J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2010 Feb;36(1):23-27. 10.5125/jkaoms.2010.36.1.23.
Reliability study of 6-axis model surgery simulator for orthognathic surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthodontics, School of Dentistry, Pusan National University, Korea. wsson@pusan.ac.kr
- 2Pretty Smile Orthodontic Clinic, Korea.
- 3Agency of Defense Development, Daejeon, Republic of Korea, Korea.
- 4Erumi Dental Clinic, Busan, Republic of Korea, Korea.
- 5Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, School of Dentistry, Pusan National University, Korea.
- KMID: 1457815
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2010.36.1.23
Abstract
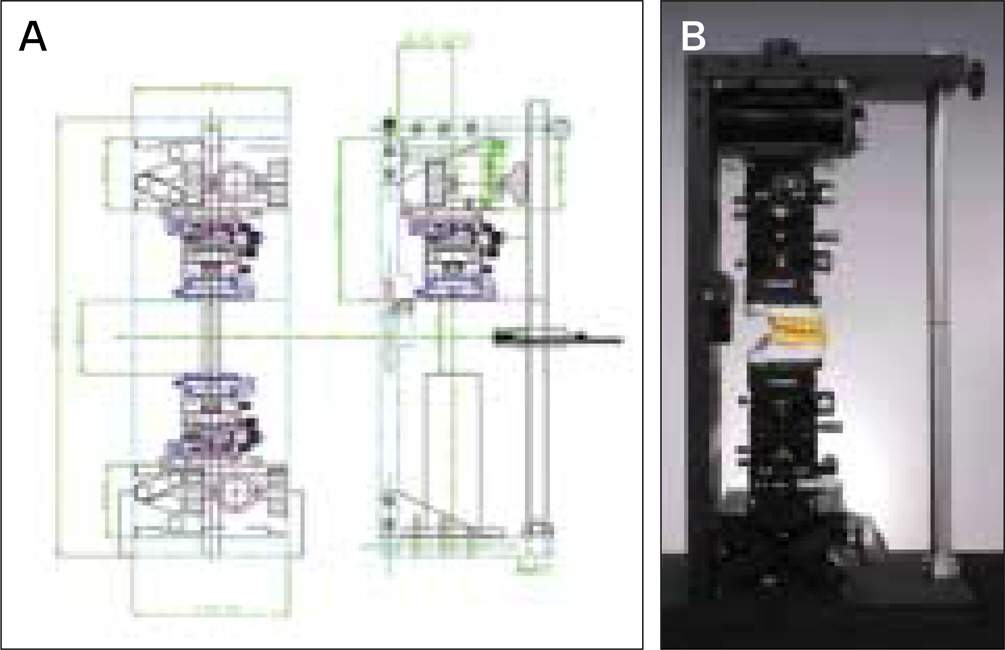
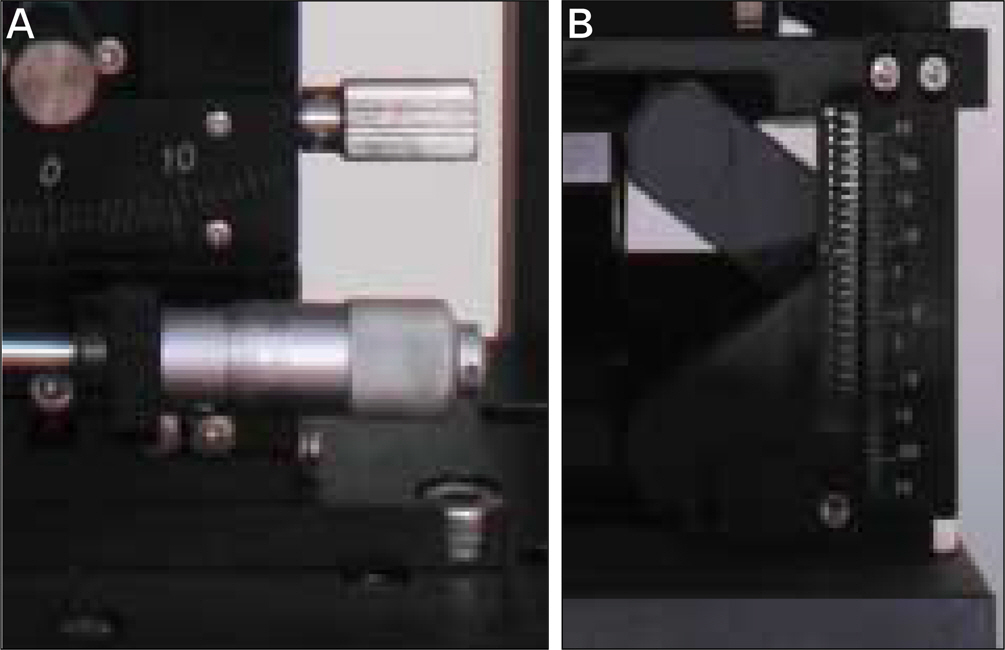
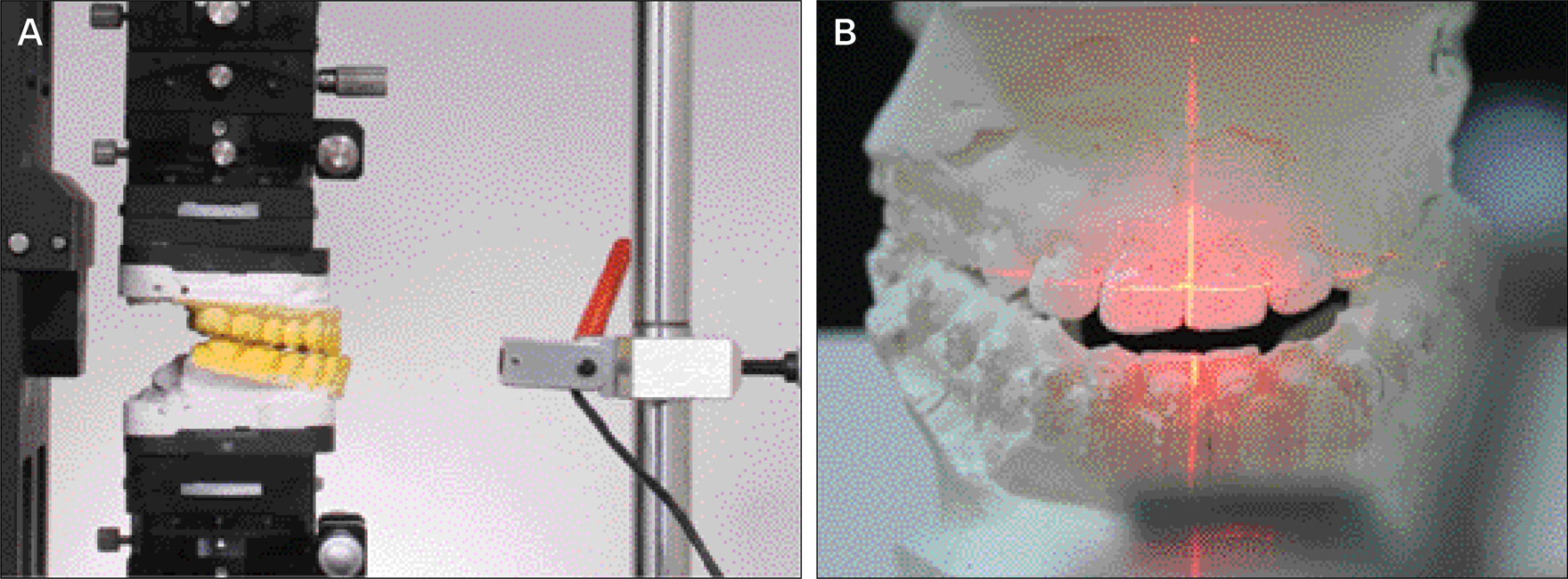
- The purpose of this study was to evaluate the reliability of 6-axis model surgery simulator (6AMSS) for orthognathic surgery. A rectangular parallelepiped plastic block was assembled to model-mounting plate of 6AMSS. Left-right (X), anterior-posterior (Y), up-down (Z) translation and pitching (empty set X), rolling (empty set Y) and yawing (empty set Z) rotation was planned and performed using 6AMSS. The actual translation and rotation were measured with dial gauge and precisional protractor, respectively. Comparison between the planned and actual movements of plastic block for each variable were made using paired t- test. Statistical analysis for X, Y, Z, empty set X, empty set Y and empty set Z movement have shown no significant differences between planned and actual movement (P > 0.05). This indicate that model surgery performed with the aid of the 6AMSS is accurate in 3D translation and rotation. The 6AMSS is practically useful for accurate fabrication of surgical splint for orthognathic surgery.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
New bimaxillary orthognathic surgery planning and model surgery based on the concept of six degrees of freedom
Jaeho Jeon, Yongdeok Kim, Jongryoul Kim, Heejea Kang, Hyunjin Ji, Woosung Son
Korean J Orthod. 2013;43(1):42-52. doi: 10.4041/kjod.2013.43.1.42.
