Imaging Sci Dent.
2011 Jun;41(2):63-69. 10.5624/isd.2011.41.2.63.
Quantitative localization of impacted mesiodens using panoramic and periapical radiographs
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology and Research Institute of Oral Science, College of Dentistry, Gangneung-Wonju National University, Gangneung, Korea. imagchoi@gwnu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Ilsan Paik Hospital, Inje University, Goyang, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatric Dentistry and Research Institute of Oral Science, College of Dentistry, Gangneung-Wonju National University, Gangneung, Korea.
- KMID: 1449937
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5624/isd.2011.41.2.63
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to evaluate a new technique for localizing impacted mesiodens using its horizontal magnification ratio on panoramic radiographs.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
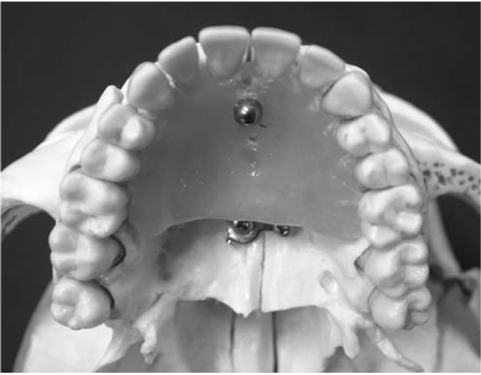
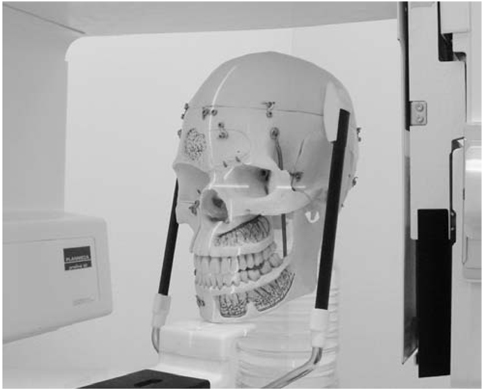
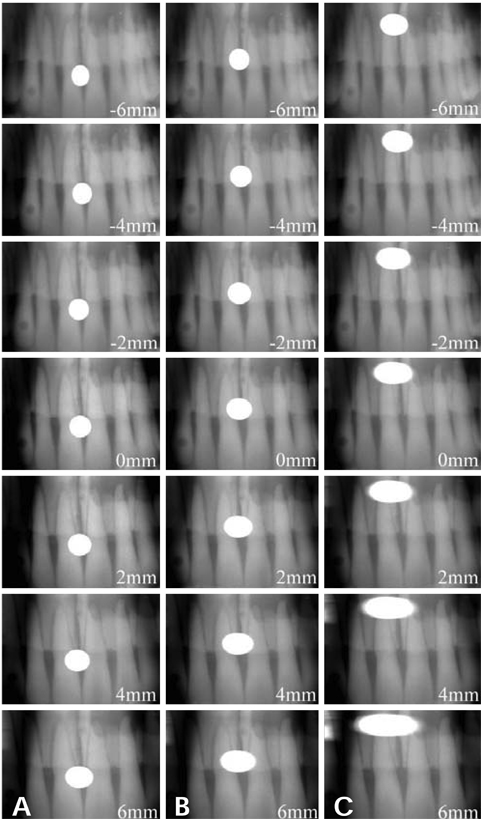
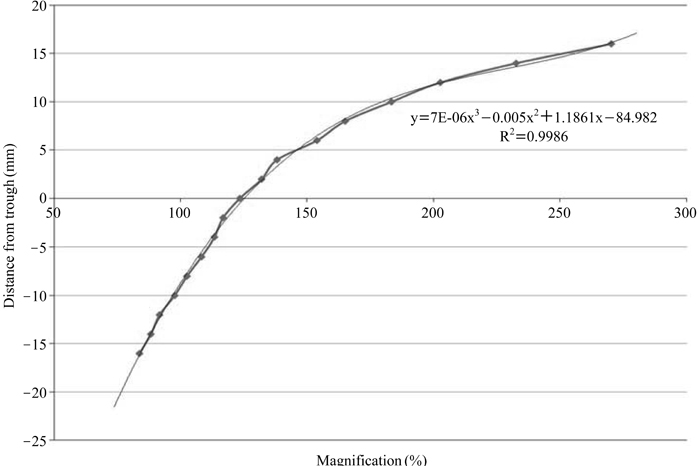
Location-magnification equation of a panoramic equipment was obtained from horizontal magnification ratio of a metal ball which was located variable positions from the center of image layer at interval of 2 mm. Panoramic radiographs were obtained from a skull phantom with a metal ball which was a substitute for impacted mesiodens and was embedded 10mm(Group 1), 15mm(Group 2), and 20mm(Group 3) posterior to the central incisor. Each group obtained 7 panoramic radiographs at variable positions and one periapical radiograph. Three methods were used to estimate the actual width of the incisors and the balls which were used to calculate the magnification ratio. The methods included using the actual incisor width and the calculated ball width (Method 1), using the actual incisor width and the ball widths measured on periapical radiograph (Method 2), and using the incisor and the ball widths measured on periapical radiograph (Method 3). The location of the metal ball was calculated by using the location-magnification equation.
