Treatment of the Unstable Intertrochanteric Fracture with Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation: Comparison with Compression Hip Screw with Trochanteric Stabilizing Plate
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Mokdong Hospital, Ewha Woman's University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ewhamdos@korea.com
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Sahmyook Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1461491
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.4.353
Abstract
- PURPOSE
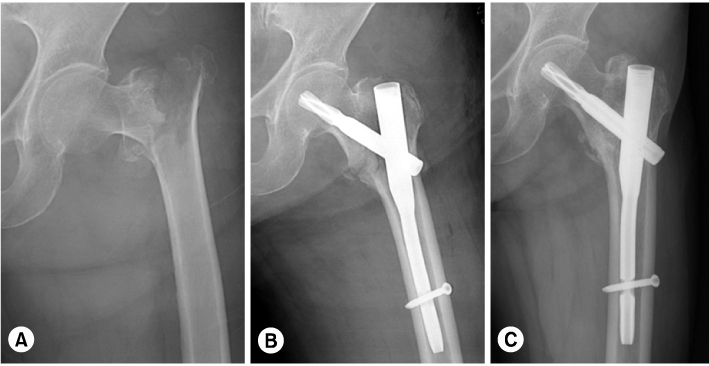
To evaluate the effectiveness of Proximal Femoral Nail Anti-rotation (PFNA) for the treatment of unstable intertrochanteric fracture comparing with Compression Hip Screw (CHS) with Trochanteric Stabilizing Plate (TSP).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
With clinical study, 43 patients who were treated surgically for unstable intertrochanteric fractures were retrospectively evaluated. One group was treated with CHS and TSP (Group 1, 22 cases) and the other was treated with PFNA (Group 2, 21 cases). By postoperative radiograph and last follow up radiograph we measured Tip-apex distance, Cleveland index, Lag screw slippage, Neck-shaft angle change and Union time. And By retrospective medical record review, the clinical results were evaluated with the operation time, intraoperative estimated blood loss, amount of drainage, amount of transfusion, walking ability change and complication.
RESULTS
There was a lower operation time, intraoperative estimated blood loss, amount of drainage, amount of transfusion, lag screw slippage and neck shaft angle change in the Group 2 than in the Group 1 (p<0.05).
CONCLUSION
PFNA showed better results than CHS with TSP in operation time, estimated blood loss, amount of drainage and transfusion, lag screw slippage and neck-shaft angle change.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 7 articles
-
Operative Treatment with Gamma 3 Nail in Femur Intertrochanteric Fracture
Ki-Do Hong, Jae-Chun Sim, Sung-Sik Ha, Tae-Ho Kim, Yoon-Ho Choi, Jong-Hyun Kim
J Korean Fract Soc. 2011;24(1):7-15. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2011.24.1.7.The Treatment of Intertrochanteric Femoral Fracture with Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation
Jong Won Kim, Hyun Soo Park, Young Soo Jang, Jae Hyuk Choi, Sung Ju Bae, Chan Il Bae
J Korean Fract Soc. 2012;25(4):257-262. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.4.257.Comparative Study of Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation and Zimmer Natural Nail for the Treatment of Stable Intertrochanteric Fractures
Jee-Hoon Kim, Oog-Jin Shon
J Korean Fract Soc. 2013;26(4):305-313. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.4.305.Comparative Study of Intertrochanteric Fracture Treated with the Proximal Femoral Nail Anti-Rotation and the Third Generation of Gamma Nail
Jae-Cheon Sim, Tae-Ho Kim, Ki-Do Hong, Sung-Sik Ha, Jong-Seong Lee
J Korean Fract Soc. 2013;26(1):37-43. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.1.37.A Comparison between Compression Hip Screw and Intramedullary Nail for the Treatment of AO/OTA A2.2 Intertrochanteric Femoral Fracture
Phil Hyun Chung, Suk Kang, Jong Pil Kim, Young Sung Kim, Ho Min Lee, Jong Hyun Kim
J Korean Fract Soc. 2013;26(1):44-49. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.1.44.Results of Asian Type Gamma 3 Nail in Treatment of Trochanteric Fractures
Bing Zhe Huang, Yong Wook Park, Jin Su Park, Kyu Cheol Noh, Soung Yon Kim, Kook Jin Chung, Hong Kyun Kim, Hyong Nyun Kim, Yong Hyun Yoon, Ji Hyo Hwang
J Korean Fract Soc. 2014;27(3):213-221. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.3.213.Comparison between the Results of Internal Fixation Using Proximal Femur Nail Anti-rotation and Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty in Treatment of Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures of Elderly Patients
Sung-Hwan Kim, Soo-Won Lee, Gyu-Min Kong, Mid-Um JeaGal
J Korean Hip Soc. 2012;24(1):45-52. doi: 10.5371/jkhs.2012.24.1.45.
Reference
-
1. Aune AK, Ekeland A, Odegaard B, Grøgaard B, Alho A. Gamma nail vs compression screw for trochanteric femoral fractures. 15 reoperations in a prospective, randomized study of 378 patients. Acta Orthop Scand. 1994. 65:127–130.
Article2. Babst R, Renner N, Biedermann M, et al. Clinical results using the trochanter stabilizing plate (TSP): the modular extension of the dynamic hip screw (DHS) for internal fixation of selected unstable intertrochanteric fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 1998. 12:392–399.
