J Korean Fract Soc.
2010 Jan;23(1):83-89. 10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.1.83.
A Finite Element Analysis of Biomechanical Stability of Compression Plate Fixation System in according to Existing of Fracture Gap after Bone Fracture Augmentation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Senior Products Industrial Center, Busan Techno-park, Korea.
- 2AK Project, Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan.
- 3Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Korea University College of Medcine, Seoul, Korea. jkoh@korea.ac.kr
- KMID: 1461577
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.1.83
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study using the finite element analysis (FEA) focused on evaluating the biomechanical stability of the LC-DCP in accordance with existing of the fracture gap at the facture site after bone fracture augmentation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
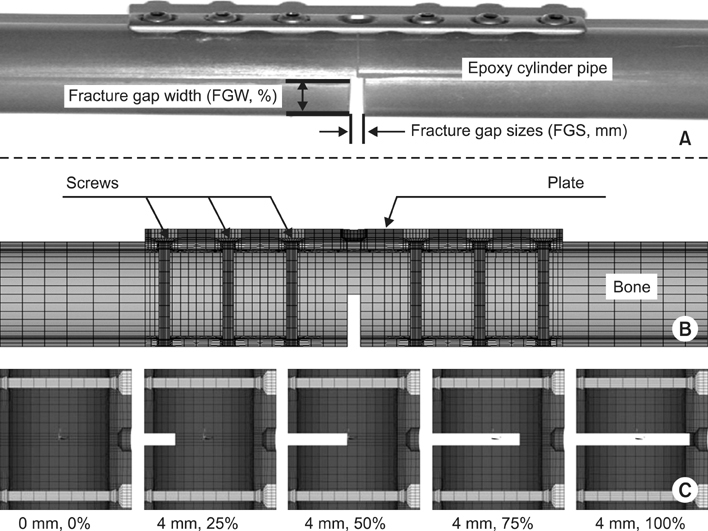
For FEM analysis, total eleven types with different fracture models considering clinical fracture cases were constructed according to the fracture gap sizes (0, 1, 4 mm)/widths (0, 25, 50, 75, 100%). Limited contact dynamic compression plate (LC-DCP) fixation system was used in this FEM analysis, and three types of load were applied to the bone-plate fixation system: compressive, torsional, bending load.
RESULTS
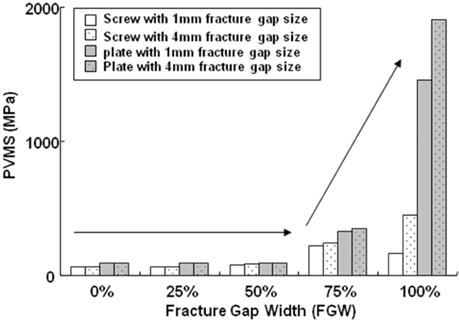
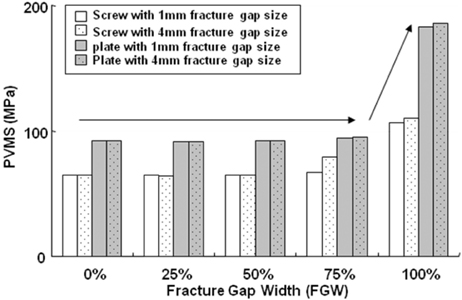
The results in FEM analysis showed that the 1, 4 mm fracture gap sizes and 75% or more fracture gap widths increased considerably the peak von Mises stress (PVMS) both the plate and the screw under all loading conditions. PVMS were concentrated on the center of the LC-DCP bone-plate, and around the necks of screws.
CONCLUSION
Based on the our findings, we recommend at least 50% contact of the fracture faces in a fracture surgery using the compression bone-plate system. Moreover, if x-ray observation after surgery finds 100% fracture gap or 50% or more fracture gap width, supplementary measures to improve biomechanical stability must be taken, such as restriction of walking of the patient or plastering.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Baumgaertel F, Buhl M, Rahn BA. Fracture healing in biological plate osteosynthesis. Injury. 1998. 29:Suppl 3. C3–C6.
Article2. Cordey J, Borgeaud M, Perren SM. Force transfer between the plate and the bone: relative importance of the bending stiffness of the screws and the friction between plate and bone. Injury. 2000. 31:Suppl 3. C21–C28.
Article3. Cordey J, Perren SM, Steinemann SG. Stress protection due to plates: myth or reality? A parametric analysis made using the composite beam theory. Injury. 2000. 31:Suppl 3. C1–C13.
Article4. Ferguson SJ, Wyss UP, Pichora DR. Finite element stress analysis of a hybrid fracture fixation plate. Med Eng Phys. 1996. 18:241–250.
Article5. Gardner MJ, Brophy RH, Campbell D, et al. The mechanical behavior of locking compression plates compared with dynamic compression plates in a cadaver radius model. J Orthop Trauma. 2005. 19:597–603.
Article6. Gautier E, Perren SM, Cordey J. Effect of plate position relative to bending direction on the rigidity of a plate ostosynthesis. A theoretical analysis. Injury. 2000. 31:Suppl 3. C14–C20.7. Korner J, Diederichs G, Arzdorf M, et al. A biomechanical evaluation of methods of distal humerus fracture fixation using locking compression plate versus conventional reconstruction plates. J Orthop Trauma. 2004. 18:286–293.
Article8. Kowalski MJ, Schemitsch EH, Harringston RM, Chapman JR, Swionthowski MF. A comparative biomechanical evaluation of a noncontacting plate and currently used devices for tibial fixation. J Trauma. 1996. 40:5–9.
Article9. Fulkerson E, Egol KA, Kubiak EN, Liporace F, Kummer FJ, Koval KJ. Fixation of diaphyseal fractures with segmental defects: a biomechanical comparison of locked and conventional plating techniques. J Trauma. 2006. 60:830–835.
Article10. Perren SM. Evolution of the internal fixation of long bone fracture. The scientific basis of biological internal fixation: choosing a new balance between stability and biology. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002. 84:1093–1110.11. Perren SM. The concept of biological plating using the limited contact-dynamic compression plate (LC-DCP) Scientific background, design and application. Injury. 1991. 22:Suppl 1. 1–41.
Article12. Ramakrishna K, Shidhar I, Sivashanker S, Khong KS, Chista DN. Design of fracture fixation plate for necessary and sufficient bone stress shielding. JSME Int J Ser C. 2004. 47:1086–1094.
Article13. Sommer C, Gautier E, Müller M, Helfet DL, Wagner M. First clinical results of the locking compression plate (LCP). Injury. 2003. 34:Suppl 2. B43–B54.
Article14. Stoffel K, Dieter U, Stachowiak G, Gächter A, Kuster MS. Biomechanical testing of the LCP - how can stability in locked internal fixators be controlled? Injury. 2003. 34:Suppl 2. B11–B19.
Article15. Stoffel K, Stachowiak G, Forster T, Gächter A, Kuster M. Oblique screws at the plate ends increase the fixation strength in synthetic bone test medium. J Orthop Trauma. 2004. 18:611–616.
Article16. Törnkvist H, Hearn TC, Schatzker J. The strength of plate fixation in relation to the number and spacing of bone screws. J Orthop Trauma. 1996. 10:204–208.
Article17. Veerabagu S, Fujihara K, Dasari GR, Ramakrishna S. Strain distribution analysis of braided composite bone plates. Compos Sci Technol. 2003. 62:427–435.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Fracture Gap on Biomechanical Stability of Compression Bone-Plate Fixation System after Bone Fracture Augmentation
- The Effect of the Cross-pins on the Fixation Stiffness using Finite Element Method in Fracture of Femoral Shaft
- Biomechanical Efficacy of Various Anterior Spinal Fixation in Treatment of Thoraco-lumbar Spine Fracture
- Additional Screw Added to the Femoral Neck System Could Enhance the Stability of Pauwel Type III Femoral Neck Fractures: a Finite Element Analysis
- Three - Dimensional Numerical analysis of the Mechanical function of the Plate Fixation for the Long bone Fracture