J Cardiovasc Ultrasound.
2009 Sep;17(3):96-98. 10.4250/jcu.2009.17.3.96.
A Case of Right Atrial Aneurysm Incidentally Found in Old Age
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Dongkang Medical Center, Ulsan, Korea. khj035@hanmail.net
- KMID: 1473733
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4250/jcu.2009.17.3.96
Abstract
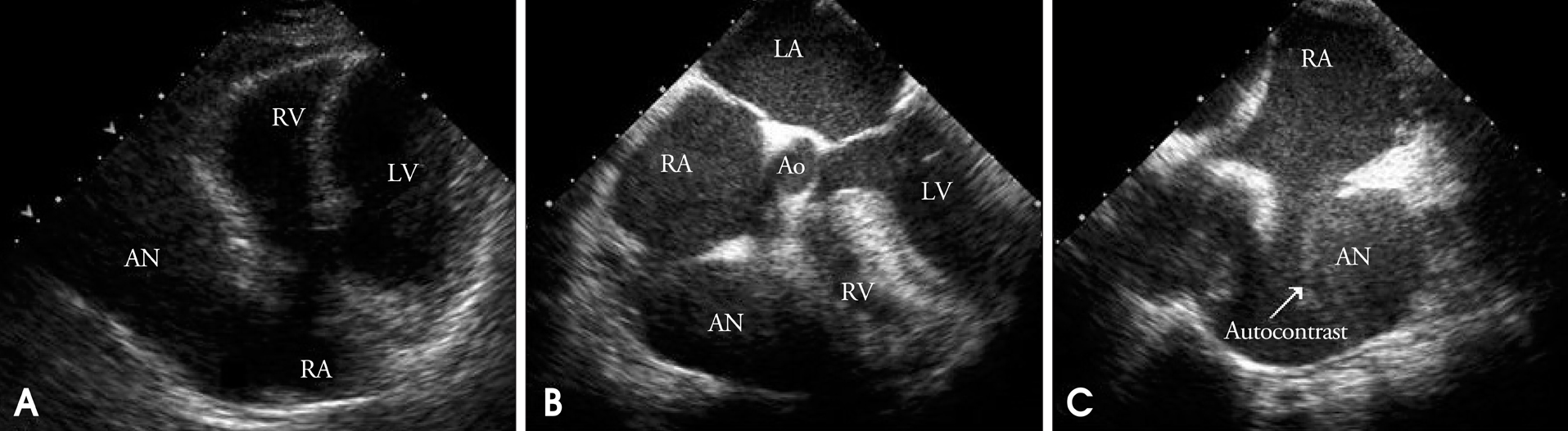
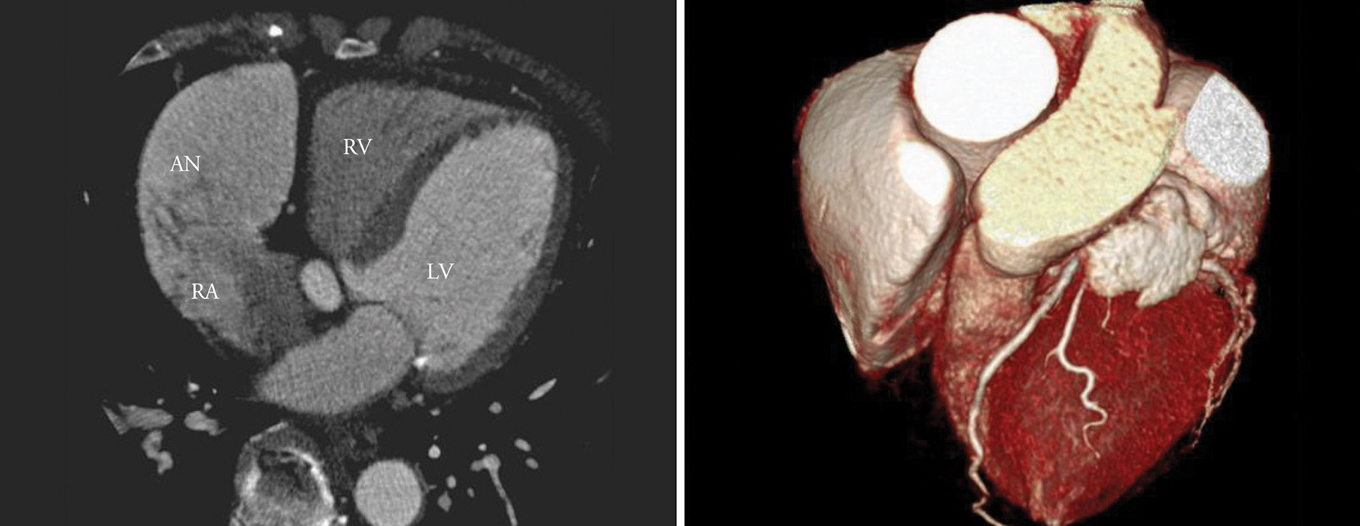
- Right atrial aneurysm is a rare abnormality of unknown origin. Approximately half of patients with right atrial aneurysm show no symptoms. Right atrial aneurysm is usually detected by chance at any time between fetal and adult life and can be associated with atrial arrhythmia and systemic embolism. The diagnosis of right atrial aneurysm can be established with echocardiography, computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Because of thromboembolic risk, aneurysmectomy is usually recommended. We review the case report of a 69-year-wold woman with right atrial appendiceal aneurysm, whose diagnosis was established by echocardiography and CT angiography.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Verma G, Lanjewar CP, Kerkar PG. Idiopathic right atrial aneurysm. J Assoc Physicians India. 2007. 55:590–592.2. Yu YG, Kim JW, Chung SH, Park JJ, Yun TJ, Seo DM, Kim YH, Ko JK, Park IS, Kim JS. Surgical repair of the congenital aneurysm of the right atrium. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2002. 35:56–59.3. Song JY, Sung JH, Lee JY, Kim SJ, Shim WS, Kim WH, Kim YM. A case of asymptomatic giant right atrial aneurysm. J Korean Pediatr Heart. 2004. 