J Korean Hip Soc.
2010 Jun;22(2):137-142. 10.5371/jkhs.2010.22.2.137.
Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty Using a Wagner Revision Stem
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, College of Medicine, Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea. kimyh1@hanyang.ac.kr
- KMID: 1461135
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5371/jkhs.2010.22.2.137
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We evaluated the results of revision total hip arthroplasty using a Wagner revision femoral stem.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
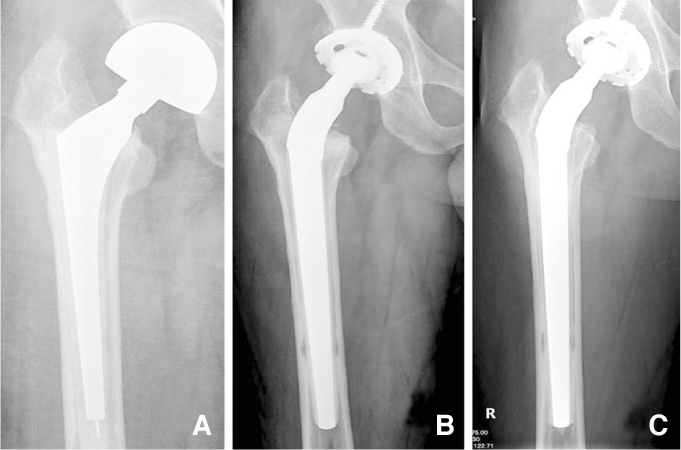
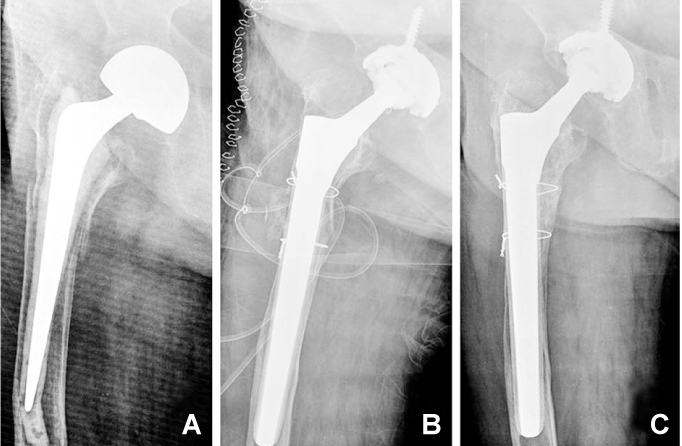
We enrolled 54 patients who underwent hip arthroplasty using a Wagner revision stem between 1996 and 2004. The mean age at revision surgery was 65.4 years and the mean follow up period was 7.2 years. There were 42 aseptic loosenings and 12 periprosthetic fractures. The pre-operative femoral defects were classified according to the Paprosky classification system. Clinical and radiological results were evaluated.
RESULTS
The mean Harris hip score improved from 43 preoperatively to 89 at the latest follow up. There were 2 cases with inguinal pain and 1 with thigh pain; in each case pain was reduced by medications. All cases showed endosteal bone formation around the stem. Five cases showed radiolucency in Gruen zones 1 and 7. Six cases had hips that showed subsidence (average=3.1 mm). There was 1 dislocation (1.8%) and 1 intraoperative periprosthetic fracture (1.8%). There were no re-revisions.
CONCLUSION
Use of a Wagner revision femoral stem for revision total hip arthroplasty elicits satisfactory results including stable fixation of the stem, a low rate of subsidence, and a low rate of dislocation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Revision Hip Arthroplasty with a Cementless Femoral Stem
Young-Yool Chung, Chae-Hyun Lim, Chung-Young Kim, Jeong-Seok Kim
Hip Pelvis. 2013;25(4):260-266. doi: 10.5371/hp.2013.25.4.260.
