J Korean Endocr Soc.
2009 Mar;24(1):58-62. 10.3803/jkes.2009.24.1.58.
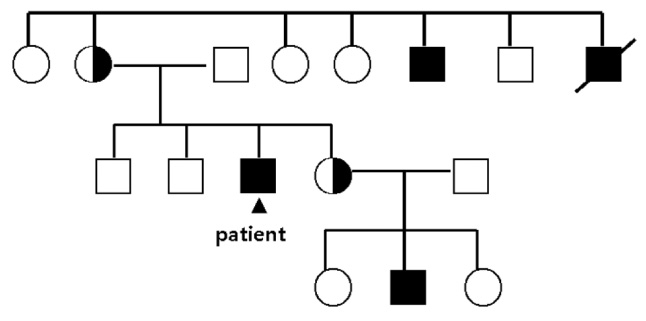
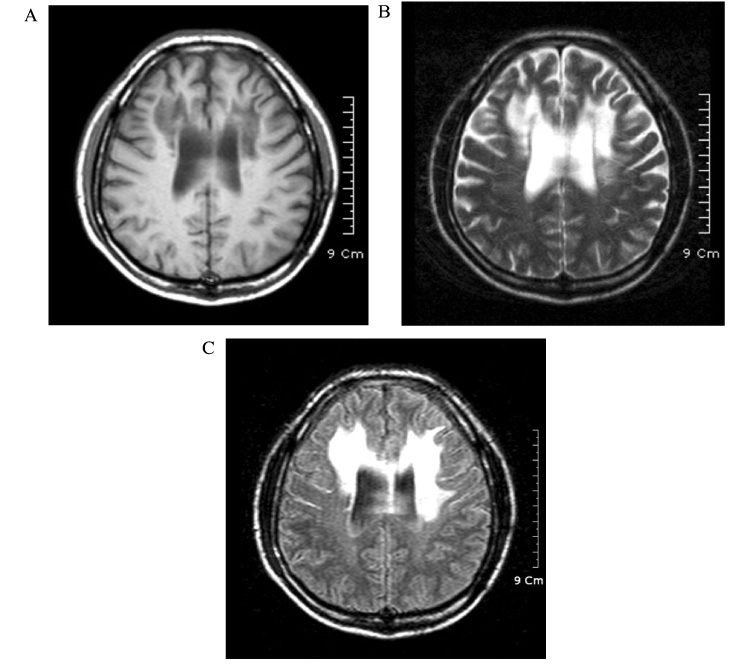
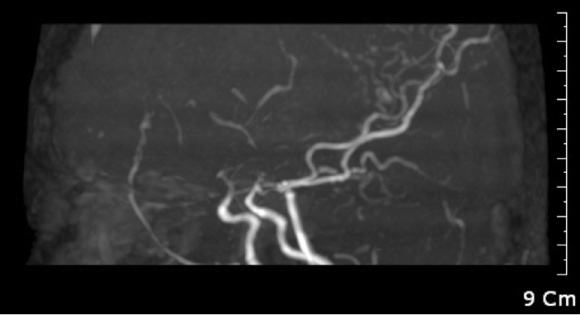
A Case of Adult-Onset Adrenoleukodystrophy Combined with Moyamoya Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, The Institute of Wonkwang Medical Sciences, Korea.
- 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, The Institute of Wonkwang Medical Sciences, Korea.
- KMID: 1468498
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2009.24.1.58
Abstract
- Adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD) is a rare inherited metabolic disease associated with the accumulation of very long chain fatty acids (VLCFA) in the central and peripheral nervous systems and adrenal glands, and leads to leukoencephaly myeloneuropathy, adrenal insufficiency, and hypogonadism. Frequent phenotypes, which account for 80% of cases, are infantile ALD and adrenomyeloneuropathy. Adult-onset ALD is rare (1~3%). The diagnosis of X-linked ALD is based on clinical findings and abnormal plasma concentrations of VLCFA. Here, we report a rare case of adult-onset ALD, which might involve a brain vascular operation as an aggravating factor, combined with moyamoya disease, in a 35-year-old male who presented with adrenal insufficiency, abnormal brain imaging, and elevated VLCFA levels.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Clinical and Genetic Aspects in Twelve Korean Patients with Adrenomyeloneuropathy
Hyung Jun Park, Ha Young Shin, Hoon-Chul Kang, Byung-Ok Choi, Bum Chun Suh, Ho Jin Kim, Young-Chul Choi, Phil Hyu Lee, Seung Min Kim
Yonsei Med J. 2014;55(3):676-682. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2014.55.3.676.