Reference
-
References
1. Bell WH. Correction of the short-face syndrome-vertical maxillary deficiency: a preliminary report. J Oral Surg. 1977; 35:110–20.2. Bell WH, Creekmore TD, Alexander RG. Surgical correction of the long face syndrome. Am J Orthod. 1977; 71:40–67.
Article3. Epker BN, Fish LC. Surgical-orthodontic correction of open-bite deformity. Am J Orthod. 1977; 71:278–99.
Article4. Hohl TA. Use of an adjustable (anatomic) articulator for case prediction in segmental surgery. Bell WH, Proffit WR, White RP, editors. Surgical correction of dentofacial deformities. Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders;1980. p. 169–77.5. Hill SC. Cephalometric planning and model surgery. Bell WH, editor. Surgical correction of dentofacial deformities-New concepts. Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders;1985. p. 217–26.6. Ellis E 3rd. Accuracy of model surgery: evaluation of an old technique and introduction of a new one. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1990; 48:1161–7.
Article7. Ha ¨rle F. Le Fort I ostectomy (using miniplates) for correction of the long face. Int J Oral Surg. 1980; 9:427–32.8. Ellis E 3rd. Modified splint design for two-jaw surgery. J Clin Orthod. 1982; 16:619–22.9. Ripley JF, Steed DL, Flanary CM. A composite surgical splint for dual arch orthognathic surgery. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1982; 40:687–8.
Article10. Turvey TA, Hall DJ, Fish LC, Epker BN. Surgical-orthodontic treatment planning for simultaneous mobilization of the maxilla and mandible in correction of dentofacial deformities. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1982; 54:491–8.11. Bell WH, Mannai C, Luhr HG. Art and science of the Le Fort I down fracture. Int J Adult Orthodon Orthognath Surg. 1988; 3:23–52.12. Luhr HG. Miniplate fixation of Le Fort I osteotomies [discussion to Rosen HM]. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1986; 78:755.13. Bell WH, Proffit WR. Maxillary excess. Surgical correction of facial deformities. Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders;1980. p. 234–441.14. Epker BN, Stella JP, Fish LC. Dentofacial deformities: integrated orthodontic and surgical correction. St Louis: Mosby;1986.15. Ehmer U, Rohling J, Dorr K, Becker R. Calibrated double split cast simulations for orthognathic surgery. Int J Adult Orthodon Orthognath Surg. 1989; 3:223–7.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of postoperative changes in condylar positions after orthognathic surgery using balanced orthognathic surgery system
- Accuracy and reliability of three-dimensional computer-assisted planning for orthognathic surgery
- Paradigm Shift in Orthognathic Surgery: Surgery First Orthognathic Approach and Aesthetic Two-jaw Surgery
- A clinical study on the reliability of preoperative prediction in orthognathic surgery with the use of computerized cephalometric program
- Two treatment approach to skeletal Class III : A case report on sisters