J Korean Surg Soc.
2010 Jul;79(1):75-78. 10.4174/jkss.2010.79.1.75.
Heterotaxia Syndrome with Intraluminal Duodenal Diverticulum
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Postgraduate School of Medicine, Pusan National University, Busan, Korea. 111160@pusan.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Postgraduate School of Medicine, Pusan National University, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, Postgraduate School of Medicine, Pusan National University, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 1455491
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2010.79.1.75
Abstract
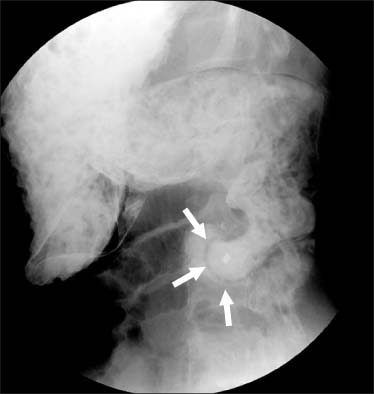
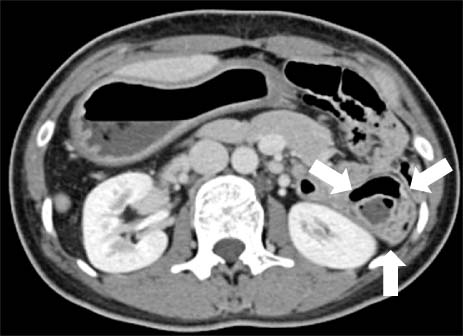
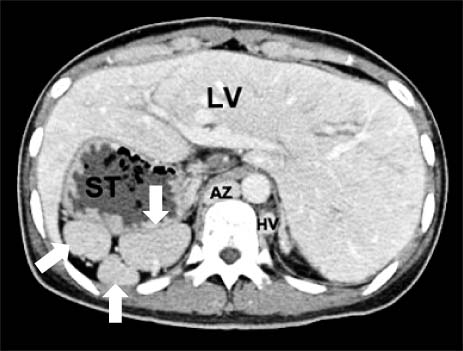
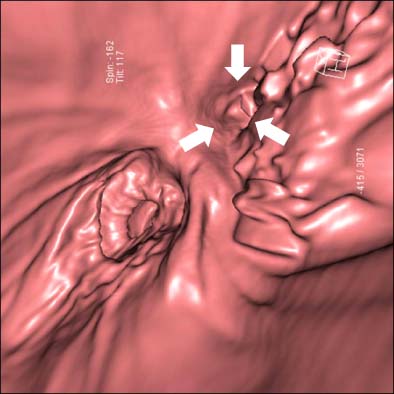
- Both heterotaxia and intraluminal duodenal diverticulum (IDD) are uncommon congenital anomalies. Heterotaxia is a group of situs anomalies and IDD is a type of duodenal atresia. Heterotaxia is commonly associated with intraabdominal abnormalities causing intestinal obstruction, but heterotaxia with IDD is extremely rare. Herein we report a case of 21-year-old female who presented with symptoms of duodenal obstruction due to IDD associated with heterotaxia. This is the second case found as a result of a search through PubMed. We first used 3-dimentional virtual computed tomograph endoscopy for making the diagnosis and the treatment plan of this patient.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Oleszczuk-Raschke K, Set PA, von Lengerke HJ, Troger J. Abdominal sonography in the evaluation of heterotaxy in children. Pediatr Radiol. 1995. 25:Suppl 1. S150–S156.2. Winer-Muram HT, Tonkin IL. The spectrum of heterotaxic syndromes. Radiol Clin North Am. 1989. 27:1147–1170.3. Boyd R. Description of malformation of the duodenum. Lancet. 1845. 1:648.4. Kinzer RE. Intraluminal diverticulum and other lesions producing intermittent duodenal obstruction or stasis. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther. 1949. 11:212–218.5. Boyden EA, Cope JG, Bill AH Jr. Anatomy and embryology of congenital intrinsic obstruction of the duodenum. Am J Surg. 1967. 114:190–202.6. Lundstedt C, Lyttkens K, Andren S. Intraluminal duodenal diverticulum causing pancreatitis in a patient with a polysplenia syndrome. Eur Radiol. 1998. 8:454–457.7. Jacobs JP, Anderson RH, Weinberg PM, Walters HL 3rd, Tchervenkov CI, Del Duca D, et al. The nomenclature, definition and classification of cardiac structures in the setting of heterotaxy. Cardiol Young. 2007. 17:Suppl 2. 1–28.8. Lin AE, Ticho BS, Houde K, Westgate MN, Holmes LB. Heterotaxy: associated conditions and hospital-based prevalence in newborns. Genet Med. 2000. 2:157–172.9. Peoples WM, Moller JH, Edwards JE. Polysplenia: a review of 146 cases. Pediatr Cardiol. 1983. 4:129–137.10. Materne R. The duodenal wind sock sign. Radiology. 2001. 218:749–750.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of intraluminal duodenal diverticulum
- Intraluminal Duodenal Diverticulum Causing Chronic Gastrointestinal Bleeding in Adults
- Duodenal Perforation due to Hemoclipping for the Dieulafoy's Lesion in a Duodenal Diverticulum
- Intraluminal Duodenal Diverticulum: CT and Gadoxetic Acid-Enhanced MRI Findings
- A Case of Massive Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding from a Duodenal Diverticulum