Korean J Radiol.
2013 Apr;14(2):337-342. 10.3348/kjr.2013.14.2.337.
FDG PET or PET/CT in Evaluation of Renal Angiomyolipoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nuclear Medicine, Show Chwan Memorial Hospital, Changhua 500, Taiwan.
- 2Department of Radiology, China Medical University Hospital, Taichung 404, Taiwan.
- 3Department of Nuclear Medicine, E-DA Hospital I-Shou University, Kaohsiung 840, Taiwan.
- 4Department of Nuclear Medicine and PET Center, China Medical University Hospital, Taichung 404, Taiwan. d10040@mail.cmuh.org.tw
- KMID: 1482797
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2013.14.2.337
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
Angiomyolipoma is the most common benign kidney tumor. However, literature describing FDG PET findings on renal angiomyolipoma (AML) is limited. This study reports the FDG PET and PET/CT findings of 21 cases of renal AML.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The study reviews FDG PET and PET/CT images of 21 patients diagnosed with renal AML. The diagnosis is based on the classical appearance of an AML on CT scan with active surveillance for 6 months. The study is focused on the observation of clinical and radiographic features.
RESULTS
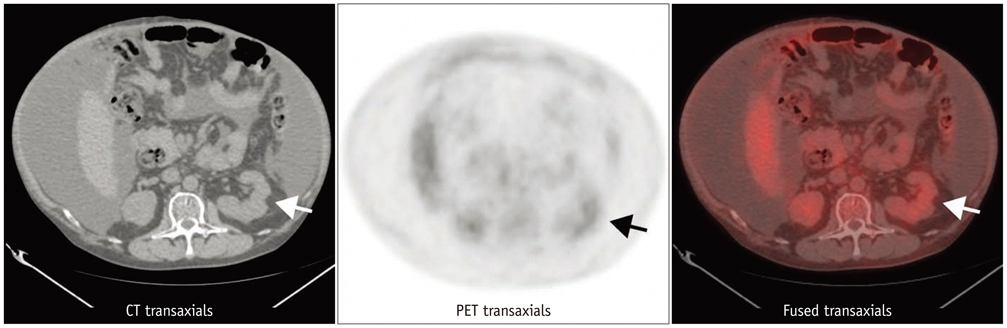
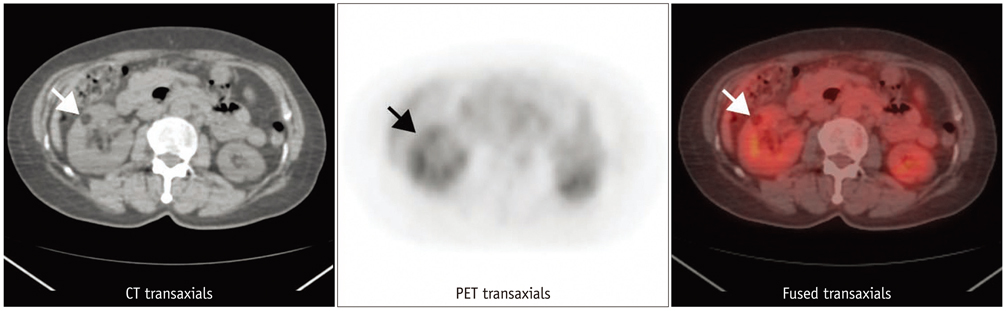
Six men and 15 women were included in our study. The mean age of the patients was 57.14 +/- 9.67 years old. The mean diameter of 21 renal AML on CT scans was 1.76 +/- 1.00 cm (Min: 0.6 cm; Max: 4.4 cm). CT scans illustrated renal masses typical of AMLs, and the corresponding FDG PET scans showed minimal FDG activities in the area of the tumors. None of the 21 AMLs showed a maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax) greater than 1.98. No statistically significant correlation was present between SUVmax and tumor size.
