J Vet Sci.
2013 Mar;14(1):91-94. 10.4142/jvs.2013.14.1.91.
Abundance of biting midge species (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae, Culicoides spp.) on cattle farms in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Animal Disease Diagnostic Division, Animal, Plant and Fisheries Quarantine and Inspection Agency, Anyang 430-757, Korea. kyusfather@Korea.kr
- 2Namwon-Branch, Jeonbuk Institute of Livestock and Veterinary Research, Namwon 590-230, Korea.
- 3Southern Branch, Gyeongnam Institute of Livestock and Veterinary Research, Tongyeong 650-817, Korea.
- 4Southern Branch, Jeollanamdo Institute of Livestock and Veterinary Science, Gangjin 590-230, Korea.
- KMID: 1482818
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2013.14.1.91
Abstract
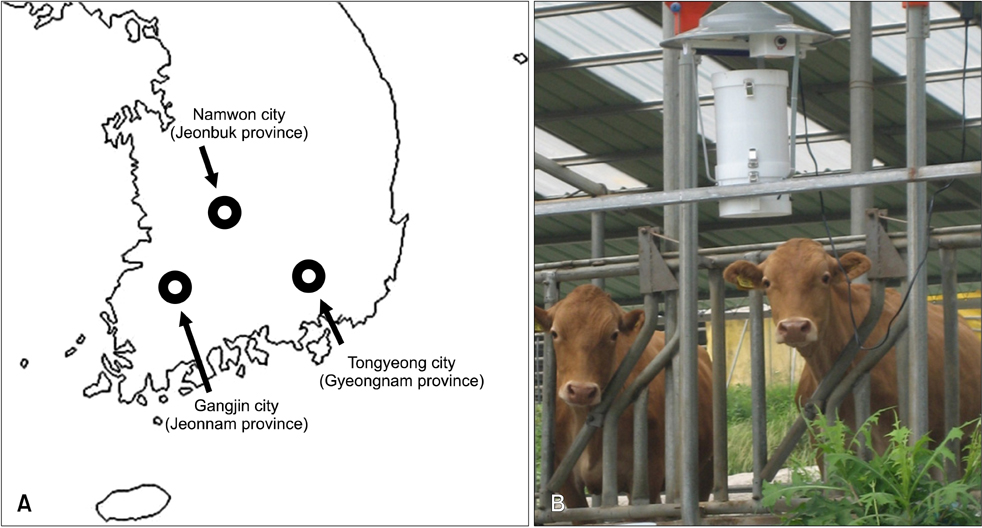
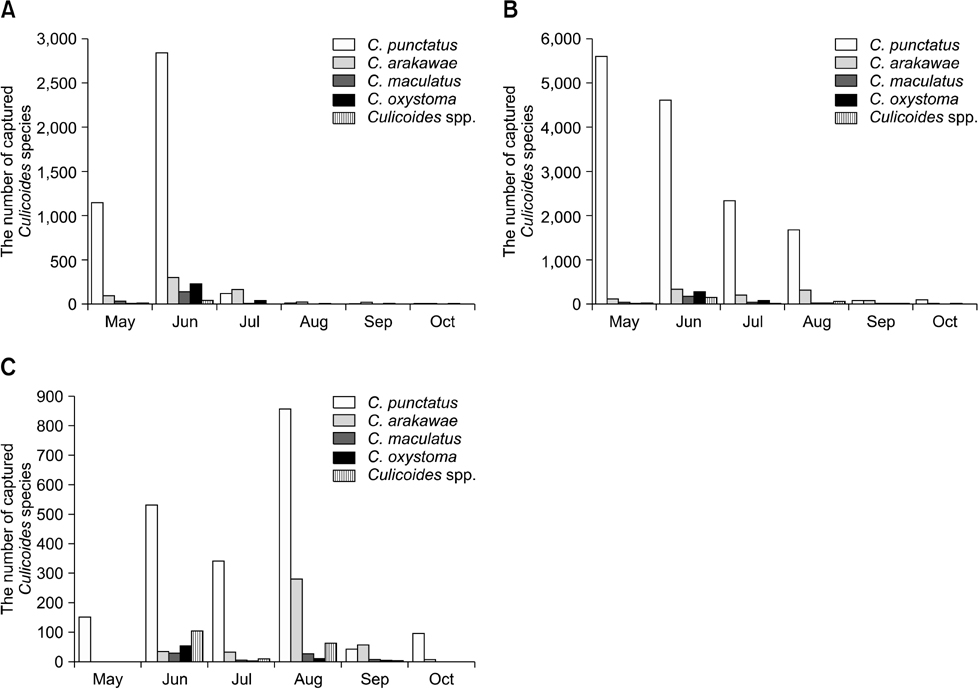
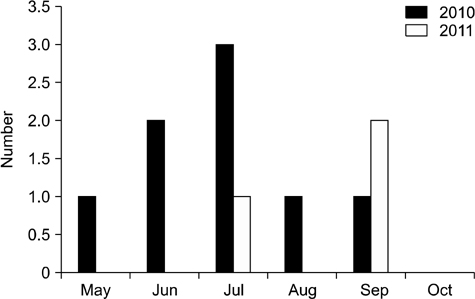
- Culicoides biting midges were collected on three cattle farms weekly using light traps overnight from May to October between 2010 and 2011 in the southern part of Korea. The seasonal and geographical abundance of Culicodes spp. were measured. A total of 16,538 biting midges were collected from 2010 to 2011, including seven species of Culicoides, four of which represented 98.42% of the collected specimens. These four species were Culicodes (C.) punctatus (n = 14,413), C. arakawae (n = 1,120), C. oxystoma (n = 427), and C. maculatus (n = 318). C. punctatus was the predominant species (87.15%).
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. An DJ, Yoon SH, Jeong W, Kim HJ, Park BK. Genetic analysis of Akabane virus isolates from cattle in Korea. Vet Microbiol. 2010. 140:49–55.
Article2. Cho HC, Chong CS. Notes on biting midges of the genus Culicoides from South Korea: with special reference to unrecorded species and distribution. Korean J Parasitol. 1974. 12:45–75.
Article3. Kitaoka S. Japanese Culicoides (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) and keys for the species. Bull Natl Inst Anim Health. 1984. 87:73–108.4. Lee JK, Park JS, Choi JH, Park BK, Lee BC, Hwang WS, Kim JH, Jean YH, Haritani M, Yoo HS, Kim DY. Encephalomyelitis associated with Akabane virus infection in adult cows. Vet Pathol. 2002. 39:269–273.
Article5. Mellor PS, Boorman J, Baylis M. Culicoides biting midges: their role as arbovirus vectors. Annu Rev Entomol. 2000. 45:307–340.
Article6. Muller MJ. Veterinary arbovirus vectors in Australia--a retrospective. Vet Microbiol. 1995. 46:101–116.7. Oem JK, Yoon HJ, Kim HR, Roh IS, Lee KH, Lee OS, Bae YC. Genetic and pathogenic characterization of Akabane viruses isolated from cattle with encephalomyelitis in Korea. Vet Microbiol. 2012. 158:259–266.
Article8. Rasmussen LD, Kristensen B, Kirkeby C, Rasmussen TB, Belsham GJ, Bødker R, Bøtner A. Culicoids as vectors of Schmallenberg virus. Emerg Infect Dis. 2012. 18:1204–1206.
Article9. Shin YK, Oem JK, Yoon SR, Hyun BH, Cho IS, Yoon SS, Song JY. Monitoring of five bovine arboviral diseases transmitted by arthropod vectors in Korea. J Bacteriol Virol. 2009. 39:353–362.
Article10. Yanase T, Hirata M, Matsumori Y, Matsumura M, Kato T, Shirafuji H, Yamakawa M, Hayama Y, Tsutsui T. Detection of Culicoides brevitarsis activity in Kyushu. J Vet Med Sci. 2011. 73:1649–1652.11. Yanase T, Kato T, Kubo T, Yoshida K, Ohashi S, Yamakawa M, Miura Y, Tsuda T. Isolation of bovine arboviruses from Culicoides biting midges (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) in southern Japan: 1985-2002. J Med Entomol. 2005. 42:63–67.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Seasonal Abundance of Biting Midges, Culicoides spp. (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae), Collected at Cowsheds in the Southern Part of the Republic of Korea
- Attraction and Repellent Behaviors of Culicoides Biting Midges toward Cow Dung, Carbon Dioxide, and Essential Oils
- Species Diversity and Seasonal Distribution of Culicoides spp. (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) in Jeju-do, Republic of Korea
- Notes on biting midges of the Genus Culicoides from South Korea - with special reference to unrecorded species and distribution
- Seasonal Abundance of Culicoides at Yongsan US Army Garrison (USAG) and Camp Humphreys USAG, Republic of Korea, 2010-2013 and 2014-2017