J Korean Soc Radiol.
2011 Apr;64(4):383-388. 10.3348/jksr.2011.64.4.383.
Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia (ADH): Can the Sonoelastography Predict the Upgrade of ADH to Malignancy?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Korea. rad-ksh@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Korea.
- 3Department of Surgery, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Korea.
- KMID: 1443543
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2011.64.4.383
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate whether the sonoelastographic features of atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH) can be used to predict an upgrade to malignancy.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
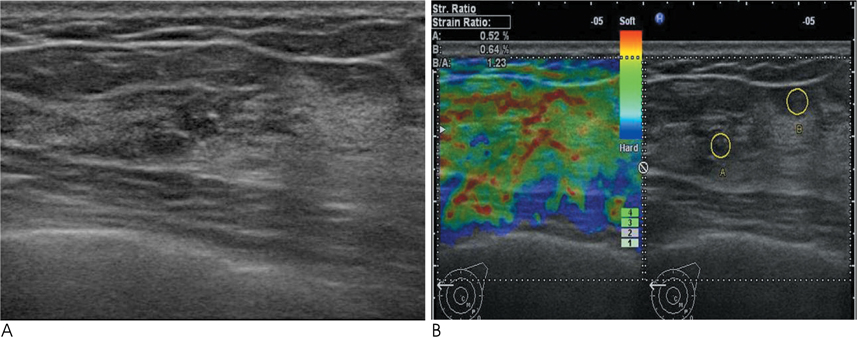
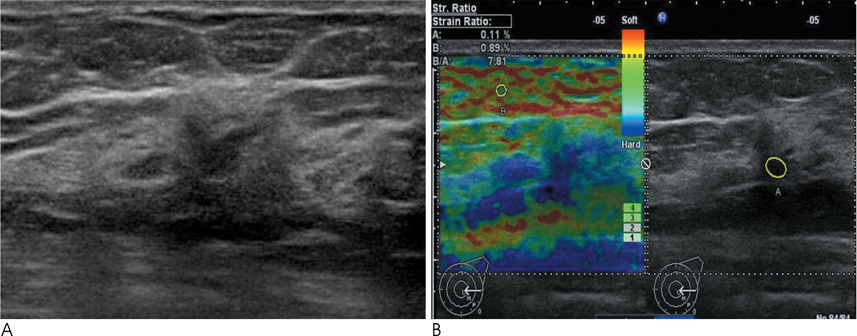
Conventional US and sonoelastographic images were available in 17 women with 18 ADH lesions diagnosed by sonographically guided core needle biopsy. Conventional US findings were analyzed according to the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System classification. Elastographic images were classified into 5 elasticity scores according to the ITOH classification. In addition, the strain ratio between the mass and surrounding fat tissue as well as the mammographic features were reviewed. All lesions underwent subsequent surgical excision and a correlation was found for sonoelastographic and conventional US findings with pathologic results.
RESULTS
Of the 18 ADH lesions that underwent surgical excision, four were found to be malignant (underestimation rate of 22.2%). Moreover, there was no significant difference in elasticity score (p=0.054) and strain ratio (p=0.375) between atypical ductal hyperplasia and lesions upgraded to malignancy on elastography. A mass with microcalcifications on mammography had a significantly higher association with malignancy and microcalcifications, as opposed to the absence of a mass, which was in all cases, benign (p=0.036).
CONCLUSION
Sonoelastography may not be a helpful indicator for the differentiation of atypical ductal hyperplasia from malignant lesions. However, a correlation with mammographic features provides insight for predicting malignancy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Page DL, Dupont WD, Rogers LW, Rados MS. Atypical hyperplastic lesions of the female breast. A long-term follow-up study. Cancer. 1985; 55:2698–2708.2. Tavassoli FA, Norris HF. A comparison of long-term follow-up for atypical intraductal hyperplasia and intraductal hyperplasia of the breast. Cancer. 1990; 65:518–529.3. Jackman RJ, Burbank F, Parker SH, Evans WP 3rd, Lechner MC, Richardson TR, et al. Atypical ductal hyperplasia diagnosed at stereotactic breast biopsy: improved reliability with 14-gauge, directional, vacuum-assisted biopsy. Radiology. 1997; 204:485–488.4. Meyer JE, Smith DN, Lester SC, Kaelin C, DiPiro PJ, Denison CM, et al. Large-core needle biopsy of nonpalpable breast lesions. JAMA. 1999; 281:1638–1641.5. Darling ML, Smith DN, Lester SC, Kaelin C, Selland DL, Denison CM, et al. Atypical ductal hyperplasia and ductal carcinoma in situ as revealed by large-core needle breast biopsy: results of surgical excision. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000; 175:1341–1346.6. Philpotts LE, Shaheen NA, Carter D, Lange RC, Lee CH. Comparison of rebiopsy rates after stereotactic core needle biopsy of the breast with 11-gauge vacuum suction probe versus 14-gauge needle and automatic gun. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1999; 172:683–687.7. Kettritz U, Rotter K, Schreer I, Murauer M, Schulz-Wendtland R, Peter D, et al. Stereotactic vacuum-assisted breast biopsy in 2874 patients: a multicenter study. Cancer. 2004; 100:245–251.8. Winchester DJ, Bernstein JR, Jeske JM, Nicholson MH, Hahn EA, Goldschmidt RA, et al. Upstaging of atypical ductal hyperplasia after vacuum-assisted 11-gauge stereotactic core needle biopsy. Arch Surg. 2003; 138:619–622.9. Pfarl G, Helbich TH, Riedl CC, Wagner T, Gnant M, Rudas M, et al. Stereotactic 11-gauge vacuum-assisted breast biopsy: a validation study. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002; 179:1503–1507.10. Burbank F. Stereotactic breast biopsy of atypical ductal hyperplasia and ductal carcinoma in situ lesions: improved accuracy with directional, vacuum-assisted biopsy. Radiology. 1997; 202:843–847.11. Jackman RJ, Burbank F, Parker SH, Evans WP 3rd, Lechner MC, Richardson TR, et al. Stereotactic breast biopsy of nonpalpable lesions: determinants of ductal carcinoma in situ underestimation rates. Radiology. 