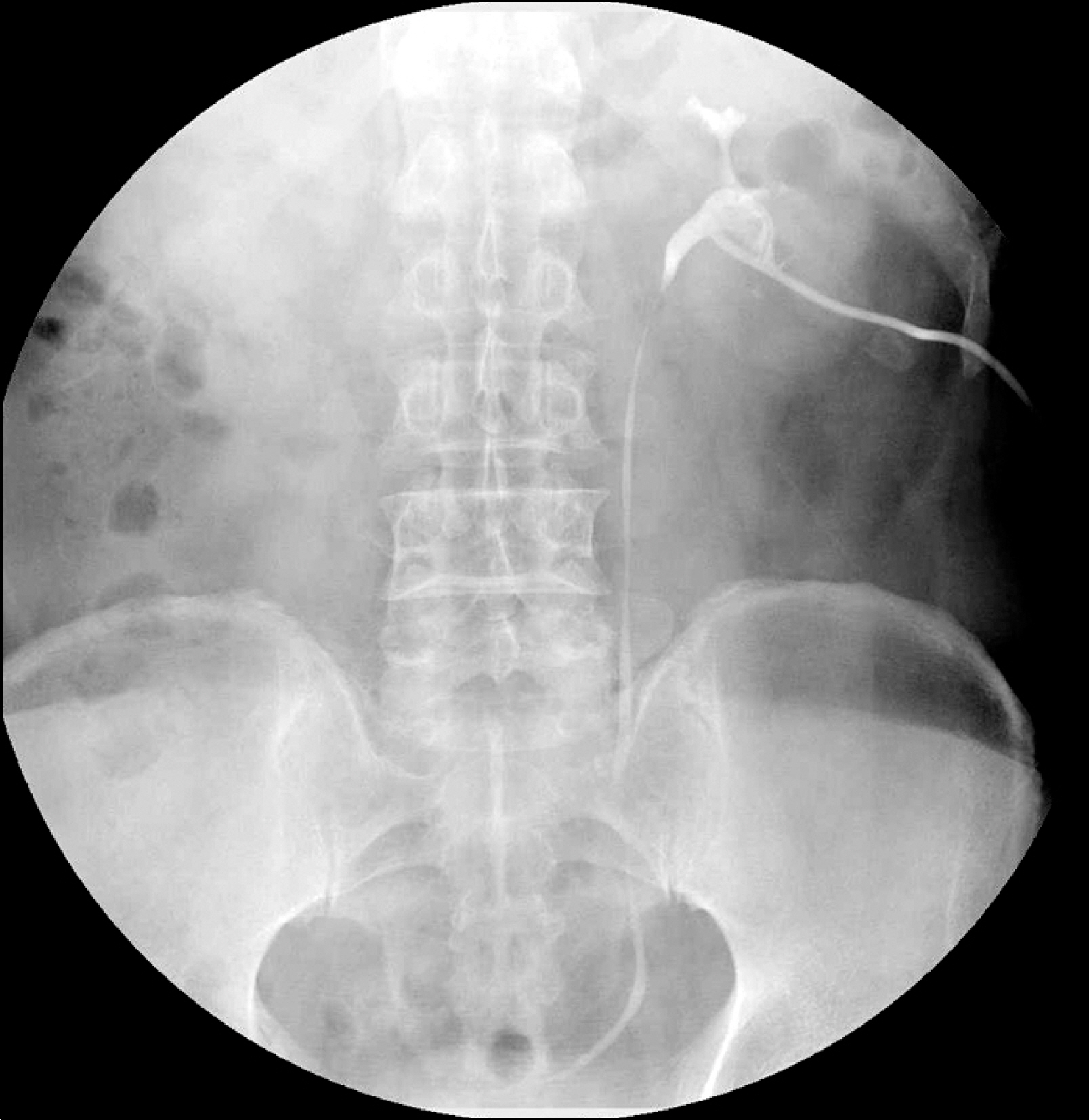
- Spontaneous renal rupture is a rare condition. Renal rupture most often occurs as a result of traumatic injury, a rare entity of obstructive uropathy with stones, and spontaneous causes such as malignancy. We report on a rare case of renal rupture caused by a ureter stone measuring 5 mm in size with acute pyelonephritis (APN) in a patient with renal papillary necrosis (RPN). The patient, who suffers from attacks of gouty arthritis, frequently used analgesic for pain relief. The patient was treated with temporary percutaneous drainage and antibiotics. This case demonstrates that RPN with APN can induce renal rupture even when ureter stones are small. Thus, consideration of all medical problems is important when deciding on treatment of patients with ureter stones.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bach PH, Nguyen TK. Renal papillary necrosis–40 years on. Toxicol Pathol. 1998; 26:73–91.
Article2. Carlton WW, Engelhardt JA. Experimental renal papillary necrosis in the Syrian hamster. Food Chem Toxicol. 1989; 27:331–40.
Article3. Kaplan LM, Farrer JH, Lupu AN. Spontaneous rupture of ureter. Urology. 1987; 29:313–6.
Article4. Johnson CM, Wilson DM, O'Fallon WM, Malek RS, Kurland LT. Renal stone epidemiology: a 25-year study in Rochester, Minnesota. Kidney Int. 1979; 16:624–31.
Article5. Coe FL, Parks JH, Asplin JR. The pathogenesis and treatment of kidney stones. N Engl J Med. 1992; 327:1141–52.
Article6. Stravodimos K, Adamakis I, Koutalellis G, Koritsiadis G, Grigoriou I, Screpetis K, et al. Spontaneous perforation of the ureter: clinical presentation and endourologic management. J Endourol. 2008; 22:479–84.
Article7. Moghal NE, Hegde S, Eastham KM. Ibuprofen and acute renal failure in a toddler. Arch Dis Child. 2004; 89:276–7.
Article8. Silverman LR, Khan KN. "Have you seen this?" Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced renal papillary necrosis in a dog. Toxicol Pathol. 1999; 27:244–5.
Article9. Harris M, Bryant LR, Danaher P, Alloway J. Effect of low dose daily aspirin on serum urate levels and urinary excretion in patients receiving probenecid for gouty arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2000; 27:2873–6.