Epidemiological Characteristics of Rabies in South Korea from January 2004 to March 2011
- Affiliations
-
- 1National Veterinary Research and Quarantine Service, Anyang, Korea. yangdk@korea.kr
- KMID: 1449891
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4167/jbv.2011.41.3.165
Abstract
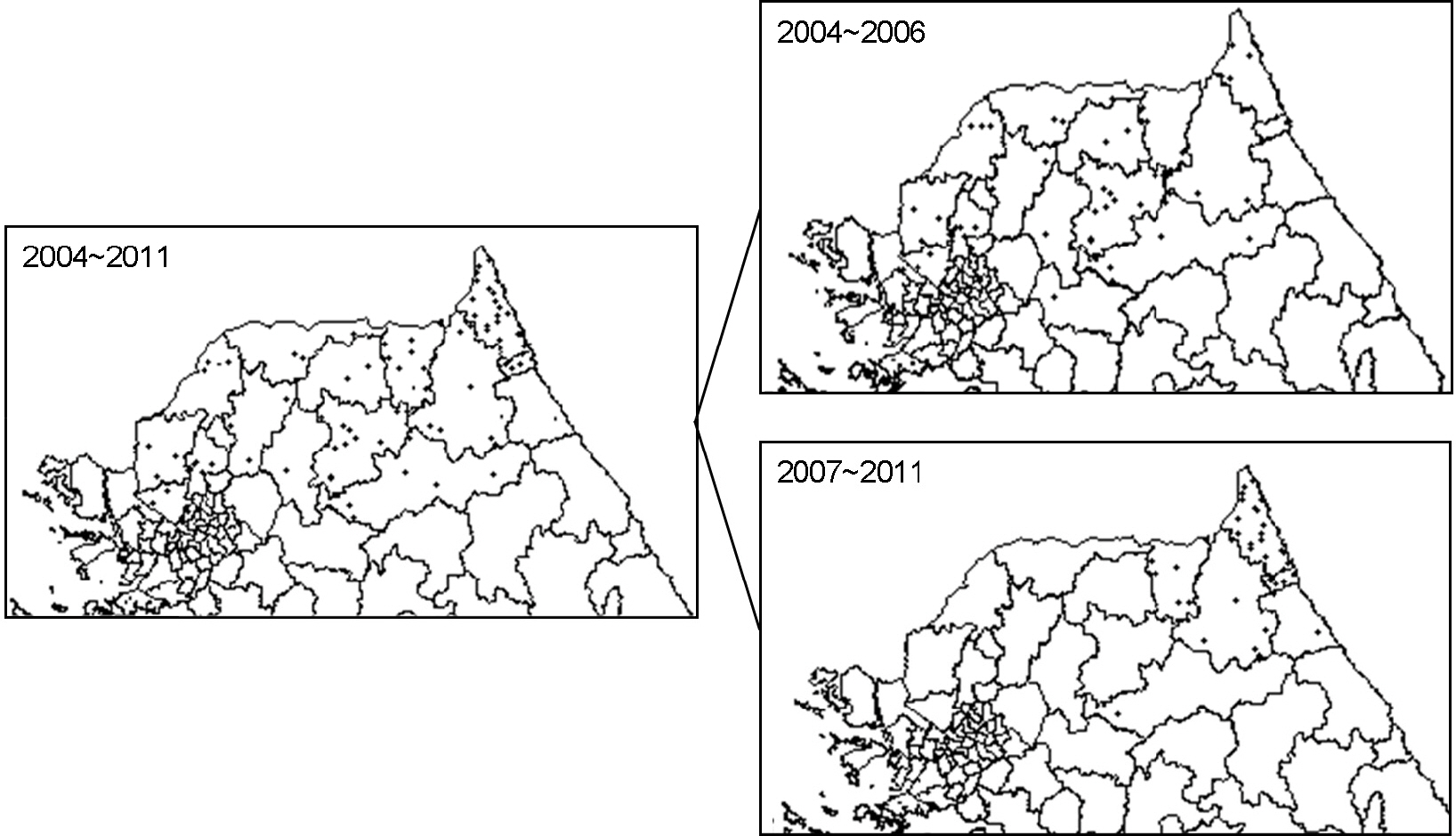
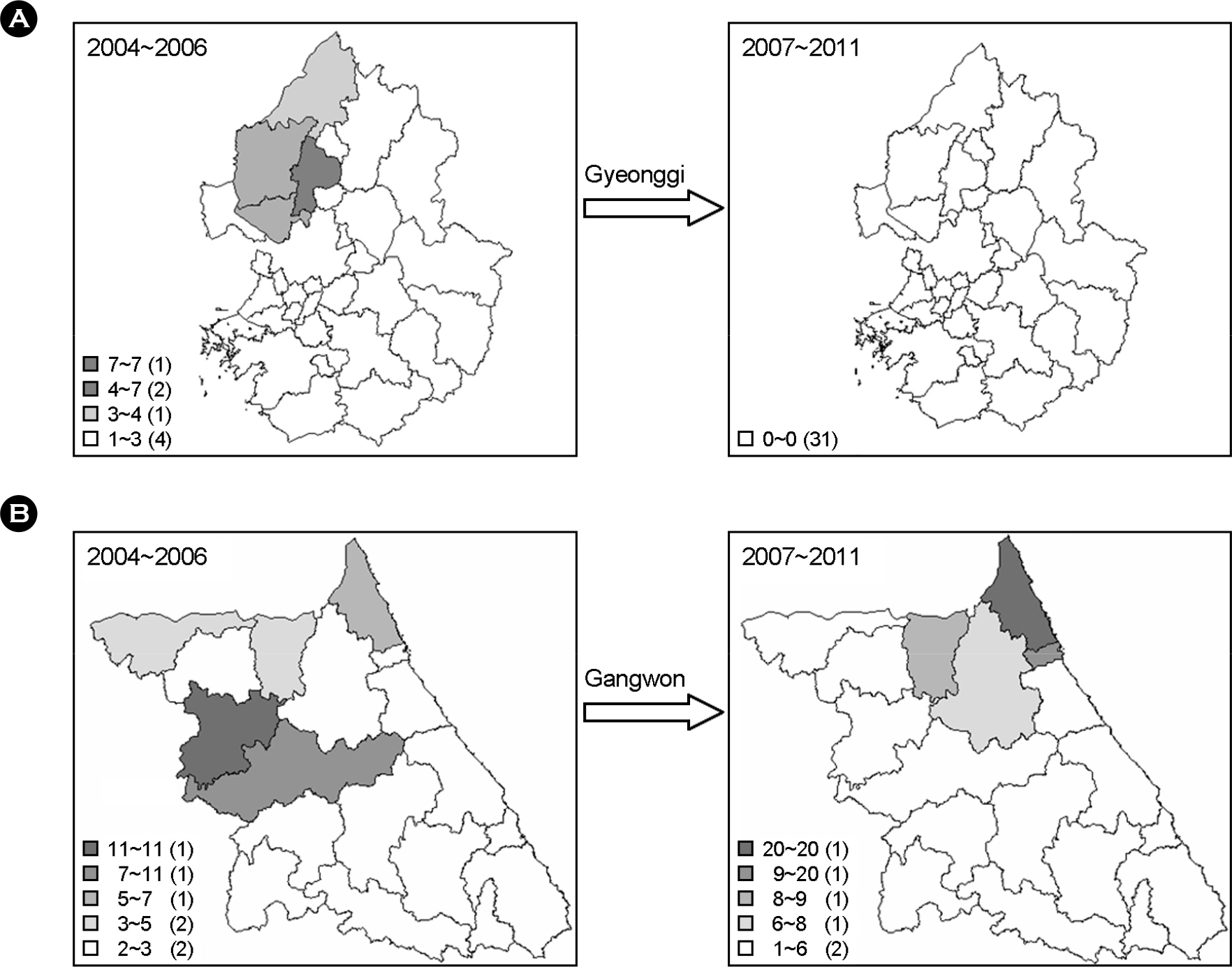
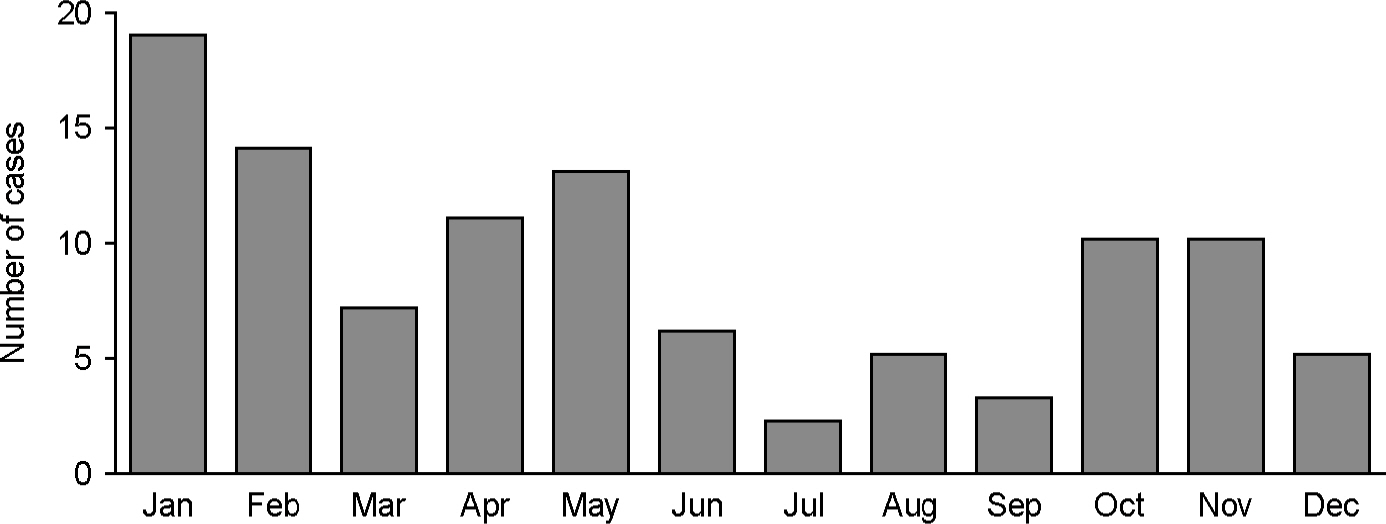
- Over the seven years from January 2004 to March 2011, 105 rabies cases in three different animal species and one case in human were recorded in South Korea. Forty three (40.6%) cattle and 33 (31.1%) dogs, 29 (27.4%) raccoon dogs were affected and one (0.9%) death in human was reported. The highest annual incidence of rabies was recorded with 27 cases in 2004, and then decreased to a median of 14 cases per year. Eighty cases (76.2%) occurred in Gangwon and 24 cases (22.9%) in Gyeonggi and one case in Seoul Province. All rabies cases occurred in the northern part of the country, namely, Seoul, Gyeonggi and Gangwon Provinces. Since 2007, rabies cases were not reported in Gyeonggi Province, but continued to occur and move eastward in Gangwon Province. The monthly distribution of animal rabies during the