J Korean Fract Soc.
2008 Oct;21(4):312-315. 10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.4.312.
Lateral Dislocation of the First Metatarsophalangeal Joint: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, School of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea. osdr69@cnu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Saeson Clinic, Daejeon, Korea.
- KMID: 1480921
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.4.312
Abstract
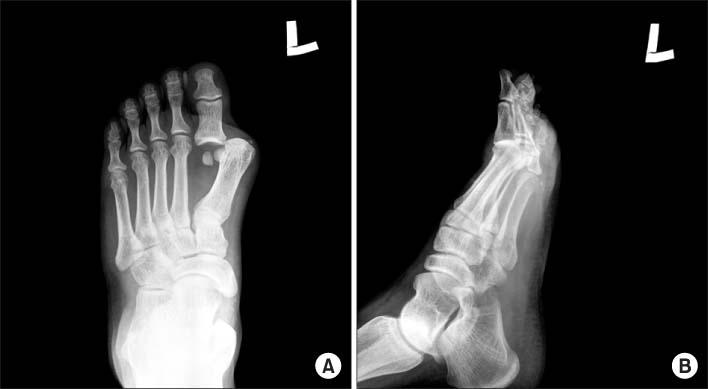
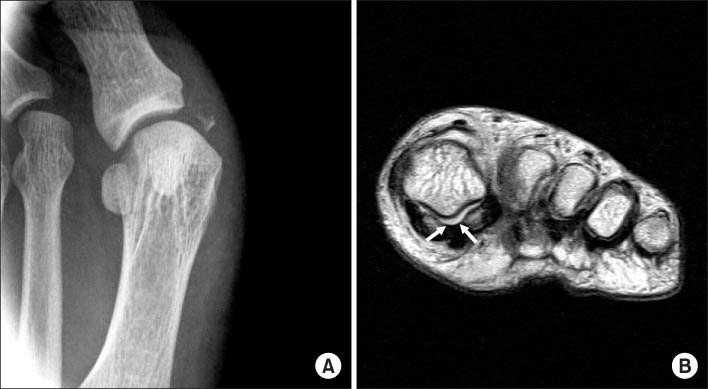
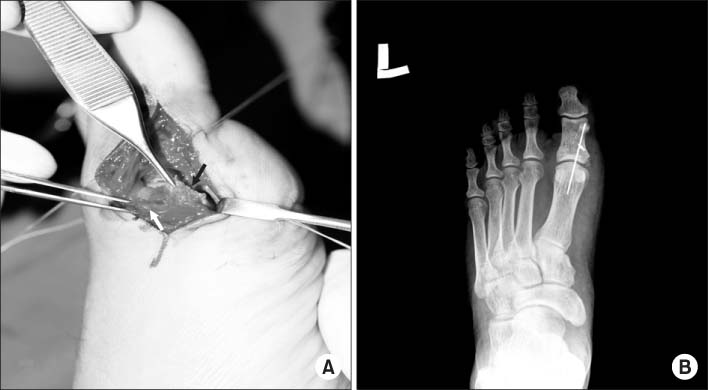
- Dislocation of the metatarsophalangeal joint is rare due to the stability of the ligaments and soft tissue surrounding the joint. The authors have experienced lateral dislocation of the first metatarsophalangeal joint, which required surgery, accompanied by complete injuries of medial collateral ligament and capsule, contributing to medial stability, differing from posterior dislocation with intersesamoid complex rupture, with a review of the relevant literature and previous reported cases.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Copeland CL, Kanat IO. A new classification for traumatic dislocations of the first metatarsophalangeal joint: type IIC. J Foot Surg. 1991; 30:234–237.2. Fabeck LG, Zekhnini C, Farrokh D, Descamps PY, Delincé PE. Traumatic hallux valgus following rupture of the medial collateral ligament of the first metatarsophalangeal joint: a case report. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2002; 41:125–128.
Article3. Gale DW. Lateral dislocation of the first metatarsophalangeal joint, a radiographic indicator of reducibility. Injury. 1991; 22:230.
Article4. Hwang CS, Kim YM, Oh HH, An YU, Kim JP. Dislocation of first metatarsophalangeal and tarsometatarsal joint -case report-. J Korean Soc Fract. 1995; 8:386–390.
Article5. Jahss MH. Traumatic dislocations of the first metat-arsophalangeal joint. Foot Ankle. 1980; 1:15–21.
Article6. Jahss MH. Disorders of the hallux and first ray. In : Wickland EH, editor. Disorders of the foot and ankle. Medical and surgical management. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders;1991. p. 1125–1129.7. Kim JH, Shin KH, Kim BJ. Irreducible dorsal dislocation of first metatarsophalangeal joint by closed method-report of a case. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1988; 23:1201–1204.
Article8. Lohrer H. MP I joint giving way-a case study. Foot Ankle Int. 2001; 22:153–157.
Article9. Piétu G. Lateral dislocation of the first metatarsophalangeal joint: report of two cases. J Trauma. 2005; 58:640–642.
Article10. Salamon PB, Gelberman RH, Huffer JM. Dorsal dislocation of the metatarsophalangeal joint of the great toe. A case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1974; 56:1073–1075.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Resection Arthroplasty for the Treatment of Joint Stiffness after Dislocation of the Four Lateral Lesser Metatarsophalangeal Joints (A Case Report)
- Irreducible Dorsal Dislocation of First Metatarsophalangeal Joint by Closed Method: Report of a Case
- Dislocation of First Metatarsophalangeal and farsornetatarsal Joint: Case Report
- Dislocations of the Interphalangeal Joint of the Great Tow with Interposition of a Seamoid Bone: A Report of Two Cases
- Synovial Chondromatosis of the First Metatarsophalangeal Joint: A Case Report