J Korean Hip Soc.
2011 Dec;23(4):297-302. 10.5371/jkhs.2011.23.4.297.
Measurement of Necrotic Lesion in Osteonecrosis of Femoral Head
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea. keelim@inha.ac.kr
- KMID: 1452638
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5371/jkhs.2011.23.4.297
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The size of the necrotic lesion is known to be the most important prognostic factor in osteonecrosis of the femoral head (ONFH). We evaluated the accuracy and relationship of three different measuring methods of necrotic lesions for ONFH.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
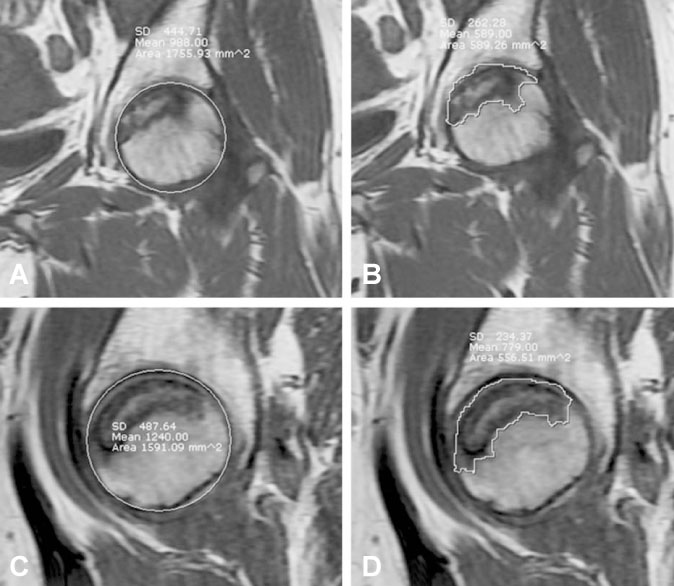
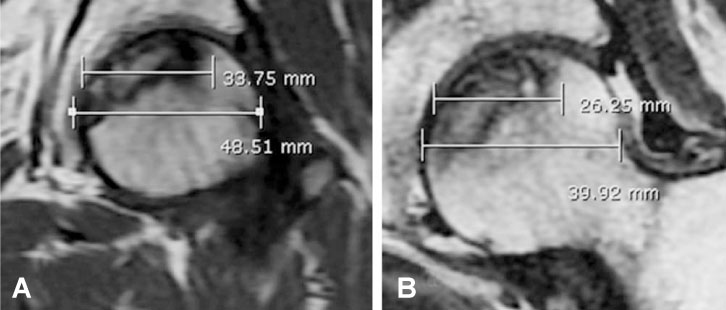
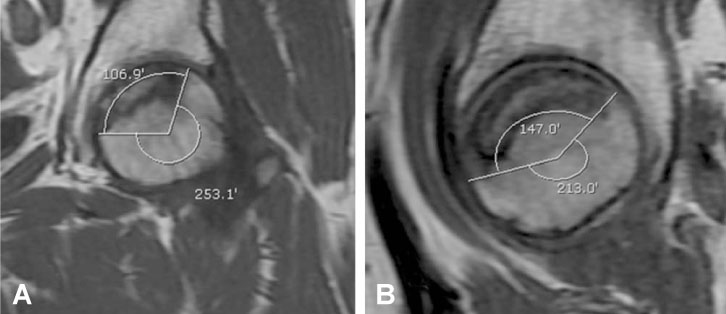
Sixty hips that had ONFH were measured on an MRI by two orthopaedic surgeons using Steinberg, Kim, and modified Kerboul methods. Based on the lesion size of the necrosis as measured with the computerized Steinberg method, the hips were divided into Group I (small lesion: less than 15%), Group II (medium lesion: 15~30%), and Group III (large lesion: more than 30%). Data of the Kim and modified Kerboul methods were reclassified by statistical analysis according to the groups classified by the Steinberg method.
RESULTS
Average lesion size of Group I (16 hips) was 10.92%, the average size of Group II (33 hips) was 21.68%, and the average size of Group III (11 hips) was 36.80%. We established a new criteria of the Kim and modified Kerboul methods based on Steinberg. The Kim method was reclassified into Groups I (less than 18%), II (18~33%), and III (33% or more). And the modified Kerboul method was divided into Groups I (less than 200.6degrees), II (200.6~262.4degrees), and III (more than 262.4degrees) as well.
