Korean Circ J.
2012 Dec;42(12):809-815. 10.4070/kcj.2012.42.12.809.
Auscultatory Measured Normative Blood Pressure of Korean Adolescents: Using the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2001-2007
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hongym@chollian.net
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Inje University College of Medicine, Sanggye Paik Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pharmacology, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan Paik Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 1491096
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2012.42.12.809
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES
In Korea, there hasn't been any previous literature that describes auscultatory blood pressure (BP) normative tables for adolescents. Using BP data, from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES), we created normative auscultatory BP percentile tables for Korean adolescents.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
A total of 3508 adolescents (boys 1852, girls 1656), aged 10-17 in 2001, 2005 and 2007 from the KNHANES database years, were included. Auscultatory BP measurement was performed, using a Baumanometer Mercury Gravity Sphygmomanometer.
RESULTS
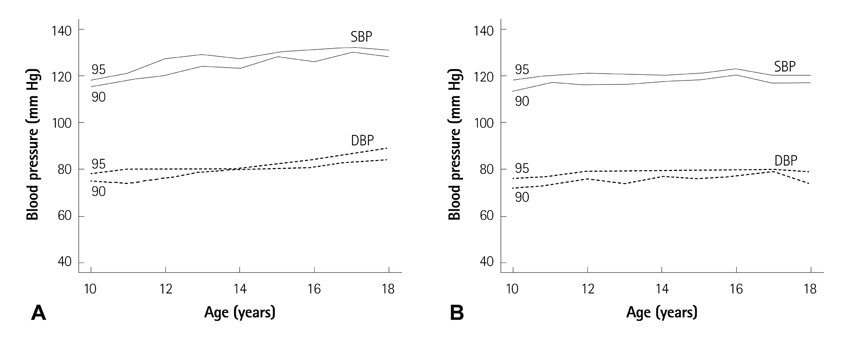
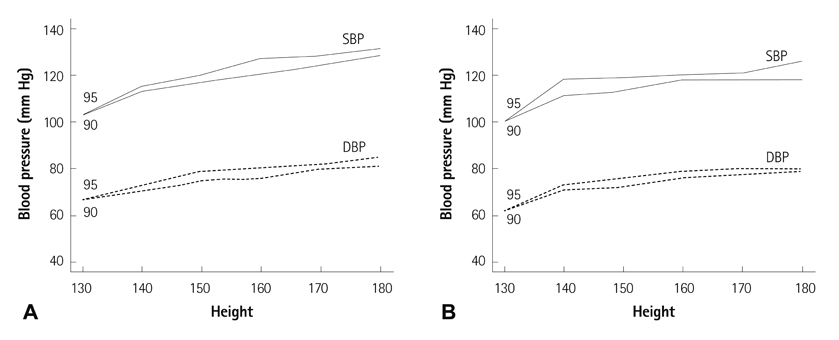
The mean systolic BP of boys was higher than that of girls in adolescents older than 13 years of age, and the mean diastolic BP of boys was higher than that of girls in those older than 15 years. Systolic and diastolic BP was correlated with weight, height and age. Age-specific normative auscultatory systolic and diastolic BP percentiles for boys and girls were completed. The graph that showed age-specific prehypertensive and hypertensive systolic and diastolic BP for boys and girls was presented. For adolescents, the height-specific auscultatory BP percentiles for boys and girls were completed. A graph that shows the height-specific prehypertensive and hypertensive BP for boys and girls was also made.
CONCLUSION
The auscultatory age-and height-specific BP percentiles for Korean adolescents are established. These can be useful in screening the prehypertension and hypertension of Korean adolescents in a clinical setting.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Blood Pressure Reference Values for Normal Weight Korean Children and Adolescents: Data from The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1998–2016: The Korean Working Group of Pediatric Hypertension
Sung Hye Kim, Youngmi Park, Young-Hwan Song, Hyo Soon An, Jae Il Shin, Jin-Hee Oh, Jung Won Lee, Seong Heon Kim, Hae Soon Kim, Hye-Jung Shin, Hae Kyoung Lee, Yeong Bong Park, Hae Yong Lee, Nam Su Kim, Il-Soo Ha, Soyeon Ahn, Woojoo Lee, Young Mi Hong
Korean Circ J. 2019;49(12):1167-1180. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2019.0075.
