Infect Chemother.
2009 Aug;41(4):245-248. 10.3947/ic.2009.41.4.245.
A Case of Acute Myopericarditis Associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infection in a Korean Adult
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan Colledge of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. Kimsunghanmd@hotmail.com
- KMID: 1473676
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2009.41.4.245
Abstract
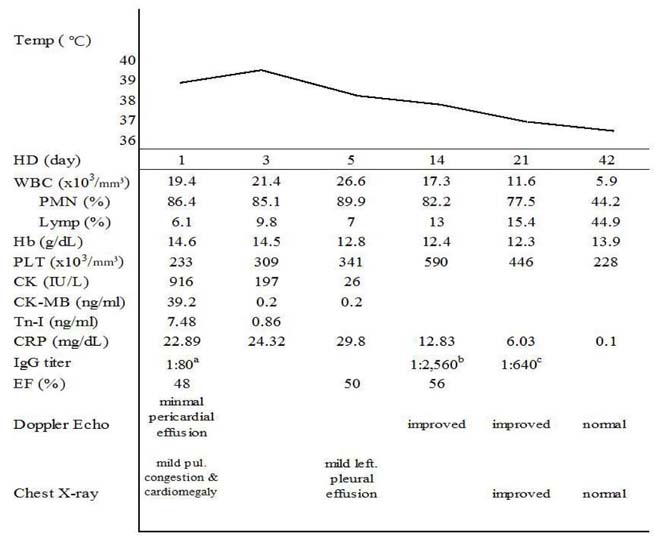
- We report on a 45-year-old man with a confirmed diagnosis of acute myopericarditis associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae. He visited our emergency department due to high fever (39degrees C) via a primary clinic. We made a diagnosis of myopericarditis based on symptoms, cardiac enzymes, electrocardiography, and transthoracic echocardiography. Serology (particle agglutination) testing for M. pneumoniae IgG antibody was also performed. The IgG antibody titer was 1:80 on the second day of admission, and increased to 1:2,560 by the 12th day of admission. Therefore, we confirmed the diagnosis of acute myopericarditis associated with M. pneumoniae and subsequently treated him with azithromycin. The symptoms and laboratory findings improved, and he recovered uneventfully.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Clinical Guideline for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Cardiovascular Infections
, , , ,
Infect Chemother. 2011;43(2):129-177. doi: 10.3947/ic.2011.43.2.129.
Reference
-
1. Waites KB. New concepts of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections in children. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2003. 36:267–278.2. Sands MJ Jr, Satz JE, Turner WE Jr, Soloff LA. Pericarditis and perimyocarditis associated with active Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Ann Intern Med. 1977. 86:544–548.
Article3. Farraj RS, McCully RB, Oh JK, Smith TF. Mycoplasma-associated pericarditis. Mayo Clin Proc. 1997. 72:33–36.
Article4. Pönkä A. Carditis associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Acta Med Scand. 1979. 206:77–86.5. Paz A, Potasman I. Mycoplasma-associated carditis. Case reports and review. Cardiology. 2002. 97:83–88.6. Duthoit G, Ou P, Sidi D, Bonnet D. Mycoplasma pneumoniae myopericarditis in children. Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss. 2006. 99:511–513.7. Esposito S, Colombo C, Ravaglia R, Faelli N, Tagliabue C, Corti F, Costantini D, Principi N. Mycoplasma pneumoniae pericarditis and cardiac tamponade in a 7-year-old girl with cystic fibrosis. Infection. 2006. 34:355–356.
Article8. Jeon CH, Hong SY, Song MS, Kim CH, Hwang YH, Cho KH. Pericardial Effusion: Report of Three Unusual Cases. J Korean Pediatr Cardiol Soc. 2002. 6:97–103.9. Koo GD, Ahn SH, Kim HS, Cho BS, Cha SH. A Case of Pericarditis Associated with Mycoplasma and Salmonella co-Infection. Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis. 1997. 4:155–159.
Article10. Lee JM, Lee SJ, Kim WD, Cho SM, Lee DS, Kim DK, Choi SM. A case of pericarditis with pericardiac effusion caused by Mycoplasma pneumonia. Dongguk J Med. 2003. 10:473–479.11. Imazio M, Trinchero R. Myopericarditis: Etiology, management, and prognosis. Int J Cardiol. 2008. 127:17–26.
Article12. Finkelstein D, Klainer MJ. Pericarditis associated with primary atypical pneumonia. Am Heart J. 1944. 28:385–394.
Article13. Echevarría JM, León P, Balfagón P, López JA, Fernández MV. Diagnosis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection by microparticle agglutination and antibody-capture enzyme-immunoassay. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1990. 9:217–220.
Article14. Yoo SJ, Oh HJ, Shin BM. Evaluation of Four Commercial IgG- and IgM-specific Enzyme Immunoassays for Detecting Mycoplasma pneumoniae Antibody: Comparison with Particle Agglutination Assay? J Korea Med Sci. 2007. 22:795–801.
Article15. Liu FC, Chen PY, Huang F, Tsai CR, Lee CY, Wang LC. Rapid diagnosis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in children by polymerase chain reaction. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2007. 40:507–512.16. Jacobs E. Serological diagnosis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections: a critical review of current procedures. Clin Infect Dis. 1993. 17:Suppl 1. 79–82.17. Barker CE, Sillis M, Wreghitt TG. Evaluation of Serodia Myco II particle agglutination test for detecting Mycoplasma pneumoniae antibody: comparison with µ-capture ELISA and indirect immunofluorescence. J Clin Pathol. 1990. 43:163–165.
Article18. Chan PW, Lum LC, Ngeow YF, Yasim MY. Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in Malaysian children admitted with community acquired pneumonia. Southeast Asain J Trop Med Public Health. 2001. 32:397–401.19. Kim NH, Lee JA, Eun BW, Shin SH, Chung EH, Park KW, Choi EH, Lee HJ. Comparison of polymerase chain reaction and the indirect particle agglutination antibody test for the diagnosis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children during two outbreaks. Pediatric Infect Dis J. 2007. 26:897–903.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Erythema Multiforme in Adults Associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infection
- A Case of Acute Myopericarditis Associated With Mycoplasma Pneumoniae Infection in a Child
- A Case of Cerebral Infarction Complicated by Mycoplasma pneumoniae Pneumonia
- A Case of Mycoplasma Pneumoniae Infection Associated Acute Interstitial Nephritis
- A Case Report of Acute Pancreatitis Caused by Mycoplasma Pneumoniae Infection