Article3. Bong MR, Patel V, Iesaka K, Egol KA, Kummer FJ, Koval KJ. Comparison of a sliding hip screw with a trochanteric lateral support plate to an intramedullary hip screw for fixation of unstable intertrochanteric hip fractures: a cadaver study. J Trauma. 2004. 56:791–794.
Article4. Buciuto R, Uhlin B, Hammerby S, Hammer R. RAB-plate vs Richards CHS plate for unstable trochanteric hip fractures. A randomized study of 233 patients with 1-year follow-up. Acta Orthop Scand. 1998. 69:25–28.
Article5. Cleveland M, Bosworth DM, Thompson FR, Wilson HJ Jr, Ishizuka T. A ten-year analysis of intertrochanteric fractures of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1959. 41:1399–1408.
Article6. Doppelt SH. The sliding compression screw--today's best answer for stabilization of intertrochanteric hip fractures. Orthop Clin North Am. 1980. 11:507–523.
Article7. Fogagnolo F, Kfuri M Jr, Paccola CA. Intramedullary fixation of pertrochanteric hip fractures with the short AO-ASIF proximal femoral nail. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2004. 124:31–37.
Article8. Forte ML, Virnig BA, Kane RL, et al. Geographic variation in device use for intertrochanteric hip fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008. 90:691–699.
Article9. Harrington P, Nihal A, Singhania AK, Howell FR. Intramedullary hip screw versus sliding hip screw for unstable intertrochanteric femoral fractures in the elderly. Injury. 2002. 33:23–28.
Article10. Karunakar M, McLaurin TM, Morgan SJ, Egol KA. Improving outcomes after pertrochanteric hip fractures. Instr Course Lect. 2009. 58:91–104.11. Koval KJ, Cantu RV. Rookwood CA, Green DP, editors. Intertrochanteric fractures. Fractures in adults. 2006. 6th ed. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott;1793–1825.
Article12. Koval KJ, Skovron ML, Aharonoff GB, Meadows SE, Zuckerman JD. Ambulatory ability after hip fracture. A prospective study in geriatric patients. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995. 310:150–159.13. Koval KJ, Zuckerman JD. Functional recovery after fracture of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994. 76:751–758.
Article14. Kyle RF, Cabanela ME, Russell TA, et al. Fractures of the proximal part of the femur. Instr Course Lect. 1995. 44:227–253.
Article15. Lee JY, Lee SY. Treatment of the proximal femoral extracapsular fracture with proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA): comparison with proximal femoral nail (PFN). J Korean Hip Soc. 2007. 19:183–189.
Article16. Loch DA, Kyle RF, Bechtold JE, Kane M, Anderson K, Sherman RE. Forces required to initiate sliding in second-generation intramedullary nails. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998. 80:1626–1631.
Article17. Madsen JE, Naess L, Aune AK, Alho A, Ekeland A, Strømsøe K. Dynamic hip screw with trochanteric stabilizing plate in the treatment of unstable proximal femoral fractures: a comparative study with the Gamma nail and compression hip screw. J Orthop Trauma. 1998. 12:241–248.
Article18. Müller ME, Nazarian S. Classificaiton et documentation aoedes fractures femur. Rev Chir Orthop. 1981. 67:297.19. Nakata K, Ohzono K, Hiroshima K, Toge K. Serial change of sliding in intertrochanteric femoral fractures treated with sliding screw system. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1994. 113:276–280.
Article20. Park JH, Park JW, Wang JH, Lee JW, Lee JI, Kim JG. Treatment of intertrochanteric fracture: comparison of proximal femoral nail and proximal femoral nail A. J Korean Fract Soc. 2008. 21:103–109.
Article21. Park MS, Lim YJ, Kim YS, Kim KH, Cho HM. Treatment of the proximal femoral fractures with proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA). J Korean Fract Soc. 2009. 22:91–97.
Article22. Rha JD, Kim YH, Yoon SI, Park TS, Lee MH. Factors affecting sliding of the lag screw in intertrochanteric fractures. Int Orthop. 1993. 17:320–324.
Article23. Simmermacher RK, Ljungqvist J, Bail H, et al. The new proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA) in daily practice: results of a multicentre clinical study. Injury. 2008. 39:932–939.
Article24. Steinberg GG, Desai SS, Kornwitz NA, Sullivan TJ. The intertrochanteric hip fracture. A retrospective analysis. Orthopedics. 1988. 11:265–273.
Article25. Templeman D, Baumgaertner MR, Leighton RK, Lindsey RW, Moed BR. Reducing complications in the surgical treatment of intertrochanteric fractures. Instr Course Lect. 2005. 54:409–415.26. Utrilla AL, Reig JS, Muñoz FM, Tufanisco CB. Trochanteric gamma nail and compression hip screw for trochanteric fractures: a randomized, prospective, comparative study in 210 elderly patients with a new design of the gamma nail. J Orthop Trauma. 2005. 19:229–233.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation versus Compression Hip Screw with Trochanter Stabilizing Plate for Unstable Intertrochanteric Hip Fractures
- Surgical Treatment of Femoral Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures in Elderly Patients: Comparative Study between Compressive Hip Screws and Additional Trochanteric Stabilizing Plates
- Comparison of the Compression Hip Screw (CHS) and the Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation (PFNA) for Intertrochanteric Femoral Fracture
- Results of Use of Compression Hip Screw with Trochanter Stabilizing Plate for Reverse Oblique Intertrochanteric Fracture
- Treatment of Unstable Interochanteric Femoral Fracture using Compression Hip Screw with additional Transfixations Screw