Tuberc Respir Dis.
2013 Apr;74(4):163-168. 10.4046/trd.2013.74.4.163.
Incidence and Risk Factors of Contrast-Induced Nephropathy after Bronchial Arteriography or Bronchial Artery Embolization
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hjyoon@hanyang.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, HanMaEum Medical Center, Changwon, Korea.
- KMID: 1495856
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2013.74.4.163
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
In uncontrolled hemoptysis patient, bronchial arteriography and bronchial artery embolization (BAE) is a important procedure in diagnosis and treatment. The aim of this study is to assess the incidence of contrast-induced nephropathy and the risk factors of contrast-induced nephropathy (CIN) after bronchial arteriography and BAE.
METHODS
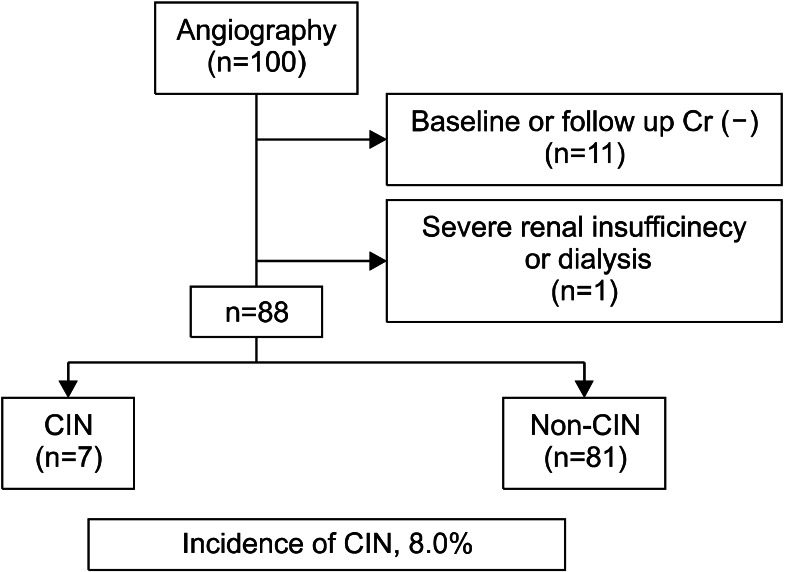
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of the patients who underwent bronchial arteriography and BAE in two university hospitals from January 2003 to December 2011. CIN was defined as rise of serum creatinine more than 25% of baseline value or 0.5 mg/dL at between 48 hours and 96 hours after bronchial arteriography and BAE. We excluded patients who already had severe renal insufficiency (serum creatinine> or =4.0) or had been receiving dialysis.
RESULTS
Of the total 100 screened patients, 88 patients met the enrollment criteria. CIN developed in 7 patients (8.0%). The mean duration between the exposure and development of CIN was 2.35+/-0.81 days. By using multivariate analysis, serum albumin level was found to be significantly associated with the development of CIN (p=0.0219).
CONCLUSION
These findings suggest that the incidence of CIN was higher than expected and patients with hypoalbuminemia should be monitored more carefully to prevent the development of CIN after bronchial arteriography and BAE.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Murphy SW, Barrett BJ, Parfrey PS. Contrast nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2000; 11:177–182. PMID: 10616853.
Article2. Hou SH, Bushinsky DA, Wish JB, Cohen JJ, Harrington JT. Hospital-acquired renal insufficiency: a prospective study. Am J Med. 1983; 74:243–248. PMID: 6824004.
Article3. Lasser EC, Lyon SG, Berry CC. Reports on contrast media reactions: analysis of data from reports to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Radiology. 1997; 203:605–610. PMID: 9169676.
Article4. Fishbane S, Durham JH, Marzo K, Rudnick M. N-acetylcysteine in the prevention of radiocontrast-induced nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004; 15:251–260. PMID: 14747371.
Article5. Gleeson TG, Bulugahapitiya S. Contrast-induced nephropathy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004; 183:1673–1689. PMID: 15547209.
Article6. Maeder M, Klein M, Fehr T, Rickli H. Contrast nephropathy: review focusing on prevention. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004; 44:1763–1771. PMID: 15519005.
Article7. Goldenberg I, Matetzky S. Nephropathy induced by contrast media: pathogenesis, risk factors and preventive strategies. CMAJ. 2005; 172:1461–1471. PMID: 15911862.
Article8. Thompson AB, Teschler H, Rennard SI. Pathogenesis, evaluation, and therapy for massive hemoptysis. Clin Chest Med. 1992; 13:69–82. PMID: 1582150.
Article9. Yoon W, Kim JK, Kim YH, Chung TW, Kang HK. Bronchial and nonbronchial systemic artery embolization for life-threatening hemoptysis: a comprehensive review. Radiographics. 2002; 22:1395–1409. PMID: 12432111.
Article10. Nash K, Hafeez A, Hou S. Hospital-acquired renal insufficiency. Am J Kidney Dis. 2002; 39:930–936. PMID: 11979336.
Article12. Waybill MM, Waybill PN. Contrast media-induced nephrotoxicity: identification of patients at risk and algorithms for prevention. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2001; 12:3–9. PMID: 11200350.
Article13. Nikolsky E, Mehran R, Turcot D, Aymong ED, Mintz GS, Lasic Z, et al. Impact of chronic kidney disease on prognosis of patients with diabetes mellitus treated with percutaneous coronary intervention. Am J Cardiol. 2004; 94:300–305. PMID: 15276092.
Article14. Russo D, Minutolo R, Cianciaruso B, Memoli B, Conte G, De Nicola L. Early effects of contrast media on renal hemodynamics and tubular function in chronic renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1995; 6:1451–1458. PMID: 8589322.
Article15. Tumlin JA, Wang A, Murray PT, Mathur VS. Fenoldopam mesylate blocks reductions in renal plasma flow after radiocontrast dye infusion: a pilot trial in the prevention of contrast nephropathy. Am Heart J. 2002; 143:894–903. PMID: 12040355.
Article16. Heinrich MC, Kuhlmann MK, Grgic A, Heckmann M, Kramann B, Uder M. Cytotoxic effects of ionic high-osmolar, nonionic monomeric, and nonionic iso-osmolar dimeric iodinated contrast media on renal tubular cells in vitro. Radiology. 2005; 235:843–849. PMID: 15845795.
Article17. Persson PB, Hansell P, Liss P. Pathophysiology of contrast medium-induced nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2005; 68:14–22. PMID: 15954892.
Article18. Farrugia A. Albumin usage in clinical medicine: tradition or therapeutic? Transfus Med Rev. 2010; 24:53–63. PMID: 19962575.
Article19. Nicholson JP, Wolmarans MR, Park GR. The role of albumin in critical illness. Br J Anaesth. 2000; 85:599–610. PMID: 11064620.
Article20. Choi H, Kim Y, Kim SM, Shin J, Jang HR, Lee JE, et al. Intravenous albumin for the prevention of contrast-induced nephropathy in patients with liver cirrhosis and chronic kidney disease undergoing contrast-enhanced CT. Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2012; 31:106–111.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case Report of Aberrant Bronchial Artery from Common Carotid Artery: A Potential Hazard in Bronchial Artery Embolization
- A Case of Bronchial Artery Aneurysm Demonstrating Hilar Mass
- A Case of Bronchial Artery Aneurysm with Bronchiectasis and Successful Coil Embolization
- Bronchial Artery Aneurysm Treated with NBCA: A Case Report
- Left Bronchial Artery Arising from a Replaced Left Hepatic Artery in a Patient with Massive Hemoptysis