Reference
-
1. Sinaiko AR. Hypertension in children. N Engl J Med. 1996. 335:1968–1973.2. Chiolero A, Bovet P, Paradis G, Paccaud F. Has blood pressure increased in children in response to the obesity epidemic? Pediatrics. 2007. 119:544–553.3. Ippisch HM, Daniels SR. Hypertension in overweight and obese children. Prog Pediatr Cardiol. 2008. 25:177–182.4. Francischetti EA, Genelhu VA. Obesity-hypertension: an ongoing pandemic. Int J Clin Pract. 2007. 61:269–280.5. National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents. The fourth report on the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2004. 114:2 Suppl 4th Report. 555–576.6. Harding S, Maynard M, Cruickshank JK, Gray L. Anthropometry and blood pressure differences in black Caribbean, African, South Asian and white adolescents: the MRC DASH study. J Hypertens. 2006. 24:1507–1514.7. Lee CG, Moon JS, Choi JM, et al. Normative blood pressure references for Korean children and adolescents. Korean J Pediatr. 2008. 51:33–41.8. Lee CG, Park HM, Shin HJ, et al. Validation study of the Dinamap Pro-Care 200 upper arm blood pressure monitor in children and adolescents. Korean J Pediatr. 2011. 54:463–469.9. Park MK, Menard SW, Yuan C. Comparison of auscultatory and oscillometric blood pressures. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2001. 155:50–53.10. Recommendations for human blood pressure determination by sphygmomanometers. Circulation. 1988. 77:501A–514A.11. Hansen ML, Gunn PW, Kaelber DC. Underdiagnosis of hypertension in children and adolescents. JAMA. 2007. 298:874–879.12. Flynn JT. Pediatric hypertension update. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2010. 19:292–297.13. Sorof J, Daniels S. Obesity hypertension in children: a problem of epidemic proportions. Hypertension. 2002. 40:441–447.14. Blumenthal S, Epps RP, Heavenrich R, et al. Report of the task force on blood pressure control in children. Pediatrics. 1977. 59:5 2 suppl. I–II. 797–820.15. Report of the Second Task Force on Blood Pressure Control in Children--1987. Task Force on Blood Pressure Control in Children. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Bethesda, Maryland. Pediatrics. 1987. 79:1–25.16. National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on Hypertension Control in Children and Adolescents. Update on the 1987 Task Force Report on High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents: a working group report from the National High Blood Pressure Education Program. Pediatrics. 1996. 98(4 Pt 1):649–658.17. Park MK, Menard SW, Schoolfield J. Oscillometric blood pressure standards for children. Pediatr Cardiol. 2005. 26:601–607.18. Mitchell CK, Theriot JA, Sayat JG, Muchant DG, Franco SM. A simplified table improves the recognition of paediatric hypertension. J Paediatr Child Health. 2011. 47:22–26.19. Kaelber DC, Pickett F. Simple table to identify children and adolescents needing further evaluation of blood pressure. Pediatrics. 2009. 123:e972–e974.20. Sung RY, Choi KC, So HK, et al. Oscillometrically measured blood pressure in Hong Kong Chinese children and associations with anthropometric parameters. J Hypertens. 2008. 26:678–684.21. Chio SS, Urbina EM, Lapointe J, Tsai J, Berenson GS. Korotkoff sound versus oscillometric cuff sphygmomanometers: comparison between auscultatory and DynaPulse blood pressure measurements. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2011. 5:12–20.22. Londe S, Klitzner TS. Auscultatory blood pressure measurement--effect of pressure on the head of the stethoscope. West J Med. 1984. 141:193–195.23. Park MK, Menard SW, Yuan C. Comparison of blood pressure in children from three ethnic groups. Am J Cardiol. 2001. 87:1305–1308.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Dietary patterns of children and adolescents analyzed from 2001 Korea National Health and Nutrition Survey
- A Case of Anesthesia for a Patient of Pulseless Disease
- Moderate Alcohol Consumption Does Not Prevent the Hypertension among Korean: the 2001 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Blood Pressure Reference Values for Normal Weight Korean Children and Adolescents: Data from The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1998–2016: The Korean Working Group of Pediatric Hypertension
- Factors associated with Obesity among Korean Adolescents based on the Seventh Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016)