7:138–141.4. Chatrath R, Turek O, Quivers ES, Driscoll DJ, Edwards WD, Danielson GK. Asymptomatic giant right atrial aneurysm. Tex Heart Inst J. 2001. 28:301–303.5. Lee SP, Kwon DA, Shin DH, Chung JW, Chang HJ, Kim KI, Cho YS, Youn TJ, Chung WY, Chae IH, Choi DJ, Kim CH. A case of congenital left atrial appendage aneurysm. J Kor Soc Echo. 2005. 13:80–82.
Article6. Moon CS, Her MY, Seo WS, Jeong SR, Cho KH, Kim DK, Kim DI, Kim DS. A case of congenital left atrial appendage aneurysm. J Kor Soc Echo. 2002. 10:55–59.
Article7. Morrow AG, Behrendt DM. Congenital aneurysm (diverticulum) of the right atrium. Clinical manifestations and results of the operative treatment. Circulation. 1968. 38:124–128.
Article8. Beder SD, Nihill MR, McnaMara DG. Idiopathic dilation of the right atrium in a child. Am Heart J. 1982. 103:134–137.
Article9. Barberato SH, Barberato MF, Avila BM, Perretto S, Blume Ld Ldo R, Chamma Neto M. Aneurysm of the right atrial appendage. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2002. 78:236–241.
Article10. Zeebregts CJ, Hensens AG, Lacquet LK. Asymptomatic right atrial aneurysm : fotuitous finding and resection. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 1997. 11:591–593.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Incidentally Found, Growing Congenital Aneurysm of the Left Atrium
- Congenital Left Atrial Appendage Aneurysm: A Case Report
- A Case of Atrial Septal Aneurysm with Recurrent Atrial Fibrillation and Cerebellar Infarction
- A Case of Atrial Septal Aneurysm Associated with Atrial Septal Defect
- Resection of a Congenital Left Atrial Appendage Aneurysm without Extracorporeal Circulation