Reference
-
1. van Geel BM, Assies J, Wanders RJA, Barth PG. X linked adrenoleukodystrophy: clinical presentation, diagnosis, and therapy. J Neutrol neurosurg Psychiatry. 1997. 63:4–14.2. Bezman L, Moser AB, Raymond GV, Rinaldo P, Watkins PA, Smith KD, Kass NE, Moser HW. Adrenoleukodystrophy: incidence, new mutation rate, and results of extended family screening. Ann Neurol. 2001. 49:512–517.3. Igarshi M, Schaumburg HH, Powers JM, Kishimoto Y, Kolodny E, Suzuki K. Fatty acid abnormality in adrenoleukodystrophy. J Neurochem. 1976. 26:851–860.4. Kumar AJ, Kohler W, Kruse B, Naidu S, Bergin A, Edwin D, Moser HW. MR findings in adult-onset adrenoleukodystrophy. Am J Neuroradiol. 1995. 16:1227–1237.5. Kubota M, Kurihara E, Yonezawa M, Mizuno Y, Tamagawa K, Komiya K, Suzuki Y. Adrenoleukodystrophy associated with cerebral arteriovenous malformation. Acta Paediatr Jpn. 1990. 32:543–547.6. Jeong JP, Kim CH, Lee SA. A case of adrenomyeloneuropathy. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 2001. 19:431–434.7. Moser HW, Smith KD, Watkins PA, Powers J, Moser AB. Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Vallwe D, editors. X-linked Adrenoleukodystrophy. The metabolic and molecular bases of inherited disease. 2001. 8th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill company;3257–3301.8. Moser HW, Fatemi A, Zackowski K, Smith S, Golay X, Muenz L, Raymond G. Evaluation of therapy of X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Neurochem Res. 2004. 29:1003–1016.9. Korenke GC, Fuchs S, Krasemann E, Doerr HG, Wilichowski E, Hunneman DH, Hanefeld . Cerebral adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD) in only one of monozygotic twins with an identical ALD genotype. Ann Neurol. 1996. 40:254–257.10. Weller M, Liedtke W, Peterson D, Opit H, Poremba M. Very-late-onset adrenoleukodystrophy: possible precipitation of demyelination by cerebral contusion. Neurology. 1992. 42:367–370.11. Wilkinson IA, Hopkins IJ, Pellard AC. Can head injury influence the site of demyelination in adrenoleukodystrophy? Dev Med Child Neurol. 1987. 29:797–800.12. Turpin JC, Paturneau-Jouas M, Sereni C, Pluot M, Baumann N. Revelation a l'age adulte d'un cas d'adrenoleucodystrophie familiale. Rev Neurol(Paris). 1985. 141:289–295.13. Yoon KH, Suh DC, Lee SA, Lee HK, Choi CG, Yoo SJ. Delayed-onset adrenoleukodystrophy after cerebral contusion: progressive pattern of demyelination on serial MRImaging. J Korean Radiol Soc. 1996. 35:173–176.14. Kumar AJ, Kőhler W, Kruse B, Naidu S, Bergin A, Edwin D, Moser HW. MR findings in Adult-onset adrenoleukodystrophy. Am J Neuroradiol. 1995. 16:1227–1237.15. Moser AB, Kreiter N, Bezman L, Lu S, Raymond GV, Naidu S, Moser HW. Plasma very long chain fatty acids in 3,000 peroxisome disease patients and 29,000 controls. Ann Neurol. 1999. 45:100–110.16. Kemp S, Wei HM, Lu JF, Braiterman LT, McGuinness MC, Moser AB, Watkins PA, Smith KD. Gene redundancy and pharmacological gene therapy: implications for X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Nat Med. 1998. 4:1261–1268.17. Shapiro E, Krivit W, Lockman L, Jambaque I, Peters C, Cowan M, Harris R, Blanche S, Bordigoni P, Loes D, Ziegler R, Crittenden M, Ris D, Berg B, Cox C, Moser H, Fischer A, Aubourg P. Long-term effect of bone-marrow transplantation for childhood-onset cerebral X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Lancet. 2000. 356:71–78.18. Odone A, Odone M. Lorenzo's oil: a new treatment for adrenoleukodystrophy. J Pediatr Neurosci. 1989. 5:55–61.19. Moser HW, Raymond GV, Lu SE, Muenz LR, Moser AB, Xu J, Jones RO, Loes DJ, Melhem ER, Dubey P, Bezman L, Brereton NH, Odone A. Follow-up of 89 asymptomatic patients with adrenoleukodystrophy treated with Lorenzo's oil. Arch Neurol. 2005. 62:1073–1080.20. Kim HJ, Kim EY, Woo YJ, Kook H. Lorenzo's oil treatment x-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Korean J Pediatr. 2005. 48:1232–1238.