RESULTS
The smallest difference between the calculated and the actual distance was 0.1+/-0.7 mm in Group 1/Method 3. The largest difference was -4.2+/-1.6 mm in Group 3/Method 2. In all groups, method 3 was the most accurate.
CONCLUSION
Quantitative localization of impacted mesiodens is possible by using panoramic radiograph.
Figure
Reference
-
1. White SC, Pharoah MJ. Oral radiology; principles and interpretation. 2004. 5th ed. St. Louis: Mosby-Year Book Inc.2. Zhu JF, Marcushamer M, King DL, Henry RJ. Supernumerary and congenitally absent teeth: a literature review. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 1996. 20:87–95.3. Fernández Montenegro P, Valmaseda Castellón E, Berini Aytés L, Gay Escoda C. Retrospective study of 145 supernumerary teeth. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2006. 11:E339–E344.4. Mukhopadhyay S. Mesiodens: a clinical and radiographic study in children. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent. 2011. 29:34–38.
Article5. Hyun HK, Lee SJ, Lee SH, Hahn SH, Kim JW. Clinical characteristics and complications associated with mesiodentes. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009. 67:2639–2643.
Article6. Lee DH, Lee JS, Yoon SJ, Kang BC. Three dimensional evaluation of impacted mesiodens using dental cone beam CT. Korean J Oral Maxillofac Radiol. 2010. 40:109–114.7. Kim JD, Lee CY, You CH. The radiographic localization of unerupted maxillary incisors and supernumeraries. Korean J Oral Maxillofac Radiol. 2003. 33:217–221.8. Jung YH, Nah KS, Cho BH. The relationship between the position of mesiodens and complications. Korean J Oral Maxillofac Radiol. 2008. 38:103–107.9. Ludlow JB. Dose and risk in dental diagnostic imaging: with emphasis on dosimetry of CBCT. Korean J Oral Maxillofac Radiol. 2009. 39:175–184.10. Langlais RP, Langland OE, Nortje CJ. Diagnostic imaging of the jaws. 1995. 1st ed. Malvern: Williams & Wikin;87–102.11. Langland OE, Langlais RP, McDavid WD, DelBalso AM. Panoramic radiology. 1989. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger;38–75.12. Noh JJ, Choi BR, Jeong HS, Huh KH, Yi WJ, Heo MS, et al. Diagnostic imaging analysis of the impacted mesiodens. Korean J Oral Maxillofac Radiol. 2010. 40:69–74.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The radiographic localization of unerupted maxillary incisors and supernumeraries
- The relationship between the position of mesiodens and complications
- Prediction of osteoporosis using fractal analysis on periapical and panoramic radiographs
- Evaluation of Impacted Maxillary Canine Position Using Panoramic Radiographs and Cone-beam Computed Tomography
- Screening panoramic radiographs in a group of patients visiting a Health Promotion Center