seven year period peaked in January, and the incidence was the highest during winter, from December to February, and the least common in summer, from June to September. The epidemiological study indicated that preventive measures including distribution of bait vaccine for the control of rabies in wild animals was helpful to a substantial decrease in number of rabies cases in South Korea.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 11 articles
-
Antibody Response in Korean Raccoon Dogs Inoculated with Inactivated Rabies Vaccines
Dong-Kun Yang, Tae-Oh Go, Young-Hee Nam, Ha-Hyun Kim, Soo-Dong Cho, Kyung-Woo Lee, Sung-Suk Choi, Jae-Young Song
J Bacteriol Virol. 2012;42(3):242-246. doi: 10.4167/jbv.2012.42.3.242.Prophylaxis of Human Hydrophobia in South Korea
Yang Ree Kim
Infect Chemother. 2014;46(3):143-148. doi: 10.3947/ic.2014.46.3.143.Animal bite injuries and vaccination
Hyunggoo Kang
J Korean Med Assoc. 2015;58(3):227-234. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2015.58.3.227.Five Year Experience of Preexposure and Postexposure Rabies Prophylaxis in Korean Children at the National Medical Center
Jin Chul Noh, Hyang Mi Park, Jong Hyun Park, Youn Kyung Won, Chang Hyu Lee, Jae Yoon Kim
Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis. 2013;20(1):9-16. doi: 10.14776/kjpid.2013.20.1.9.The present and future of rabies vaccine in animals
Dong-Kun Yang, Ha-Hyun Kim, Kyung-Woo Lee, Jae-Young Song
Clin Exp Vaccine Res. 2013;2(1):19-25. doi: 10.7774/cevr.2013.2.1.19.A single immunization with recombinant rabies virus (ERAG3G) confers complete protection against rabies in mice
Dong-Kun Yang, Keisuke Nakagawa, Naoto Ito, Ha-Hyun Kim, Bang-Hun Hyun, Jin-Ju Nah, Makoto Sugiyama, Jae-Young Song
Clin Exp Vaccine Res. 2014;3(2):176-184. doi: 10.7774/cevr.2014.3.2.176.Oral immunization of mice with recombinant rabies vaccine strain (ERAG3G) induces complete protection
Dong-Kun Yang, Ha-Hyun Kim, Sung-Suk Choi, Jong-Taek Kim, Woong-Ho Jeong, Jae-Young Song
Clin Exp Vaccine Res. 2015;4(1):107-113. doi: 10.7774/cevr.2015.4.1.107.Application of recombinant adenoviruses expressing glycoprotein or nucleoprotein of rabies virus to Korean raccoon dogs
Jiyoung Choi, Dong-Kun Yang, Ha-Hyun Kim, Hyun-Ye Jo, Sung-Suk Choi, Jong-Taek Kim, In-Soo Cho, Hee-Won Kim
Clin Exp Vaccine Res. 2015;4(2):189-194. doi: 10.7774/cevr.2015.4.2.189.Mass vaccination has led to the elimination of rabies since 2014 in South Korea
Dong-Kun Yang, Ha-Hyun Kim, Kyoung-Ki Lee, Jae-Young Yoo, Hong Seomun, In-Soo Cho
Clin Exp Vaccine Res. 2017;6(2):111-119. doi: 10.7774/cevr.2017.6.2.111.Antibody Response in Cattle and Guinea Pigs Inoculated with Rabies Vaccines
Dong-Kun Yang, Woong-Ho Jeong, Ha-Hyun Kim, Jin-Ju Nah, Jae-Jo Kim, Sung-Suk Choi, Jong-Taek Kim, Jae-Young Song
J Bacteriol Virol. 2014;44(1):67-74. doi: 10.4167/jbv.2014.44.1.67.Safety and Immunogenicity of a Recombinant Rabies Virus Strain (ERAG3G) in Korean Raccoon Dogs
Dong-Kun Yang, Ha-Hyun Kim, Hyun-Ye Jo, Hee-Won Kim, Sung-Suk Choi, In-Soo Cho
J Bacteriol Virol. 2015;45(3):250-255. doi: 10.4167/jbv.2015.45.3.250.
Reference
-
1). World Health Organization (WHO). WHO expert committee on Rabies. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser. 1992. 824:1–84.2). Tordo N., Bahloul C., Jacob Y., Jallet C., Perrin P., Badrane H. Rabies: epidemiological tendencies and control tools. Dev Biol (Basel). 2006. 125:3–13.3). Lee JB., Lee HJ., Hyun BH., Bang JH., Nam KO., Jeong YE, et al. Epidemiology and prevention strategies of rabies in Korea. Korean J Epidemiol. 2005. 27:53–68.4). Park YJ., Shin MK., Kwon HM. Genetic characterization of rabies virus isolates in Korea. Virus Genes. 2005. 30:341–7.
