J Korean Soc Transplant.
2013 Mar;27(1):24-28. 10.4285/jkstn.2013.27.1.24.
A Case of Rapidly Progressive Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Requiring Liver Transplantation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei Institute of Gastroenterology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. mjchung@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Surgery, Research Institute for Transplantation, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1488439
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4285/jkstn.2013.27.1.24
Abstract
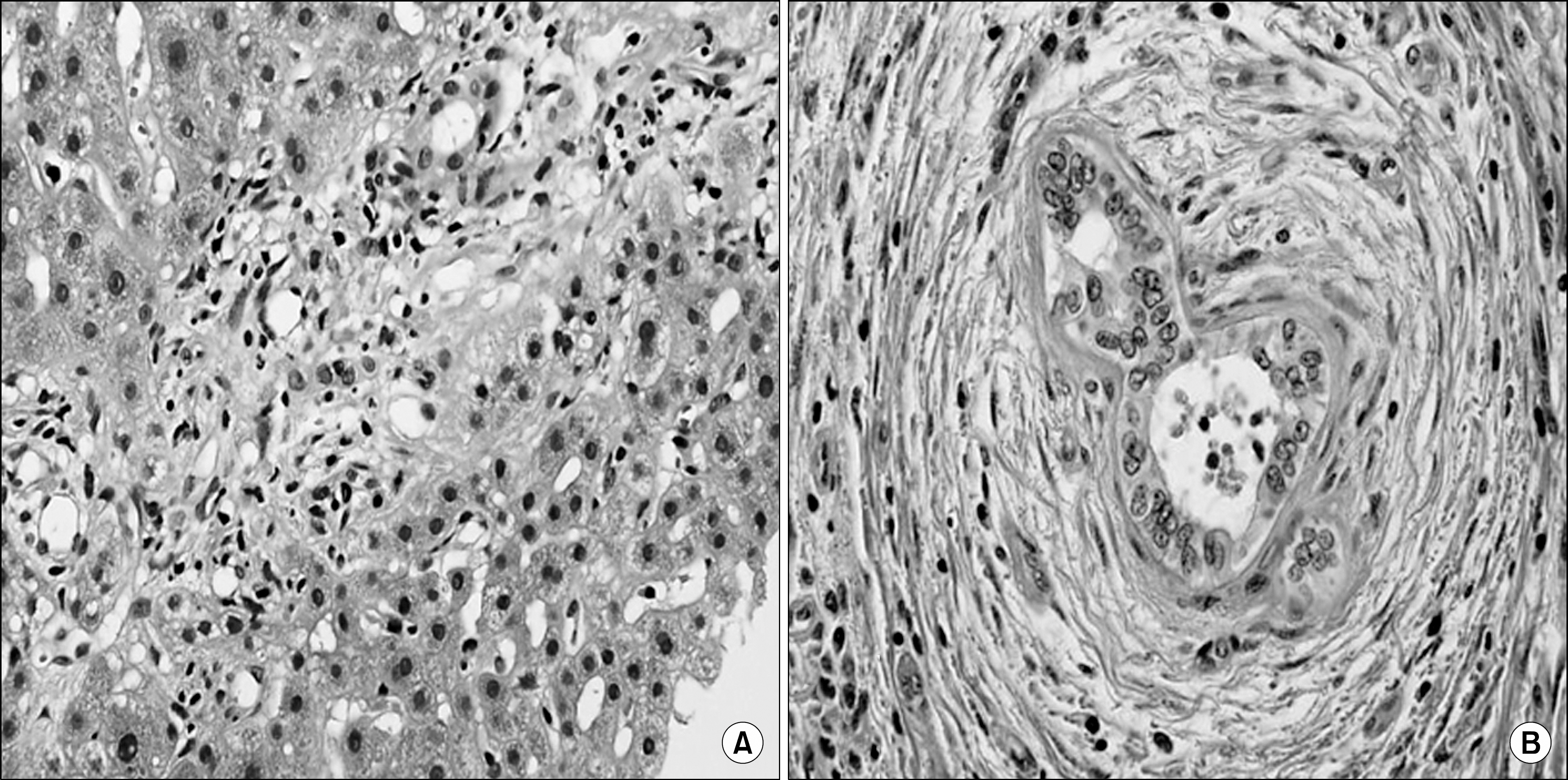
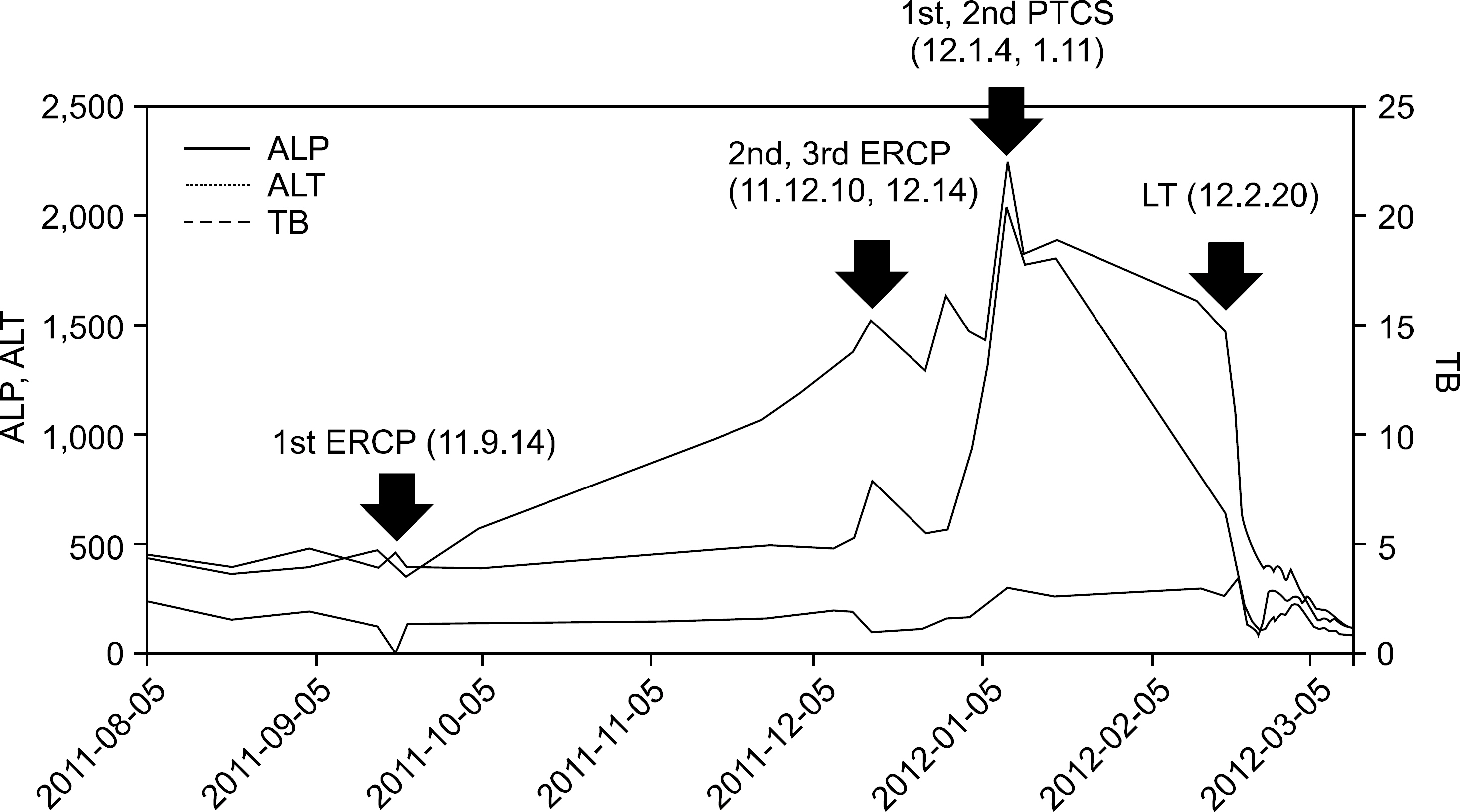
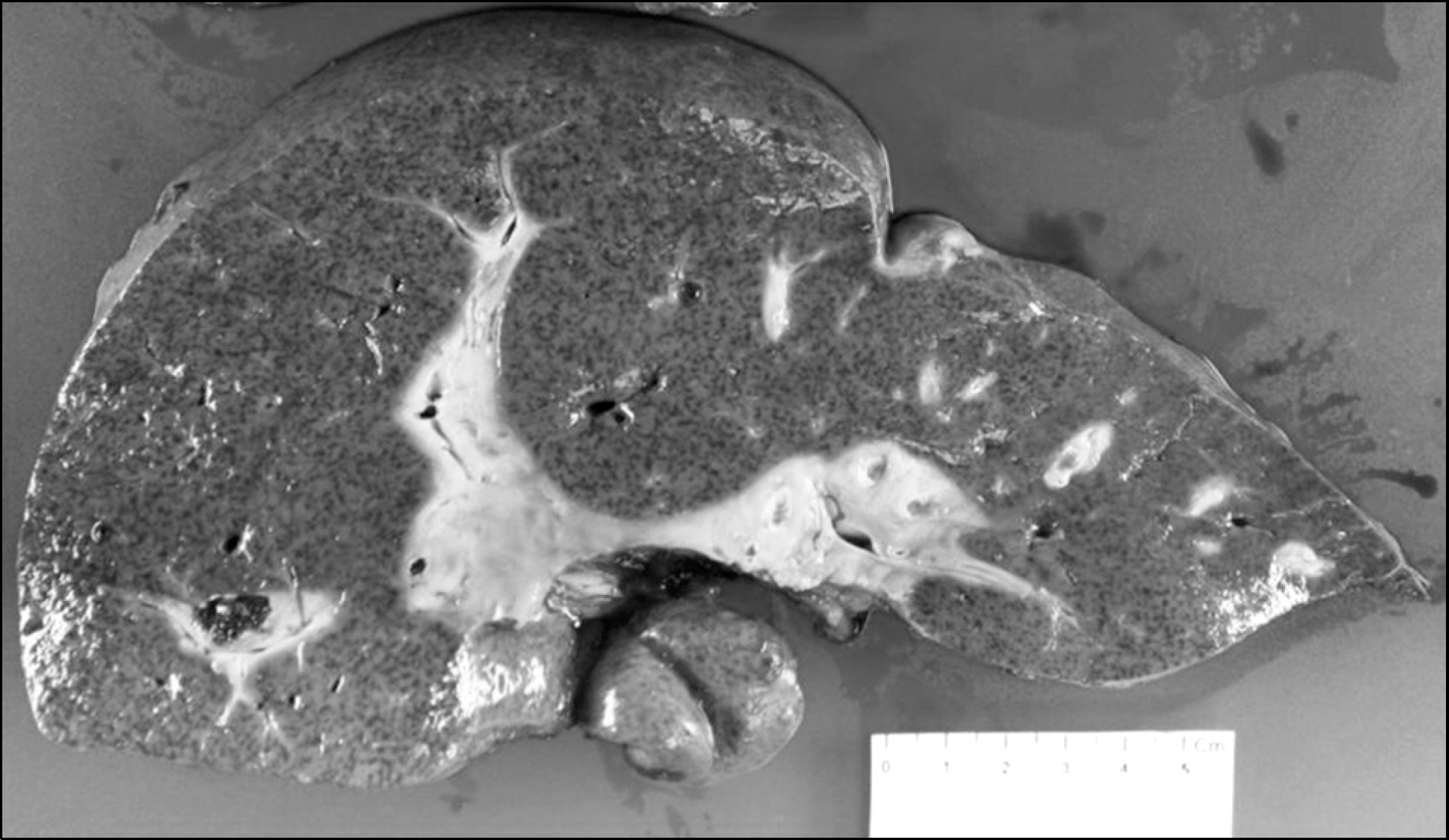
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a slowly progressive cholestatic liver disease. In cases of PSC, liver transplantation is the only effective treatment that can delay the disease's natural course. We report a case of rapidly progressive PSC requiring liver transplantation. A 52-year-old woman visited our hospital with abdominal pain. There was no evidence of PSC, as there was no elevation in cholestatic liver enzymes at her first visit. Although her total bilirubin was in a normal range at the initial visit, liver dysfunction progressed rapidly. Despite endoscopic procedures and ursodeoxycholic acid intake, total bilirubin levels rose to 18.9 mg/dL, and liver transplantation was performed 17 months after her first visit. PSC was pathologically confirmed after liver transplantation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Molodecky NA, Kareemi H, Parab R, Barkema HW, Quan H, Myers RP, et al. Incidence of primary sclerosing cholangitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hepatology. 2011; 53:1590–9.
Article2). Milkiewicz P, Wunsch E. Primary sclerosing cholangitis. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2011; 185:117–33.
Article3). Rosen CB, Nagorney DM, Wiesner RH, Coffey RJ Jr, LaRusso NF. Cholangiocarcinoma complicating primary sclerosing cholangitis. Ann Surg. 1991; 213:21–5.
Article4). Broomé U, Olsson R, Lööf L, Bodemar G, Hultcrantz R, Danielsson A, et al. Natural history and prognostic factors in 305 Swedish patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis. Gut. 1996; 38:610–5.
Article5). Tischendorf JJ, Hecker H, Krüger M, Manns MP, Meier PN. Characterization, outcome, and prognosis in 273 patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis: a single center study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007; 102:107–14.
Article6). Mehal WZ, Lo YM, Wordsworth BP, Neuberger JM, Hubscher SC, Fleming KA, et al. HLA DR4 is a marker for rapid disease progression in primary sclerosing cholangitis. Gastroenterology. 1994; 106:160–7.
Article7). Farrant JM, Doherty DG, Donaldson PT, Vaughan RW, Hayllar KM, Welsh KI, et al. Amino acid substitutions at position 38 of the DR beta polypeptide confer suscept-ibility to and protection from primary sclerosing cholangitis. Hepatology. 1992; 16:390–5.8). Olerup O, Olsson R, Hultcrantz R, Broome U. HLA- DR and HLA-DQ are not markers for rapid disease progression in primary sclerosing cholangitis. Gastroenterology. 1995; 108:870–8.9). Chapman R, Fevery J, Kalloo A, Nagorney DM, Boberg KM, Shneider B, et al. Diagnosis and management of primary sclerosing cholangitis. Hepatology. 2010; 51:660–78.
Article10). Burak KW, Angulo P, Lindor KD. Is there a role for liver biopsy in primary sclerosing cholangitis? Am J Gastroenterol. 2003; 98:1155–8.
Article11). Baluyut AR, Sherman S, Lehman GA, Hoen H, Chalasani N. Impact of endoscopic therapy on the survival of patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001; 53:308–12.
Article12). Gluck M, Cantone NR, Brandabur JJ, Patterson DJ, Bredfeldt JE, Kozarek RA. A twenty-year experience with endoscopic therapy for symptomatic primary sclerosing cholangitis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2008; 42:1032–9.S.
Article13). Stiehl A, Rudolph G, Klöters-Plachky P, Sauer P, Walker S. Development of dominant bile duct stenoses in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis treated with ursodeoxycholic acid: outcome after endoscopic treatment. J Hepatol. 2002; 36:151–6.
Article14). Shi J, Li Z, Zeng X, Lin Y, Xie WF. Ursodeoxycholic acid in primary sclerosing cholangitis: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Hepatol Res. 2009; 39:865–73.
Article15). Poropat G, Giljaca V, Stimac D, Gluud C. Bile acids for primary sclerosing cholangitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011; (1):CD003626.
Article16). Triantos CK, Koukias NM, Nikolopoulou VN, Burroughs AK. Meta-analysis: ursodeoxycholic acid for primary sclerosing cholangitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2011; 34:901–10.
Article17). Lindor KD, Kowdley KV, Luketic VA, Harrison ME, McCashland T, Befeler AS, et al. High-dose ursodeox-ycholic acid for the treatment of primary sclerosing cholangitis. Hepatology. 2009; 50:808–14.
Article18). Imam MH, Sinakos E, Gossard AA, Kowdley KV, Luketic VA, Edwyn Harrison M, et al. High-dose urso-deoxycholic acid increases risk of adverse outcomes in patients with early stage primary sclerosing cholangitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2011; 34:1185–92.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Secondary Sclerosing Cholangitis in Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis
- Novel Insights of Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Primary Biliary Cholangitis
- Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis: Two Case Reports
- Erratum to: A Case of Rapidly Progressive Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Requiring Liver Transplantation
- Biliary Tract & Pancreas; A Case of Cholangiocarcinoma Suggested as Developing in the Patient with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis