Korean J Radiol.
2013 Apr;14(2):350-360. 10.3348/kjr.2013.14.2.350.
Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia: New High Resolution Computed Tomography Scoring System and Correlation between the High Resolution Computed Tomography Score and Clinical Severity
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology and the Institute of Radiation Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 110-744, Korea. kimws@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 110-744, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center, Seoul 156-707, Korea.
- KMID: 1482799
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2013.14.2.350
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To develop an high resolution computed tomography (HRCT) scoring system for the assessment of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) and determine its usefulness as compared with the chest radiographic score.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
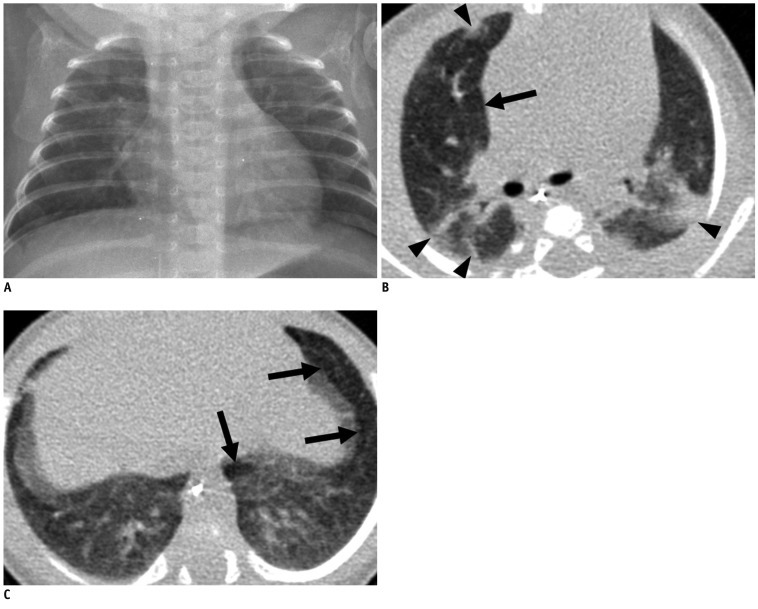
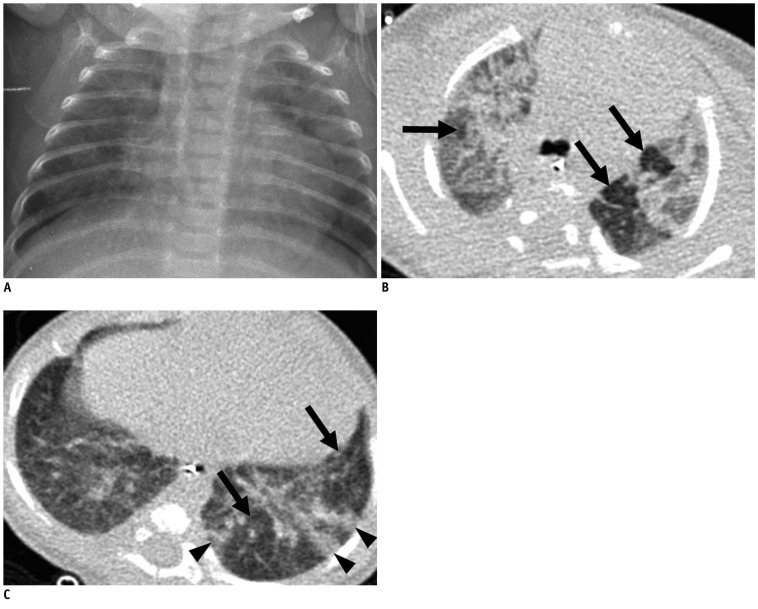
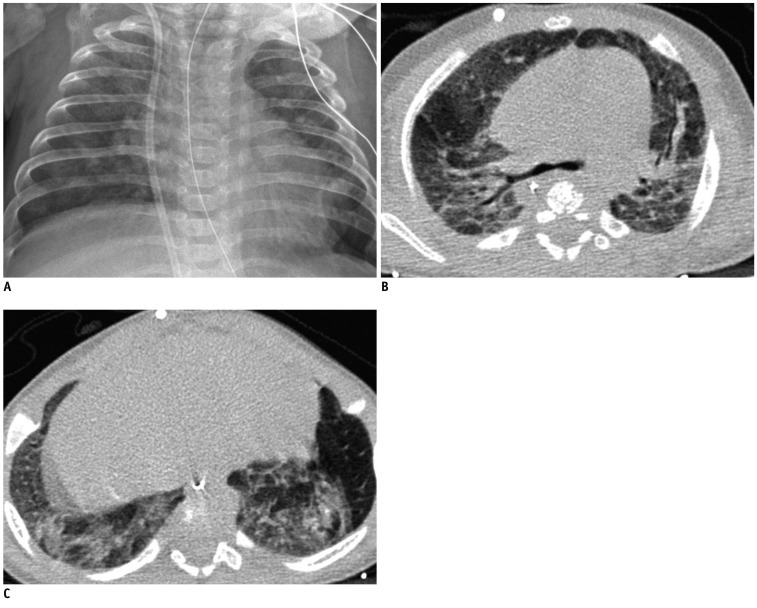
Forty-two very low-birth-weight preterm infants with BPD (25 male, 17 female) were prospectively evaluated with HRCT performed at the mean age of 39.1-week postmenstrual age. Clinical severity of BPD was categorized as mild, moderate or severe. The HRCT score (0-36) of each patient was the sum of the number of bronchopulmonary segments with 1) hyperaeration and 2) parenchymal lesions (linear lesions, segmental atelectasis, consolidation and architectural distortion), respectively. We compared the HRCT scores with the chest radiographic scores (the Toce system) in terms of correlation with clinical severity.