Reference
-
1. Roberson JR. Proximal femoral bone loss after total hip arthroplasty. Orthop Clin North Am. 1992. 23:291–302.
Article2. Gie GA, Linder L, Ling RS, Simon JP, Slooff TJ, Timperley AJ. Impacted cancellous allografts and cement for revision total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1993. 75:14–21.
Article3. Gross AE, Allan DG, Lavoie GJ, Oakeshott RD. Revision arthroplasty of the proximal femur using allograft bone. Orthop Clin North Am. 1993. 24:705–715.
Article4. Paprosky WG, Greidanus NV, Antoniou J. Minimum 10-year-results of extensively porous-coated stems in revision hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999. 369:230–242.
Article5. Wagner H. Revision prosthesis for the hip joint in severe bone loss. Orthopade. 1987. 16:295–300.6. Franzén H, Mjöberg B, Onnerfält R. Early loosening of femoral components after cemented revision. A roentgen stereophotogrammetric study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1992. 74:721–724.7. Engelbrecht DJ, Weber FA, Sweet MB, Jakim I. Long-term results of revision total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1990. 72:41–45.
Article8. Kavanagh BF, Ilstrup DM, Fitzgerald RH Jr. Revision total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1985. 67:517–526.
Article9. Lee JR, Roh JY, Suh JM. 5-12 year results of femoral revision total hip arthroplasty using the Wagner revision stem. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2006. 41:785–792.
Article10. Han CD, Yang IW, Park J. Femoral revision with the Wagner SL revision stem. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2007. 42:241–248.
Article11. Böhm P, Bischel O. Femoral revision with the Wagner SL revision stem : evaluation of one hundred and twenty-nine revisions followed for a mean of 4.8 years. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001. 83-A:1023–1031.12. Grünig R, Morscher E, Ochsner PE. Three-to 7-year results with the uncemented SL femoral revision prosthesis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1997. 116:187–197.
Article13. Bourne RB, Mehin R. The dislocating hip: what to do, what to do. J Arthroplasty. 2004. 19:111–114.14. Gruen TA, McNeice GM, Amstutz HC. "Modes of failure" of cemented stem-type femoral components: a radiographic analysis of loosening. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979. 141:17–27.15. Callaghan JJ, Salvati EA, Pellicci PM, Wilson PD Jr, Ranawat CS. Results of revision for mechanical failure after cemented total hip replacement, 1979 to 1982. A two to five-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1985. 67:1074–1085.
Article16. Brooker AF, Bowerman JW, Robinson RA, Riley LH Jr. Ectopic ossification following total hip replacement. Incidence and a method of classification. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1973. 55:1629–1632.17. Valle CJ, Paprosky WG. Classification and an algorithmic approach to the reconstruction of femoral deficiency in revision total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003. 85-A:Suppl. 1–6.18. Isacson J, Stark A, Wallensten R. The Wagner revision prosthesis consistently restores femoral bone structure. Int Orthop. 2000. 24:139–142.
Article19. Kolstad K, Adalberth G, Mallmin H, Milbrink J, Sahlstedt B. The Wagner revision stem for severe osteolysis. 31 hips followed for 1.5-5 years. Acta Orthop Scand. 1996. 67:541–544.
Article20. Gutierrez Del Alamo J, Garcia-Cimbrelo E, Castellanos V, Gil-Garay E. Radiographic bone regeneration and clinical outcome with the Wagner SL revision stem: a 5-year to 12-year follow-up study. J Arthroplasty. 2007. 22:515–524.21. Padgett DE, Warashina H. The unstable total hip replacement. Clini Orthop Relat Res. 2004. 420:72–79.
Article22. Boucher HR, Lynch C, Young AM, Engh CA Jr, Engh C Sr. Dislocation after polyethylene liner exchange in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2003. 18:654–657.
Article23. Weber M, Hempfing A, Orler R, Ganz R. Femoral revision using the Wagner stem: results at 2-9 years. Int Orthop. 2002. 26:36–39.
Article24. Sporer SM, Paprosky WG. Femoral fixation in the face of considerable bone loss: the use of modular stems. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004. 429:227–231.