J Korean Fract Soc.
2008 Jan;21(1):51-56. 10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.1.51.
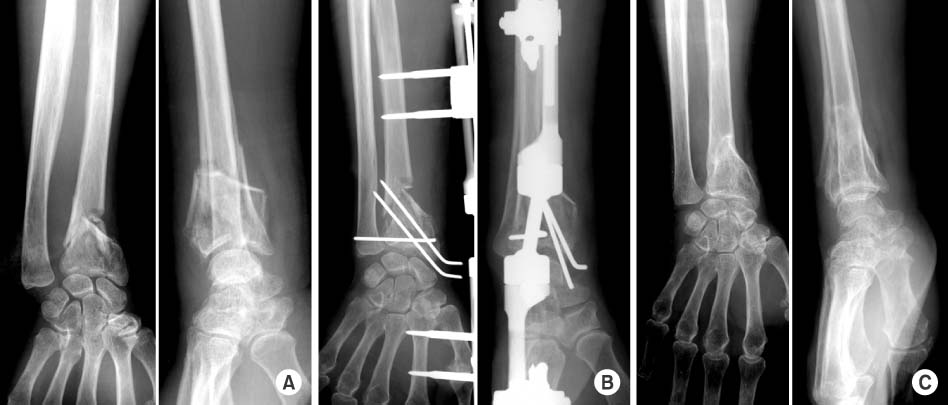
Comparison of Outcomes for Unstable Distal Radius Intraarticular Fractures: T-locking Compression Plate versus External Fixator
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, College of Medicine, Keimyung University, Daegu, Korea. os@dsmc.or.kr
- KMID: 1480964
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.1.51
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: To compare the outcomes between T-locking compression plate (T-LCP) and external fixator (EF) for unstable distal radius intraarticular fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We retrospectively analysed the results in 22 cases with T-LCP, 20 cases with EF. We evaluated the clinical results according to the Mayo Wrist Scoring System, radiographic results.
RESULTS
The mean score was 84.6 in the T-LCP group and 80.5 in the EF group respectively. Final radiographic measurements for the T-LCP group averaged 10.5 mm radial length, 21.7degrees radial inclination, 9.8degrees volar tilt and 0.25 mm intraarticular step-off. The EF group averaged 10.1 mm radial length, 20.3 degrees radial inclination, 6.3 degrees volar tilt and 0.73 mm intraarticular step-off.
CONCLUSION
Both groups showed satisfactory final clinical outcomes. But T-LCP group allowed return to daily living, resulting in early postsurgical wrist motion. By the anatomical reduction, final volar tilt, intraarticular step-off were statistically better in the T-LCP group.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Treatment for Unstable Distal Radius Fracture with Osteoporosis -Internal Fixation versus External Fixation-
Jin Rok Oh, Tae Yean Cho, Sung Min Kwan
J Korean Fract Soc. 2010;23(1):76-82. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.1.76.Comparative Analysis of the Results of Fixed-angle versus Variable-angle Volar Locking Plate for Distal Radius Fracture Fixation
Seung-Do Cha, Jai-Hyung Park, Hyung-Soo Kim, Soo-Tae Chung, Jeong-Hyun Yoo, Joo-Hak Kim, Jung-Hwan Park
J Korean Fract Soc. 2012;25(3):197-202. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.3.197.
Reference
-
1. Arora R, Lutz M, Fritz D, Zimmermann R, Oberladstatter J, Gabl M. Palmar locking plate for treatment of unstable dorsal dislocated distal radius fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2005; 125:399–404.
Article2. Cheon SJ, Ku JG, Lee DH, Kim HT, Suh JT. Treatment of distal radius fractures using the percutaneous K-wire reduction-fixation and external fixator. J Korean Fract Soc. 2006; 19:228–235.
Article3. Constantine KJ, Clawson MC, Stern PJ. Volar neutralization plate fixation of dorsally displaced distal radius fractures. Orthopedics. 2002; 25:125–128.
Article4. Cooney WP. External fixation of distal radial fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983; 180:44–49.
Article5. Cooney WP, Bussey R, Dobyns JH, Linscheid RL. Difficult wrist fractures. Perilunate fracture-dislocations of the wrist. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987; 214:136–147.6. Frykman G. Fracture of the distal radius including sequelae--shoulder-hand-finger syndrome, disturbance in the distal radio-ulnar joint and impairment of nerve function. A clinical and experimental study. Acta Orthop Scand. 1967; 108:3+.
Article7. Horesh Z, Volpin G, Hoerer D, Stein H. The surgical treatment of severe comminuted intra-articular fractures of the distal radius with small AO external fixation device. A prospective three-and-one-half-year follow-up study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991; 263:147–153.8. Huh CY, Yoon JR, Ha HS. Treatment of fractures of the distal radius with external fixator. J Korean Soc Fract. 1999; 12:995–1002.
Article9. Kamano M, Honda Y, Kazuki K, Yasuda M. Palmar plating for dorsally displaced fractures of the distal radius. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002; 397:403–408.
Article10. Knirk JL, Jupiter JB. Intra-articular fractures of the distal end of the radius in young abults. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1986; 68:647–659.
Article11. Lidstrom A. Fractures of distal end of the radius. A clinical and statistical study of end results. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl. 1959; 41:1–118.12. Orbay JL. The treatment of unstable distal radius fractures with volar fixation. Hand Surg. 2000; 5:103–112.
Article13. Papadonikolakis A, Shen J, Garrett JP, Davis SM, Ruch DS. The effect of increasing distraction on distal motion after external fixation on the wrist. J Hand Surg Am. 2005; 30:773–779.
Article14. Scheck M. Long term follow-up of treatment of comminuted fractures of the distal end of the radius by transfixation with kirschner wires and cast. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1962; 44:337–351.
Article15. Sim JC, Chung NS, Hong KD, Ha SS, Kang JH. Treatment of fractures of the distal radius using locking compression plate. J Korean Fract Soc. 2005; 18:100–104.
Article16. Wright TW, Horodyski M, Smith DW. Functional outcome of unstable distal radius fractures: ORIF with a volar fixed-angle tine plate versus external fixation. J Hand Surg Am. 2005; 30:289–299.
Article17. Zagorski JB. Comminuted fractures of the distal radius. Instr Course Lect. 1990; 39:255–258.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Failure of Distal Locking Screws in an Intraarticular Distal Radius Fracture Treated with Volar Locking Plate Fixation
- Treatment of Unstable Intraarticular Fracture of Distal Radius with External Fixator and Minimal open Reduction
- 2.4 mm Volar Locking Compression Plate for Treatment of Unstable Distal Radius Fractures
- External Fixation for Distal Radius Fractures
- K-wire Fixation Supplemented with External Fixator Versus Volar Locked Plating for Unstable Fractures of the Distal Radius