J Korean Soc Radiol.
2011 Jul;65(1):69-76. 10.3348/jksr.2011.65.1.69.
Differentiation of Acute Perforated from Non-Perforated Appendicitis: Usefulness of High-Resolution Ultrasonography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Soonchunhyang University Gumi Hospital, Gumi, Korea. cgc3@schmc.ac.kr
- KMID: 1443495
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2011.65.1.69
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the usefulness of high-resolution ultrasonography (US) for the differentiation of acute perforated appendicitis from non-perforated appendicitis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
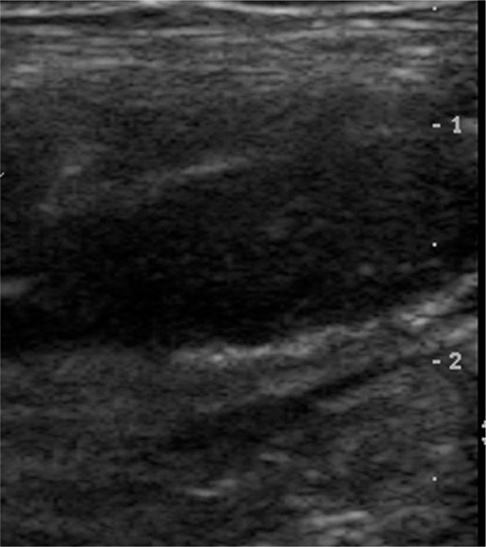
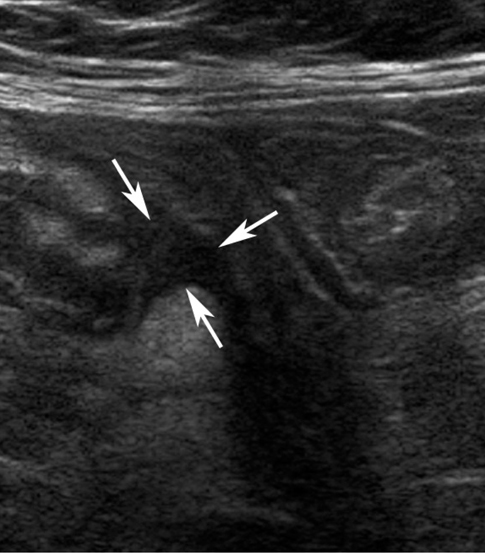
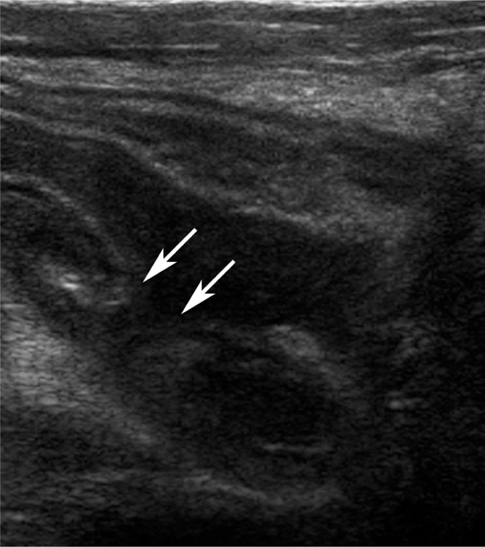
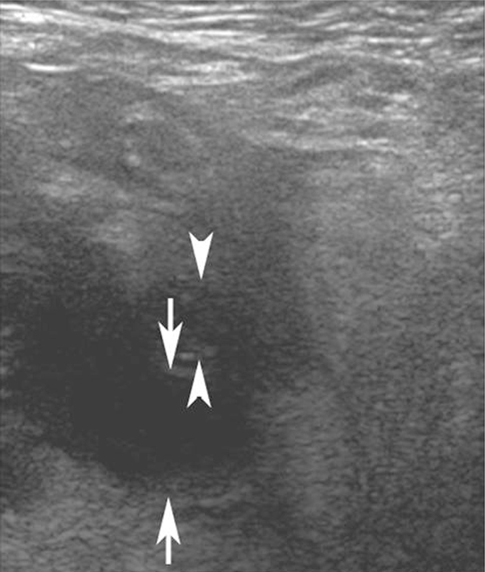
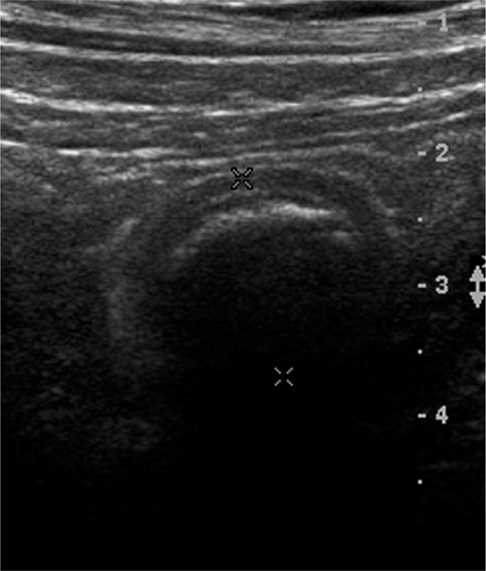
The high-resolution US features in 96 patients (49 males, 47 females; mean age, 33.8 years; age range, 4-80 years) with pathologically proven acute appendicitis were evaluated. The following US findings were evaluated for differentiation of acute perforated appendicitis from non-perforated appendicitis: circumferential loss of the echogenic submucosal layer, periappendiceal fluid collection, disruption of the serosal layer, asymmetrical wall thickening, maximum overall diameter > 10.5 mm, and the presence of appendicoliths. The sensitivity and specificity of the US features in the diagnosis of acute perforated appendicitis were calculated.
RESULTS
All of the US findings, except for appendicoliths, were significantly more common in the acute perforated appendicitis group (p < 0.001). The sensitivity of circumferential loss of the echogenic submucosal layer, periappendiceal fluid collection, disruption of the serosal layer, asymmetrical wall thickening, maximum overall diameter > 10.5 mm, and the presence of appendicoliths was 85.4, 73.2, 68.3, 70.7, 80.5, and 36.6%, respectively, while the specificity was 65.5, 89.1, 96.4, 98.2, 81.8, and 80.0%, respectively.
CONCLUSION
High-resolution US was found to be useful for differentiating acute perforated appendicitis from non-perforated appendicitis.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Addiss DG, Shaffer N, Fowler BS, Tauxe RV. The epidemiol ogy of appendicitis and appendectomy in the United States. Am J Epidemiol. 1990; 132:910–925.2. Körner H, Söndenaa K, Söreide JA, Andersen E, Nysted A, Lende TH, et al. Incidence of acute nonperforated and perforated appendicitis: age-specific and sex-specific analysis. World J Surg. 1997; 21:313–317.3. Al-Omran M, Mamdani M, McLeod RS. Epidemiologic features of acute appendicitis in Ontario, Canada. Can J Surg. 2003; 46:263–268.4. Hale DA, Molloy M, Pearl RH, Schutt DC, Jaques DP. Appendectomy: a contemporary appraisal. Ann Surg. 1997; 225:252–261.5. Quillin SP, Siegel MJ. Diagnosis of appendiceal abscess in children with acute appendicitis: value of color Doppler sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1995; 164:1251–1254.6. Oliak D, Yamini D, Udani VM, Lewis RJ, Vargas H, Arnell T, et al. Nonoperative management of perforated appendicitis without periappendiceal mass. Am J Surg. 2000; 179:177–181.7. Jeffrey RB Jr, Federle MP, Tolentino CS. Periappendiceal inflammatory masses: CT-directed management and clinical outcome in 70 patients. Radiology. 1988; 167:13–16.8. Velanovich V, Satava R. Balancing the normal appendectomy rate with the perforated appendicitis rate: implications for quality assurance. Am Surg. 1992; 58:264–269.9. Siewert B, Raptopoulos V, Liu SI, Hodin RA, Davis RB, Rosen MP. CT predictors of failed laparoscopic appendectomy. Radiology. 2003; 229:415–420.10. Liu SI, Siewert B, Raptopoulos V, Hodin RA. Factors associated with conversion to laparotomy in patients undergoing laparoscopic appendectomy. J Am Coll Surg. 2002; 194:298–305.11. Puylaert JB, Rutgers PH, Lalisang RI, de Vries BC, van der Werf SD, Dörr JP, et al. A prospective study of ultrasonography in the diagnosis of appendicitis. N Engl J Med. 1987; 317:666–669.12. Borushok KF, Jeffrey RB Jr, Laing FC, Townsend RR. Sonographic diagnosis of perforation in patients with acute appendicitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1990; 154:275–278.13. Quillin SP, Siegel MJ, Coffin CM. Acute appendicitis in children: value of sonography in detecting perforation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1992; 159:1265–1268.14. Choi GC, Kim S, Im HH, Lee SJ, Yang SB, Lee SW, et al. High-resolution ultrasonography of appendiceal specimens: differentiation of acute non-perforated appendicitis from perforated appendicitis. J Korean Soc Ultrasound Med. 2007; 26:145–153.15. Abu-Yousef MM, Bleicher JJ, Maher JW, Urdaneta LF, Franken EA Jr, Metcalf AM. High-resolution sonography of acute appendicitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1987; 149:53–58.16. Gaensler EH, Jeffrey RB Jr, Laing FC, Townsend RR. Sonography in patients with suspected acute appendicitis: value in establishing alternative diagnoses. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1989; 152:49–51.17. Jeffrey RB Jr, Laing FC, Lewis FR. Acute appendicitis: high-resolution real-time US findings. Radiology. 1987; 163:11–14.18. Jeffrey RB Jr, Laing FC, Townsend RR. Acute appendicitis: sonographic criteria based on 250 cases. Radiology. 1988; 167:327–329.19. Puylaert JB. Acute appendicitis: US evaluation using graded compression. Radiology. 1986; 158:355–360.20. Lee JH, Jeong YK, Park KB, Park JK, Jeong AK, Hwang JC. Operator-dependent techniques for graded compression sonography to detect the appendix and diagnose acute appendicitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005; 184:91–97.21. Tsuboi M, Takase K, Kaneda I, Ishibashi T, Yamada T, Kitami M, et al. Perforated and nonperforated appendicitis: defect in enhancing appendiceal wall--depiction with multi-detector row CT. Radiology. 2008; 246:142–147.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- High-Resolution Ultrasonography (US) of Appendiceal Specimens: Differentiation of Acute Non-perforated Appendicitis from Perforated Appendicitis
- I Gee Score: Scoring System for Perforated Appendicitis: Effective Usage of Health Care Resources in COVID-19 Pandemic
- Idiopathic Perforated Cecitis Mistaken as Perforated Appendicitis
- Value of ultrasonography in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis
- The US Findings of Acute Nonperforated and Perforated Appendicitis in Children