RESULTS
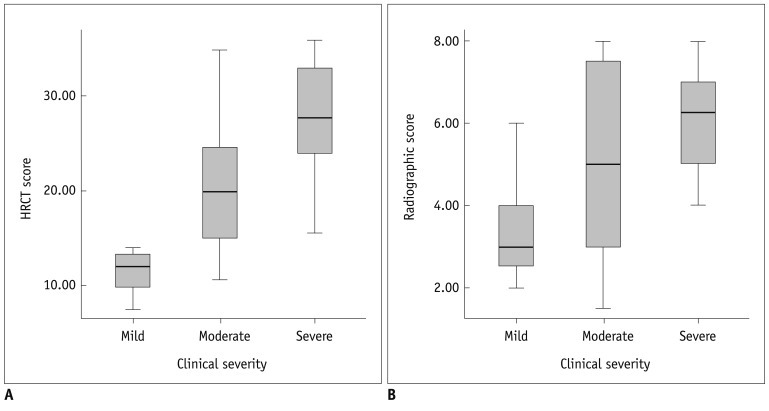
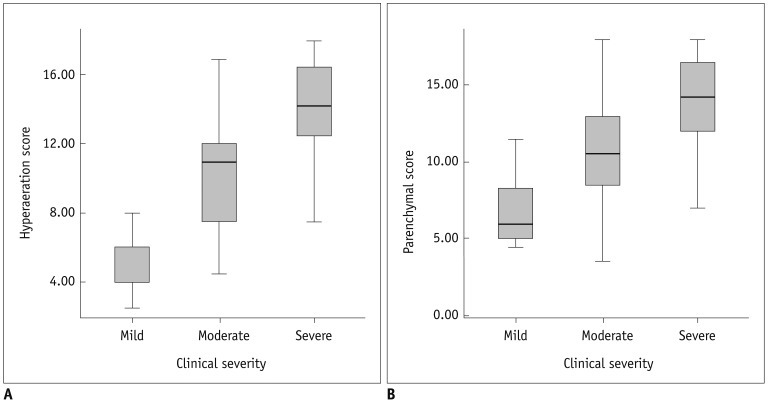
The HRCT score had good interobserver (r = 0.969, p < 0.001) and intraobserver (r = 0.986, p < 0.001) reproducibility. The HRCT score showed better correlation (r = 0.646, p < 0.001) with the clinical severity of BPD than the chest radiographic score (r = 0.410, p = 0.007). The hyperaeration score showed better correlation (r = 0.738, p < 0.001) with the clinical severity of BPD than the parenchymal score (r = 0.523, p < 0.001).
CONCLUSION
We have developed a new HRCT scoring system for BPD based on the quantitative evaluation of pulmonary abnormalities of BPD consisting of the hyperaeration score and the parenchymal score. The HRCT score shows better correlation with the clinical severity of BPD than the radiographic score.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mahut B, De Blic J, Emond S, Benoist MR, Jarreau PH, Lacaze-Masmonteil T, et al. Chest computed tomography findings in bronchopulmonary dysplasia and correlation with lung function. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2007; 92:F459–F464. PMID: 17379740.
Article2. Jobe AH, Bancalari E. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001; 163:1723–1729. PMID: 11401896.
Article3. Toce SS, Farrell PM, Leavitt LA, Samuels DP, Edwards DK. Clinical and roentgenographic scoring systems for assessing bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Dis Child. 1984; 138:581–585. PMID: 6720645.
Article4. Palta M, Sadek M, Barnet JH, Evans M, Weinstein MR, McGuinness G, et al. Evaluation of criteria for chronic lung disease in surviving very low birth weight infants. Newborn Lung Project. J Pediatr. 1998; 132:57–63. PMID: 9470001.5. Weinstein MR, Peters ME, Sadek M, Palta M. A new radiographic scoring system for bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Newborn Lung Project. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1994; 18:284–289. PMID: 7898966.6. Moya MP, Bisset GS 3rd, Auten RL Jr, Miller C, Hollingworth C, Frush DP. Reliability of CXR for the diagnosis of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatr Radiol. 2001; 31:339–342. PMID: 11373921.
Article7. Jin YM, Chung DC, Chang YP, Lee YS, Lee ES. High-resolution computed tomography findings of lung parenchyme changes in very low birth weight infants treated with oxygen. Korean J Pediatr. 2007; 50:255–261.