CONCLUSION
Renal AMLs demonstrate very low to low uptake on FDG PET and PET/CT imaging in this study. When a fat-containing tumor in the kidney is found on a CT scan, it is critical to differentiate an AML from a malignant tumor including an RCC, liposarcoma, and Wilms tumor. This study suggests that FDG PET or PET/CT imaging is useful for differentiating a renal AML from a fat-containing malignant tumor.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Angiomyolipoma/*radionuclide imaging
Contrast Media/diagnostic use
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
Female
Fluorodeoxyglucose F18/diagnostic use
Humans
Kidney Neoplasms/*radionuclide imaging
Male
Middle Aged
*Positron-Emission Tomography
*Positron-Emission Tomography and Computed Tomography
Radiopharmaceuticals/diagnostic use
Retrospective Studies
Contrast Media
Radiopharmaceuticals
Fluorodeoxyglucose F18
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mues AC, Palacios JM, Haramis G, Casazza C, Badani K, Gupta M, et al. Contemporary experience in the management of angiomyolipoma. J Endourol. 2010. 24:1883–1886.2. Kawashima A, Sandler CM, Ernst RD, Tamm EP, Goldman SM, Fishman EK. CT evaluation of renovascular disease. Radiographics. 2000. 20:1321–1340.3. Bissler JJ, Kingswood JC. Renal angiomyolipomata. Kidney Int. 2004. 66:924–934.4. Sherman JL, Hartman DS, Friedman AC, Madewell JE, Davis CJ, Goldman SM. Angiomyolipoma: computed tomographic-pathologic correlation of 17 cases. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1981. 137:1221–1226.5. Halpenny D, Snow A, McNeill G, Torreggiani WC. The radiological diagnosis and treatment of renal angiomyolipoma-current status. Clin Radiol. 2010. 65:99–108.6. Kochhar R, Brown RK, Wong CO, Dunnick NR, Frey KA, Manoharan P. Role of FDG PET/CT in imaging of renal lesions. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2010. 54:347–357.7. Zapardiel I, Delafuente-Valero J, Bajo-Arenas JM. Renal angiomyolipoma during pregnancy: review of the literature. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 2011. 72:217–219.8. Lhommel R, Annet L, Bol A, Gigot JF, Sempoux C, Mathieu I, et al. PET scan with 11C-acetate for the imaging of liver masses: report of a false positive case. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2005. 32:629.9. Ho CL, Chan WK, Chen S, Leung YL, Cheng TK. Education and Imaging. Hepatobiliary and pancreatic: imaging for hepatic angiomyolipoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010. 25:1589.10. Arnold RT, Myers DT. Visualization of renal angiomyolipoma on F-18 FDG PET/CT. Clin Nucl Med. 2009. 34:539–540.11. Lemaitre L, Claudon M, Dubrulle F, Mazeman E. Imaging of angiomyolipomas. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 1997. 18:100–114.12. Davenport MS, Neville AM, Ellis JH, Cohan RH, Chaudhry HS, Leder RA. Diagnosis of renal angiomyolipoma with hounsfield unit thresholds: effect of size of region of interest and nephrographic phase imaging. Radiology. 2011. 260:158–165.13. Namura K, Minamimoto R, Yao M, Makiyama K, Murakami T, Sano F, et al. Impact of maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax) evaluated by 18-Fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography (18F-FDG-PET/CT) on survival for patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma: a preliminary report. BMC Cancer. 2010. 10:667.14. Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2007. CA Cancer J Clin. 2007. 57:43–66.15. Bachor R, Kotzerke J, Gottfried HW, Brändle E, Reske SN, Hautmann R. [Positron emission tomography in diagnosis of renal cell carcinoma]. Urologe A. 1996. 35:146–150.16. Kang DE, White RL Jr, Zuger JH, Sasser HC, Teigland CM. Clinical use of fluorodeoxyglucose F 18 positron emission tomography for detection of renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 2004. 171:1806–1809.17. Aide N, Cappele O, Bottet P, Bensadoun H, Regeasse A, Comoz F, et al. Efficiency of [(18)F]FDG PET in characterising renal cancer and detecting distant metastases: a comparison with CT. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2003. 30:1236–1245.18. Martínez de Llano SR, Delgado-Bolton RC, Jiménez-Vicioso A, Pérez-Castejón MJ, Carreras Delgado JL, Ramos E, et al. [Meta-analysis of the diagnostic performance of 18F-FDG PET in renal cell carcinoma]. Rev Esp Med Nucl. 2007. 26:19–29.19. Edinger AL, Linardic CM, Chiang GG, Thompson CB, Abraham RT. Differential effects of rapamycin on mammalian target of rapamycin signaling functions in mammalian cells. Cancer Res. 2003. 63:8451–8460.20. Jiang X, Kenerson H, Aicher L, Miyaoka R, Eary J, Bissler J, et al. The tuberous sclerosis complex regulates trafficking of glucose transporters and glucose uptake. Am J Pathol. 2008. 172:1748–1756.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Role of F-18 Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography for Diagnosis and Staging of Renal Tumors
- A Case of Hepatic Angiomyolipoma Showing Different Uptake on F-18 FDG and C-11 Acetate PET
- The Proper Use of PET/CT in Tumoring Imaging
- F-18 FDG PET/CT Finding in Solid Pseudo-papillary Tumor of the Pancreas 6 years After Initial Diagnosis
- ¹â¸F-FDG PET/MR Refines Evaluation in Newly Diagnosed Metastatic Urethral Adenocarcinoma