2001; 218:497–502.12. Philpotts LE, Lee CH, Horvath LJ, Lange RC, Carter D, Tocino I. Underestimation of breast cancer with II-gauge vacuum suction biopsy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000; 175:1047–1050.13. Kohr JR, Eby PR, Allison KH, DeMartini WB, Gutierrez RL, Peacock S, et al. Risk of upgrade of atypical ductal hyperplasia after stereotactic breast biopsy: effects of number of foci and complete removal of calcifications. Radiology. 2010; 255:723–730.14. Jackman RJ, Birdwell RL, Ikeda DM. Atypical ductal hyperplasia: can some lesions be defined as probably benign after stereotactic 11-gauge vacuum-assisted biopsy, eliminating the recommendation for surgical excision? Radiology. 2002; 224:548–554.15. Margenthaler JA, Duke D, Monsees BS, Barton PT, Clark C, Dietz JR. Correlation between core biopsy and excisional biopsy in breast highXMLLink_XYZ risk lesions. Am J Surg. 2006; 192:534–537.16. Ko E, Han W, Lee JW, Cho J, Kim EK, Jung SY, et al. Scoring system for predicting malignancy in patients diagnosed with atypical ductal hyperplasia at ultrasound - guided core needle biopsy. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2008; 112:189–195.17. Maganini RO, Klem DA, Huston BJ, Bruner ES, Jacobs HK. Upgrade rate of core biopsyXMLLink_XYZ determined atypical ductal hyperplasia by open excisional biopsy. Am J Surg. 2001; 182:355–358.18. Brown TA, Wall JW, Christensen ED, Smith DV, Holt CA, Carter PL, et al. Atypical hyperplasia in the era of stereotactic core needle biopsy. J Surg Oncol. 1998; 67:168–173.19. Hoang JK, Hill P, Cawson JN. Can mammographic findings help discriminate between atypical ductal hyperplasia and ductal carcinoma in situ after needle core biopsy? Breast. 2008; 17:282–288.20. Adrales G, Turk P, Wallace T, Bird R, Norton HJ, Greene F. Is surgical excision necessary for atypical ductal hyperplasia of the breast diagnosed by mammotome? Am J Surg. 2000; 180:313–315.21. Jang M, Cho N, Moon WK, Park JS, Seong MH, Park IA. Underestimation of atypical ductal hyperplasia at sonographically guided core biopsy of the breast. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008; 191:1347–1351.22. Youk JH, Kim EK, Kim MJ. Atypical ductal hyperplasia diagnosed at sonographically guided 14-gauge core needle biopsy of breast mass. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009; 192:1135–1141.23. Garra BS, Cespedes EI, Ophir J, Spratt SR, Zuurbier RA, Magnant CM, et al. Elastography of breast lesions: initial clinical results. Radiology. 1997; 202:79–86.24. Itoh A, Ueno E, Tohno E, Kamma H, Takahashi H, Shiina T, et al. Breast disease: clinical application of US elastography for diagnosis. Radiology. 2006; 239:341–350.25. Cho N, Moon WK, Park JS, Cha JH, Jang M, Seong MH. Nonpalpable breast masses: evaluation by US elastography. Korean J Radiol. 2008; 9:111–118.26. Scaperrotta G, Ferranti C, Costa C, Mariani L, Marchesini M, Suman L, et al. Role of sonoelastography in non-palpable breast lesions. Eur Radiol. 2008; 18:2381–2389.27. Cho N, Moon WK, Kim HY, Chang JM, Park SH, Lyou CY. Sonoelastographic strain index for differentiation of benign and malignant nonpalpable breast masses. J Ultrasound Med. 2010; 29:1–7.28. Helvie MA, Hessler C, Frank TS, Ikeda DM. Atypical hyperplasia of the breast: mammographic appearance and histologic correlation. Radiology. 1991; 179:759–764.29. Liberman L, Cohen MA, Dershaw DD, Abramson AF, Hann LE, Rosen PP. Atypical ductal hyperplasia diagnosed at stereotaxic core biopsy of breast lesions: an indication for surgical biopsy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1995; 164:1111–1113.30. Lee JY, Seo BK, Kim JH, Oh YW, Cho KR, Choi EJ, et al. Atypical ductal hyperplasia of the breast: radiologic and histopathologic correlation. J Korean Radiol Soc. 2003; 49:363–372.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia: Risk Factors for Predicting Pathologic Upgrade on Excisional Biopsy
- The Ratio of Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia Foci to Core Numbers in Needle Biopsy: A Practical Index Predicting Breast Cancer in Subsequent Excision
- Factors in the Breast Core Needle Biopsies of Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia that Can Predict Carcinoma in the Subsequent Surgical Excision Specimens
- Correlation of Breast Cancer with Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia on Fine-needle Aspiration Cytology Speciemens
- Expression of cyclins in ductal hyperplasia, atypical ductal hyperplasia and ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast