Korean J Pain.
2010 Dec;23(4):262-265. 10.3344/kjp.2010.23.4.262.
Rami Communicans Nerve Block for the Treatment of Symptomatic Schmorl's Nodes: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Chuncheon Sacred Heart Hospital, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Chuncheon, Korea. chamuszjs@naver.com
- KMID: 1454711
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2010.23.4.262
Abstract
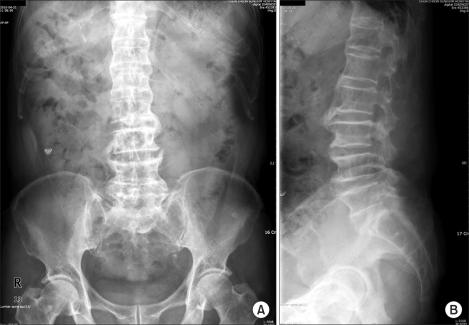
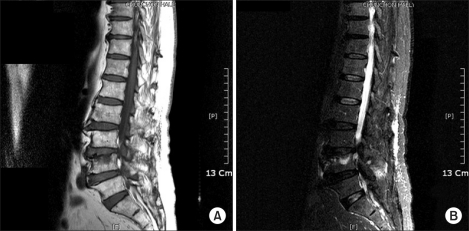
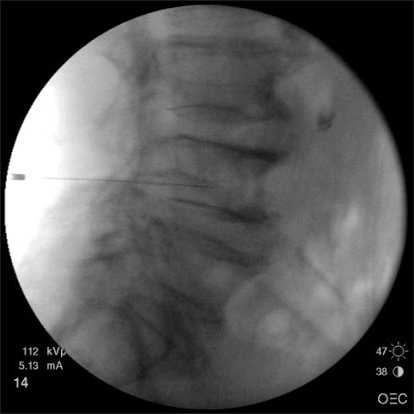
- Histologically, Schmorl's nodes are defined as the loss of nuclear material through the cartilage plate, growth plate, and end plate into the vertebral body. Most Schmorl's nodes are asymptomatic, although there are some reports of symptomatic Schmorl's nodes, which should be treated similarly to vertebral compression fractures, with conservative treatment as the first choice. We report the case that we reduced the pain by blocking the ramus communicans nerve in a patient with Schmorl's node.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Interventional therapy for chronic low back pain
Youngkwon Ko, Yoon Hee Kim
J Korean Med Assoc. 2012;55(6):562-570. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2012.55.6.562.
Reference
-
1. Hasegawa K, Ogose A, Morita T, Hirata Y. Painful Schmorl's node treated by lumbar interbody fusion. Spinal Cord. 2004; 42:124–128. PMID: 14765146.
Article2. Tsuji H, Yoshioka T, Sainoh H. Developmental balloon disc of the lumbar spine in healthy subjects. Spine. 1985; 10:907–911. PMID: 2938273.
Article3. Takahashi K, Takata K. A large painful Schmorl's node: a case report. J Spinal Disord. 1994; 7:77–81. PMID: 8186593.4. Takahashi K, Miyazaki T, Ohnari H, Takino T, Tomita K. Schmorl's nodes and low-back pain. Analysis of magnetic resonance imaging findings in symptomatic and asymptomatic individuals. Eur Spine J. 1995; 4:56–59. PMID: 7749909.5. Chandler G, Dalley G, Hemmer J Jr, Seely T. Gray ramus communicans nerve block: novel treatment approach for painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture. South Med J. 2001; 94:387–393. PMID: 11332903.6. Walters G, Coumas JM, Akins CM, Ragland RL. Magnetic resonance imaging of acute symptomatic Schmorl's node formation. Pediatr Emerg Care. 1991; 7:294–296. PMID: 1754491.
Article7. Hauger O, Cotten A, Chateil JF, Borg O, Moinard M, Diard F. Giant cystic Schmorl's nodes: imaging findings in six patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001; 176:969–972. PMID: 11264091.8. Fahey V, Opeskin K, Silberstein M, Anderson R, Briggs C. The pathogenesis of Schmorl's nodes in relation to acute trauma. An autopsy study. Spine. 1998; 23:2272–2275. PMID: 9820905.
Article9. Stäbler A, Bellan M, Weiss M, Gärtner C, Brossmann J, Reiser MF. MR imaging of enhancing intraosseous disk herniation (Schmorl's nodes). AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1997; 168:933–938. PMID: 9124143.
Article10. Wagner AL, Murtagh FR, Arrington JA, Stallworth D. Relationship of Schmorl's nodes to vertebral body endplate fractures and acute endplate disk extrusions. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000; 21:276–281. PMID: 10696008.11. Vogler JB 3rd, Murphy WA. Bone marrow imaging. Radiology. 1988; 168:679–693. PMID: 3043546.
Article12. Bogduk N. Clinical anatomy of the lumbar spine and sacrum. 1997. 3rd ed. New York: Bath press Ltd;p. 127–143.13. Tae HS, Kim SD, Park JY, Kim SH, Lim DJ, Suh JK. Gray ramus communicans nerve block: a useful therapeutic adjuvant for painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2003; 34:505–508.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Therapeutic Effect of Postganglionic Nerve Block for Symptomatic Schmorl Nodule: A Retrospective Case Series
- Clinical Efficacy of Ramus Communicans Nerve Block in Patient with Vertebral Compression Fracture
- Acute Schmorl Node in Dorsal Spine: An Unusual Cause of a Sudden Onset of Severe Back Pain in a Young Female
- Complete Separation of the Vertebral Body Associated with a Schmorl's Node Accompanying Severe Osteoporosis
- Gray Ramus Communicans Nerve Block: A Useful Therapeutic Adjuvant for Painful Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture