J Korean Soc Transplant.
2010 Sep;24(3):210-213. 10.4285/jkstn.2010.24.3.210.
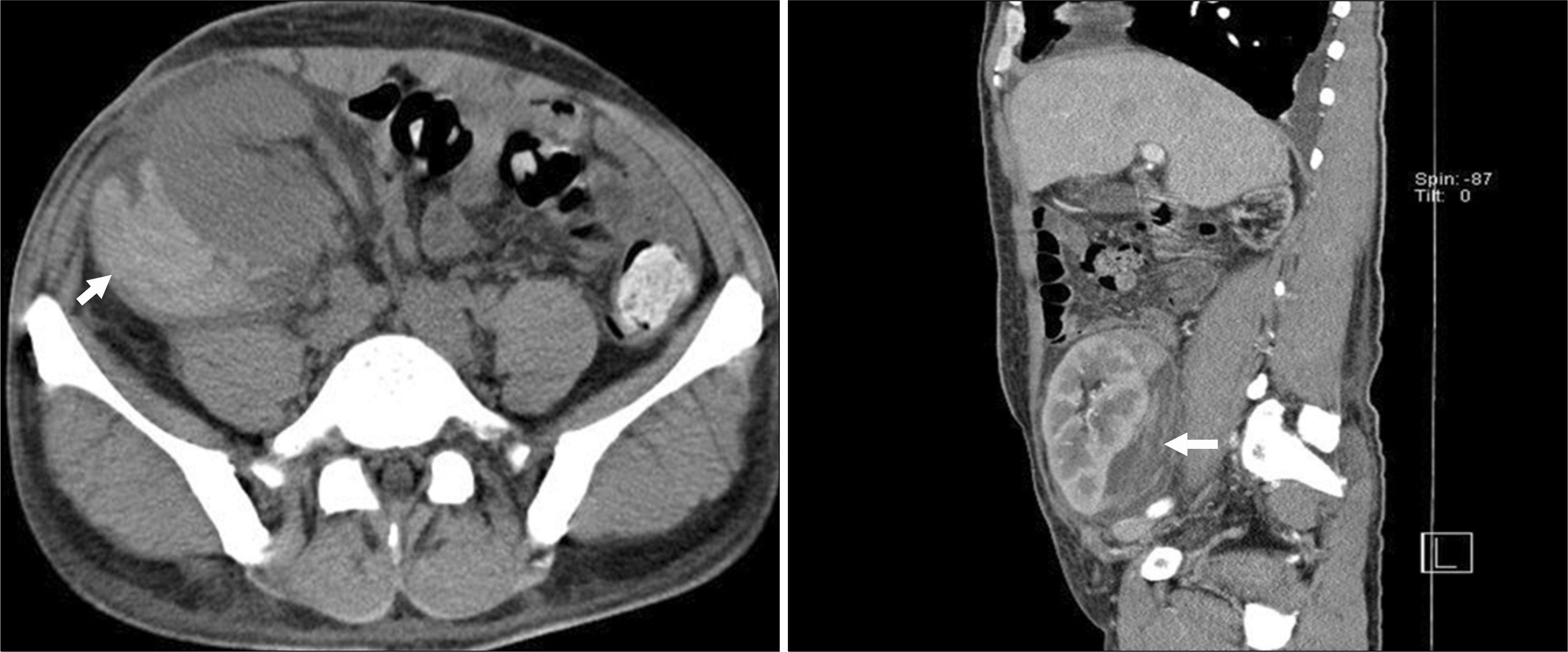
Late Spontaneous Subcapsular Hematoma in an Allograft Kidney
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. np@dsmc.or.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 3Kidney Institute, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 1464315
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4285/jkstn.2010.24.3.210
Abstract
- A spontaneous subcapsular hematoma in an allograft kidney is a rare condition with only a few cases reported in the literature. Common causes of subcapsular hematoma of an allograft include trauma, post-biopsy status, occult malignancy, vascular diseases, and infection. Chronic allograft dysfunction related to spontaneous subcapsular hematoma is extremely rare. We report a case of spontaneous subcapsular hematoma in a patient who underwent a renal transplant 14 years ago in which we could not find an associated condition.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1). Koushik RS, Ibrahim HN. Spontaneous subcapsular hematoma in chronic kidney disease. J Nephrol. 2006; 19:391–3.2). Haydar A, Bakri RS, Prime M, Goldsmith DJ. Page kidney – a review of the literature. J Nephrol. 2003; 16:329–33.3). Byun SW, Lee JY, Park JS, Park SK. Spontaneous subcapsular hematoma on a transplanted kidney. Korean J Nephrol. 2009; 28:469–73. (변승운, 이지영, 박정식, 박수길. 자발적 이식 신 피막하 혈종 1예. 대한신장학회지 2009;28: 469–73.).4). Yang MH, Loong CC, Wu CW, Lui WY. Late spontaneous kidney graft decapsulating after administration of sirolimus in a recipient with chronic hepatitis B and C infection: a case report. Transplant Proc. 2008; 40:2437–9.5). Albi G, del Campo L, Tagarro D. Wünderlich's syndrome: causes, diagnosis and radiological management. Clin Radiol. 2002; 57:840–5.
Article6). Zhang JQ, Fielding JR, Zou KH. Etiology of spontaneous perirenal haemorrhage: a metaanalysis. J Urol. 2002; 167:1593–6.7). Kamar N, Sallusto F, Rostaing L. Acute Page kidney after a kidney allograft biopsy: successful outcome from observation and medical treatment. Transplantation. 2009; 87:453–4.
Article8). Cromie WJ, Jordan MH, Leapman SB. Pseudorejection: the Page kidney phenomenon in renal allografts. J Urol. 1976; 116:658–9.
Article9). Dempsey J, Gavant ML, Cowles SJ, Gaber AO. Acute Page kidney phenomenon: a cause of reversible allograft failure. South Med J. 1993; 86:574–7.10). Casey RG, Murphy CG, Hickey DP, Creagh TA. Wünderlich's syndrome, an unusual cause of the acute abdomen. Eur J Radiol Extra. 2006; 57:91–3.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of Spontaneous Bilateral Subcapsular Hematoma of the Kidney
- Spontaneous Ruptured Subcapsular Liver Hematoma Associated with Pregnancy
- A Case of Spontaneous Renal Subcapsular Hematoma and Acute Renal Failure Developed after Cesarean Section with Severe Preeclampsia
- Hypertension Caused by Bilateral Subcapsular Hematoma (the Page Kidney); A Case Report
- Spontaneous Renal Rupture Following Urinary Tract Infection and Its Recovery through Conservative Treatment