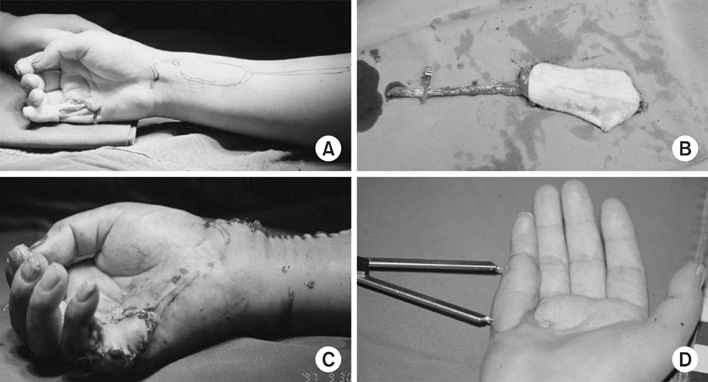
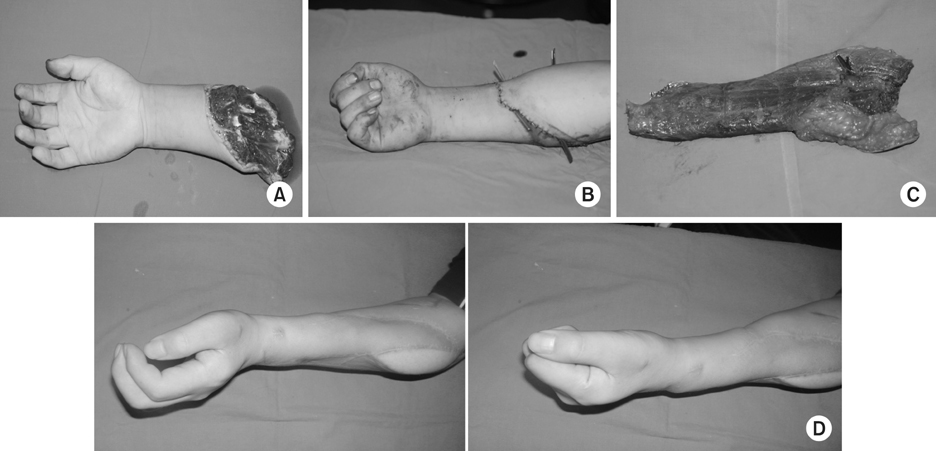
J Korean Fract Soc.
2010 Apr;23(2):257-262. 10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.2.257.
Treatment of Traumatic Soft Tissue Defect: Free Flap
- Affiliations
-
- 1ljhos@khnmc.or.kr
- KMID: 1461556
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.2.257
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Soft Tissue Reconstruction for Open Tibia Fractures
Young-Woo Kim, Ho-Youn Park, Yoo-Joon Sur
Arch Hand Microsurg. 2020;25(3):207-218. doi: 10.12790/ahm.20.0037.
Reference
-
1. Baumeister S, Germann G. Soft tissue coverage of the extremely traumatized foot and ankle. Foot Ankle Clin. 2001. 6:867–903.
Article2. Byrd HS, Spicer TE, Cierny G 3rd. Management of open tibial fractures. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1985. 76:719–730.
Article3. Carwell G. Heel reconstruction using the medial plantar fasciocutaneous flap. Contemp Orthop. 1986. 12:41.4. Chen S, Tsai YC, Wei FC, Gau YL. Emergency free flaps to the type IIIC tibial fracture. Ann Plast Surg. 1990. 25:223–229.
Article5. Cierny G 3rd, Byrd HS, Jones RE. Primary versus delayed soft tissue coverage for severe open tibial fractures. A comparison of results. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983. 178:54–63.6. Connor H, Mahdi OZ. Repetitive ulceration in neuropathic patients. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2004. 20:Suppl 1. S23–S28.
Article7. Giannoudis PV, Papakostidis C, Roberts C. A review of the management of open fractures of the tibia and femur. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006. 88:281–289.
Article8. Gorman PW, Barnes CL, Fischer TJ, McAndrew MP, Moore MM. Soft-tissue reconstruction in severe lower extremity trauma. A review. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989. 243:57–64.9. Hammert WC, Minarchek J, Trzeciak MA. Free-flap reconstruction of traumatic lower extremity wounds. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2000. 29:9 Suppl. 22–26.10. Heller L, Levin LS. Lower extremity microsurgical reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001. 108:1029–1041.
Article11. Isenberg JS, Sherman R. Zone of injury: a valid concept in microvascular reconstruction of the traumatized lower limb? Ann Plast Surg. 1996. 36:270–272.
Article12. Korompilias AV, Lykissas MG, Vekris MD, Beris AE, Soucacos PN. Microsurgery for lower extremity injuries. Injury. 2008. 39:S103–S108.
Article13. Mantey I, Foster AV, Spencer S, Edmonds ME. Why do foot ulcers recur in diabetic patients? Diabet Med. 1999. 16:245–249.
Article14. McCabe SJ, Breidenbach WC. The role of emergency free flaps for handtrauma. Hand Clin. 1999. 15:275–288.15. Park S, Han SH, Lee TJ. Algorithm for recipient vessel selection in free tissue transfer to the lower extremity. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1999. 103:1937–1948.
Article16. Saint-Cyr M, Gupta A. Indications and selection of free flaps for soft tissue coverage of the upper extremity. Hand Clin. 2007. 23:37–48.
Article17. Scheker LR, Ahmed O. Radical debridement, free flap coverage, and immediate reconstruction of the upper extremity. Hand Clin. 2007. 23:23–36.
Article18. Serafin D, Georgiade NG, Smith DH. Comparison of free flaps with pedicled flaps for coverage of defects of the leg or foot. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1977. 59:492–499.
Article19. Wei FC, Jain V, Celik N, Chen HC, Chuang DC, Lin CH. Have we found an ideal soft-tissue flap? An experience with 672 anterolateral thigh flaps. Plast Reconst Surg. 2002. 109:2219–2226.
Article20. Yaremchuk MJ, Drumback RJ, Manson PN, Burgess AR, Poka A, Weiland AJ. Acute and definitive management of traumatic osteocutaneousdefects of the lower extremity. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1987. 80:1–14.21. Yazar S, Lin CH, Lin YT, Ulusal AE, Wei FC. Outcome comparison between free muscle and free fasciocutaneous flaps for reconstructionof distal third and ankle traumatic open tibial fracture. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006. 117:2468–2475.
Article22. Yazar S, Lin CH, Wei FC. One-stage reconstruction of composite bone and soft-tissue defects in traumatic lower extremities. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004. 114:1457–1466.
Article23. Yildirim S, Avici G, Aköz T. Soft-tissue reconstruction using a free anterolateral thigh flap: Experience with 28 patients. Ann Plast Surg. 2003. 51:37–44.
Article24. Younger AS, Goetz T. Soft tissue coverage for posttraumatic reconstruction. Foot Ankle Clin. 2006. 11:217–235.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Reconstruction of the Hand Using Fabricated Great Toe Pulp and Anterolateral Thigh Chimeric Free Flap
- Clinical Applications of Venous Free Flaps
- Reconstruction of Defect After Wide Excision of Malignant Soft Tissue Tumor of Limb Using Free Flap
- Free Vasularized Scapular and Parascapular Flap
- Free Flaps for Hand Soft Tissue Reconstruction