Article8. Kuhn JP, Brody AS. High-resolution CT of pediatric lung disease. Radiol Clin North Am. 2002; 40:89–110. PMID: 11813822.
Article9. Kubota J, Ohki Y, Inoue T, Sakurai M, Shigeta M, Mochizuki H, et al. Ultrafast CT scoring system for assessing bronchopulmonary dysplasia: reproducibility and clinical correlation. Radiat Med. 1998; 16:167–174. PMID: 9715994.10. Oppenheim C, Mamou-Mani T, Sayegh N, de Blic J, Scheinmann P, Lallemand D. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia: value of CT in identifying pulmonary sequelae. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1994; 163:169–172. PMID: 8010206.
Article11. Ochiai M, Hikino S, Yabuuchi H, Nakayama H, Sato K, Ohga S, et al. A new scoring system for computed tomography of the chest for assessing the clinical status of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Pediatr. 2008; 152:90–95. 95.e1–95.e3. PMID: 18154907.
Article12. Huda W. Radiation doses and risks in chest computed tomography examinations. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2007; 4:316–320. PMID: 17652493.
Article13. Suess C, Chen X. Dose optimization in pediatric CT: current technology and future innovations. Pediatr Radiol. 2002; 32:729–734. PMID: 12244463.
Article14. Shrimpton PC, Hillier MC, Lewis MA, Dunn M. National survey of doses from CT in the UK: 2003. Br J Radiol. 2006; 79:968–980. PMID: 17213302.
Article15. Osborne D, Vock P, Godwin JD, Silverman PM. CT identification of bronchopulmonary segments: 50 normal subjects. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1984; 142:47–52. PMID: 6606964.
Article16. Jackson CL, Huber JF. Correlated applied anatomy of the bronchial tree and lungs with a system of nomenclature. Dis Chest. 1943; 9:319–326.
Article17. Hansell DM, Bankier AA, MacMahon H, McLoud TC, Müller NL, Remy J. Fleischner Society: glossary of terms for thoracic imaging. Radiology. 2008; 246:697–722. PMID: 18195376.
Article18. Aukland SM, Halvorsen T, Fosse KR, Daltveit AK, Rosendahl K. High-resolution CT of the chest in children and young adults who were born prematurely: findings in a population-based study. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006; 187:1012–1018. PMID: 16985150.
Article19. Edwards DK. Farrell PM, editor. Radiology of hyaline membrane disease, transient tachypnea of the newborn, and bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Lung Development: Biological and Clinical Perspectives. 1982. New York: Academic Press Inc;p. 47–89.
Article20. Olgar T, Onal E, Bor D, Okumus N, Atalay Y, Turkyilmaz C, et al. Radiation exposure to premature infants in a neonatal intensive care unit in Turkey. Korean J Radiol. 2008; 9:416–419. PMID: 18838850.
Article21. Hotelling H. The selection of variates for use in prediction with some comments on the general problem of nuisance parameters. Ann Math Stat. 1940; 11:271–283.
Article22. Reid L. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia--pathology. J Pediatr. 1979; 95(5 Pt 2):836–841. PMID: 490260.
Article23. Stocker JT. Pathologic features of long-standing "healed" bronchopulmonary dysplasia: a study of 28 3- to 40-month-old infants. Hum Pathol. 1986; 17:943–961. PMID: 3639056.24. Choi SJ, Choi BK, Kim HJ, Lee SH, Choi SH, Park SJ, et al. Lateral decubitus HRCT: a simple technique to replace expiratory CT in children with air trapping. Pediatr Radiol. 2002; 32:179–182. PMID: 12164350.
Article25. Sargent MA, McEachern AM, Jamieson DH, Kahwaji R. Atelectasis on pediatric chest CT: comparison of sedation techniques. Pediatr Radiol. 1999; 29:509–513. PMID: 10398785.
Article26. Lam WW, Chen PP, So NM, Metreweli C. Sedation versus general anaesthesia in paediatric patients undergoing chest CT. Acta Radiol. 1998; 39:298–300. PMID: 9571947.
Article27. Lucaya J, Piqueras J, García-Peña P, Enríquez G, García-Macías M, Sotil J. Low-dose high-resolution CT of the chest in children and young adults: dose, cooperation, artifact incidence, and image quality. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000; 175:985–992. PMID: 11000149.28. Rajaraman P, Simpson J, Neta G, Berrington de, Ansell P, Linet MS, et al. Early life exposure to diagnostic radiation and ultrasound scans and risk of childhood cancer: case-control study. BMJ. 2011; 342:d472. PMID: 21310791.
Article29. Goo HW. CT radiation dose optimization and estimation: an update for radiologists. Korean J Radiol. 2012; 13:1–11. PMID: 22247630.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Singificance of Post - arthrographic High Resolution Computed Tomography in Meniscal Tears
- High-resolution computed tomography findings of lung parenchyme changes in very low birth weight infants treated with oxygen
- High-Resolution CT Findings in Infants with Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia: Preliminary Report
- A study on the anatomical morphology of the minor fissure
- Basic principle of cone beam computed tomography