J Korean Fract Soc.
2008 Jan;21(1):31-36. 10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.1.31.
Surgical Fixation with Biodegradable Plate for the Treatment of Ankle Fractures
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Good Samsun Hospital, Busan, Korea. gyennim@yahoo.co.kr
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Goopo Sungsim Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Pusan Paik Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 1480961
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.1.31
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: The purpose of this article is to show the efficacy of a biodegradable plate for treating lateral malleolar fractures in the ankle joint.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
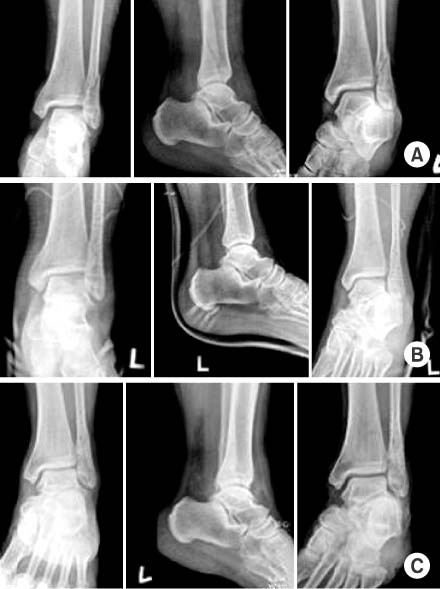
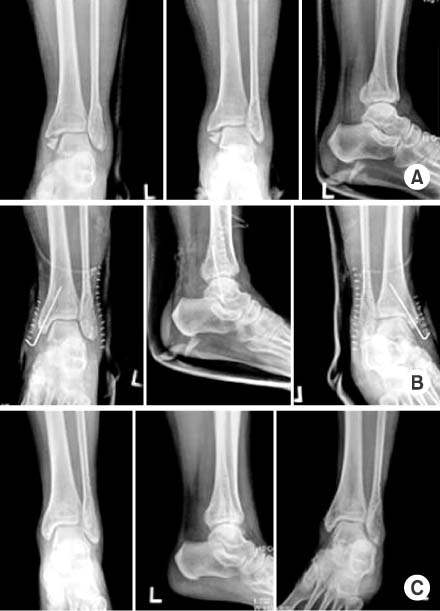
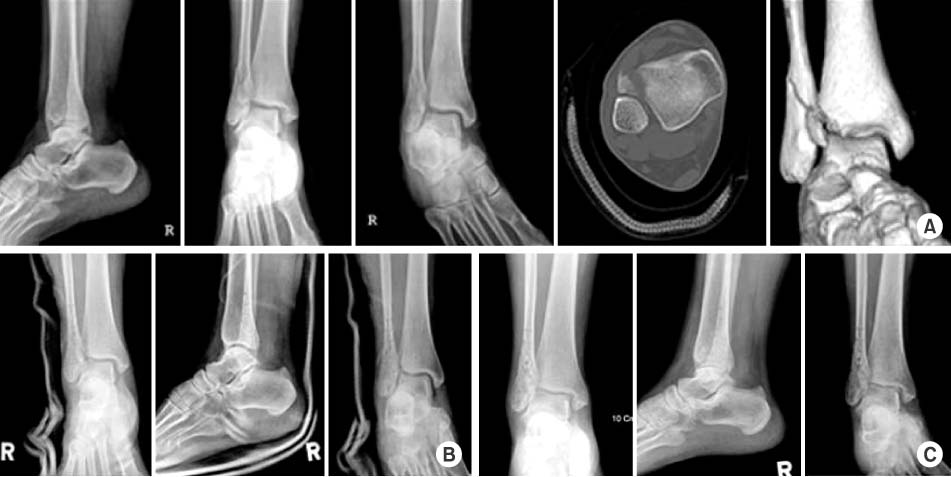
The 20 patients who underwent an open reduction and internal fixation for lateral malleolar fractures in the ankle joint from February, 2006 to February, 2007 in our hospital were enrolled into the study. The average age of the patients was 49.7 years and the average follow-up period was 5.6 months. The cases were analyzed by radiological bone union time and clinical results according to the criteria of Meyer et al.