Article5). Kim CH., Lee CG., Yoon HC., Nam HM., Park CK., Lee JC, et al. Rabies, an emerging disease in Korea. J Vet Med B Infect Dis Vet Public Health. 2006. 53:111–5.
Article6). Kim JH., Hwang EK., Sohn HJ., Kim DY., So BJ., Jean YH. Epidemiological characteristics of rabies in South Korea from 1993 to 2001. Vet Rec. 2005. 157:53–6.
Article7). Hyun BH., Lee KK., Kim IJ., Lee KW., Park HJ., Lee OS, et al. Molecular epidemiology of rabies virus isolates from South Korea. Virus Res. 2005. 114:113–25.
Article8). Yang DK., Park YN., Hong GS., Kang HK., Oh YI., Cho SD, et al. Molecular characterization of Korean rabies virus isolates. J Vet Sci. 2011. 12:57–63.
Article9). Office International des Epizooties (OIE). Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals. Rabies, 6th ed. Paris: Office Intl Des Epizooties. 2008. 304–22.10). Strano AJ. Light microscopy of selected viral diseases (morphology of viral inclusion bodies). Pathol Annu. 1976. 11:53–75.11). Coertse J., Weyer J., Nel LH., Markotter W. Improved PCR methods for detection of African rabies and rabies-related lyssaviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 2010. 48:3949–55.
Article12). Holmes EC., Woelk CH., Kassis R., Bourhy H. Genetic constraints and the adaptive evolution of rabies virus in nature. Virology. 2002. 292:247–57.
Article13). The TH., Feltkamp TE. Conjugation of fluorescein isothiocyanate to antibodies. I. Experiments on the conditions of conjugation. Immunology. 1970. 18:865–73.14). Eo KY., Kwon OD., Shin NS., Shin T., Kwak D. Sarcoptic mange in wild raccoon dogs (Nyctereutes procyonoides) in Korea. J Zoo Wildl Med. 2008. 39:671–3.
Article15). Yang DK., Yoon SS., Lee KK., Byun JW., Bae YC., Oh YI, et al. Rabies immune status in the stray and companion dogs in Korea. Korean J Vet Res. 2010. 50:133–7.16). Ernst SN., Fabrega F. A time series analysis of the rabies control programme in Chile. Epidemiol Infect. 1989. 103:651–7.
Article17). Corn JL., Méndez JR., Catalán EE. Evaluation of baits for delivery of rabies vaccine to dogs in Guatemala. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2003. 69:155–8.18). Shao XQ., Yan XJ., Luo GL., Zhang HL., Chai XL., Wang FX, et al. Genetic evidence for domestic raccoon dog rabies caused by Arctic-like rabies virus in Inner Mongolia, China. Epidemiol Infect. 2011. 139:629–35.
Article19). Lee SH., Koh IS., Kwon HK., Kang JW., Cho PZ. A case of human rabies confirmed by polymerase chain reaction. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 2002. 20:437–8.20). Bourhy H., Kissi B., Audry L., Smreczak M., Sadkowska-Todys M., Kulonen K, et al. Ecology and evolution of rabies virus in Europe. J Gen Virol. 1999. 80:2545–57.
Article21). Hwang EK. Outbreak and control of rabies in animals in Korea: a review. Kor J Vet Public Health. 1995. 19:281–93.22). Sterner RT., Meltzer MI., Shwiff SA., Slate D. Tactics and economics of wildlife oral rabies vaccination, Canada and the United States. Emerg Infect Dis. 2009. 15:1176–84.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prophylaxis of Human Hydrophobia in South Korea
- Rabies immune status of raccoon dogs residing in areas where rabies bait vaccine has been distributed
- Strategies to maintain Korea's animal rabies non-occurrence status
- General Features and Post-Exposure Prophylaxis of Rabies
- Three Cases Report of Suggestive Rabies