CONCLUSION
New criteria for the Kim and modified Kerboul method would be a useful indicator for the prognosis and treatment plan in ONFH.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ficat RP. Idiopathic bone necrosis of the femoral head. Early diagnosis and treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1985. 67:3–9.
Article2. Hernigou P, Habibi A, Bachir D, Galacteros F. The natural history of asymptomatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head in adults with sickle cell disease. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006. 88:2565–2572.
Article3. Hernigou P, Poignard A, Nogier A, Manicom O. Fate of very small asymptomatic stage-I osteonecrotic lesions of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004. 86-A:2589–2593.
Article4. Hungerford DS. Osteonecrosis: avoiding total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2002. 17:121–124.
Article5. Hungerford DS, Jones LC. Asymptomatic osteonecrosis: should it be treated? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004. 429:124–130.6. Jones JP Jr. Concepts of etiology and early pathogenesis of osteonecrosis. Instr Course Lect. 1994. 43:499–512.7. Nishii T, Sugano N, Ohzono K, Sakai T, Haraguchi K, Yoshikawa H. Progression and cessation of collapse in osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002. 400:149–157.
Article8. Stulberg BN, Davis AW, Bauer TW, Levine M, Easley K. Osteonecrosis of the femoral head. A prospective randomized treatment protocol. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991. 268:140–151.9. Ito H, Matsuno T, Kaneda K. Prognosis of early stage avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999. 358:149–157.
Article10. Ito H, Matsuno T, Omizu N, Aoki Y, Minami A. Mid-term prognosis of non-traumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003. 85:796–801.
Article11. Mont MA, Hungerford DS. Non-traumatic avascular necrosis of the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995. 77:459–474.
Article12. Patterson RJ, Bickel WH, Dahlin DC. Idiopathic avascular necrosis of the head of the femur. A study of fifty-two cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1964. 46:267–282.13. Takatori Y, Kokubo T, Ninomiya S, Nakamura S, Morimoto S, Kusaba I. Avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Natural history and magnetic resonance imaging. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1993. 75:217–221.
Article14. Smith SW, Meyer RA, Connor PM, Smith SE, Hanley EN Jr. Interobserver reliability and intraobserver reproducibility of the modified Ficat classification system of osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996. 78:1702–1706.
Article15. Kerboul M, Thomine J, Postel M, Merle d'Aubigne R. The conservative surgical treatment of idiopathic aseptic necrosis of the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1974. 56:291–296.
Article16. Kim YM, Ahn JH, Kang HS, Kim HJ. Estimation of the extent of osteonecrosis of the femoral head using MRI. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1998. 80:954–958.
Article17. Koo KH, Kim R. Quantifying the extent of osteonecrosis of the femoral head. A new method using MRI. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1995. 77:875–880.
Article18. Steinberg ME, Bands RE, Parry S, Hoffman E, Chan T, Hartman KM. Does lesion size affect the outcome in avascular necrosis? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999. 367:262–271.
Article19. Steinberg ME, Hayken GD, Steinberg DR. A quantitative system for staging avascular necrosis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1995. 77:34–41.
Article20. Totty WG, Murphy WA, Ganz WI, Kumar B, Daum WJ, Siegel BA. Magnetic resonance imaging of the normal and ischemic femoral head. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1984. 143:1273–1280.
Article21. Koo KH, Kim R, Ko GH, Song HR, Jeong ST, Cho SH. Preventing collapse in early osteonecrosis of the femoral head. A randomised clinical trial of core decompression. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1995. 77:870–874.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Early diagnostic Significance of Bone Marrow Pressure in Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head
- Bone Marrow Pressure Study in Ostoenecrosis of the Femoral Head
- The Usefulness of 3D Quantitative Analysis with Using MRI for Measuring Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head
- Subtrochanteric Femur Fracture after Multiple Drilling for Treatment of Nontraumatic Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: A Case Report
- Extension of Necrotic Area by Recurrent Ischemic Episodes in Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: A Report of Three Cases