RESULTS
Average radiological bone union time was 10.5 weeks. The clinical result was excellent in 19 cases (95%), good in 1 case (5%). There was one case of minimal displacement less than 1 mm, associated with anterior distal tibio-fibular ligament avulsion fracture.
CONCLUSION
For proper patients, a biodegradable plate is an effecttive alternative implant for stabilizing lateral malleolar fractures in the ankle joint, because there is no requirement for subsequent removal and slow resorption in vivo.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Delayed Foreign-body Reaction of Ankle Fracture Treated with a Biodegradable Plate and Screws - A Case Report -
Chul-Hyun Park, Dae-Hyun Song, Jae Ho Cho
J Korean Fract Soc. 2012;25(2):142-145. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.2.142.
Reference
-
1. Blasier RD, Bucholz R, Cole W, Johnson LL, Mäklä EA. Bioresorbable implants: applications in orthopaedic surgery. Instr Course Lect. 1997; 174:531–546.2. Böstman OM. Absorbable implants for the fixation of fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991; 73:148–153.
Article3. Böstman OM. Osteolytic changes accompanying degradation of absorbable fracture fixation implants. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991; 73:679–682.4. Böstman OM, Pihlajamäki HK. Late foreign-body reaction to an interosseous bioabsorbable polylactic acid screw. A case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998; 80:1791–1794.5. Böstman OM, Pihlajamäki HK, Partio EK, Rokkanen PU. Clinical biocompatibility and degradation of polylevolactide screws in the ankle. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995; 320:101–109.
Article6. Bucholz RW, Henry S, Henley MB. Fixation with bioabsorbable screws for the treatment of fractures of the ankle. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994; 76:319–324.
Article7. Chung DW, Soh JH, Lim CT. Fixation with bioabsorbable polylactide screws for the treatment of the ankle fracture with syndesmotic injurues. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2001; 36:395–401.
Article8. Daniels AU, Chang MK, Andriano KP. Mechanical properties of biodegradable polymers and composites proposed for internal fixation of bone. J Appl Biomater. 1990; 1:57–78.
Article9. Lee JI, Son MH, Lee JW, Namgung SH. Clinical evaluation for the ankle fractures by treatment. J Korean Soc Fract. 1997; 10:588–596.
Article10. Hovis WD, Bucholz RW. Polyglycolide bioabsorbable screws in the treatment of Ankle fractures. Foot Ankle Int. 1997; 18:128–131.
Article11. Hovis WD, Kaiser BW, Watson JT, Bucholz RW. Treatment of syndesmotic disruptions of the ankle with bioabsorbable screw fixation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002; 84:26–31.
Article12. Meyer TL Jr, Kulmer KW. A.S.I.F. technique and ankle fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1980; 150:211–221.
Article13. Park MS, Lee JM, Chae SS. Management of the ankle fracture. J Korean Soc Fract. 1990; 3:238–246.
Article14. Rokkanen PU. Absorbable materials in orthopaedic surgery. Ann Med. 1991; 23:109–115.
Article15. Rokkanen P, Majola A, Vasenius J, Vainionpaa S. Strength retention of self-reinforced polyglycolide (SR-PGA) and SR-polylactic acid (PLA) composite rods in vitro and in vivo. Acta Ortho Scand. 1990; 235:Suppl. 51.16. Simon JA, Ricci JL, Di Cesare PE. Bioreabsorbable fracture fixation in orthopedics: a comprehensive review. Part II. Clinical studies. Am J Orthop. 1997; 26:754–762.17. Thordarson DB. Fixation of ankle syndesmosis with bioabsorbable screws. Tech Orthop. 1998; 13:187–191.18. Yoon HK, Jeon KP, Kang KH, Kim KI. Biodegradable internal fixation for displaced non-communited malleolar fracture. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1998; 33:309–313.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparative Study for the Fixation Method in the Danis-Weber Type B Lateral Malleolar Fractures: An Antiglide Plate Fixation versus A Lateral Plate Fixation
- Treatment of the Distal Metaphyseal Fractures of Tibia - Comparison between Internal Fixation with a Plate and screws and External Fixation with Ilizarov Device
- Surgical Treatment of Distal Tibia Fractures
- The prognosis of fixation of mandibular fractures with biodegradable plates and screws
- Surgical Treatment of Internal Malleolar Fracture of the Ankle: Rush Rod Versus Plate Osteosynthesis