Korean J Radiol.
2013 Feb;14(1):81-85. 10.3348/kjr.2013.14.1.81.
Impotence due to External Iliac Steal Syndrome: Treatment with Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty and Stent Placement
- Affiliations
-
- 1Sifa University, Department of Radiology, 35240 Basmane, Izmir, Turkey. mserkangur@yahoo.com
- 2Baskent University, Faculty of Medicine, Department of Radiology, 01250, Yuregir, Adana, Turkey.
- KMID: 1430047
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2013.14.1.81
Abstract
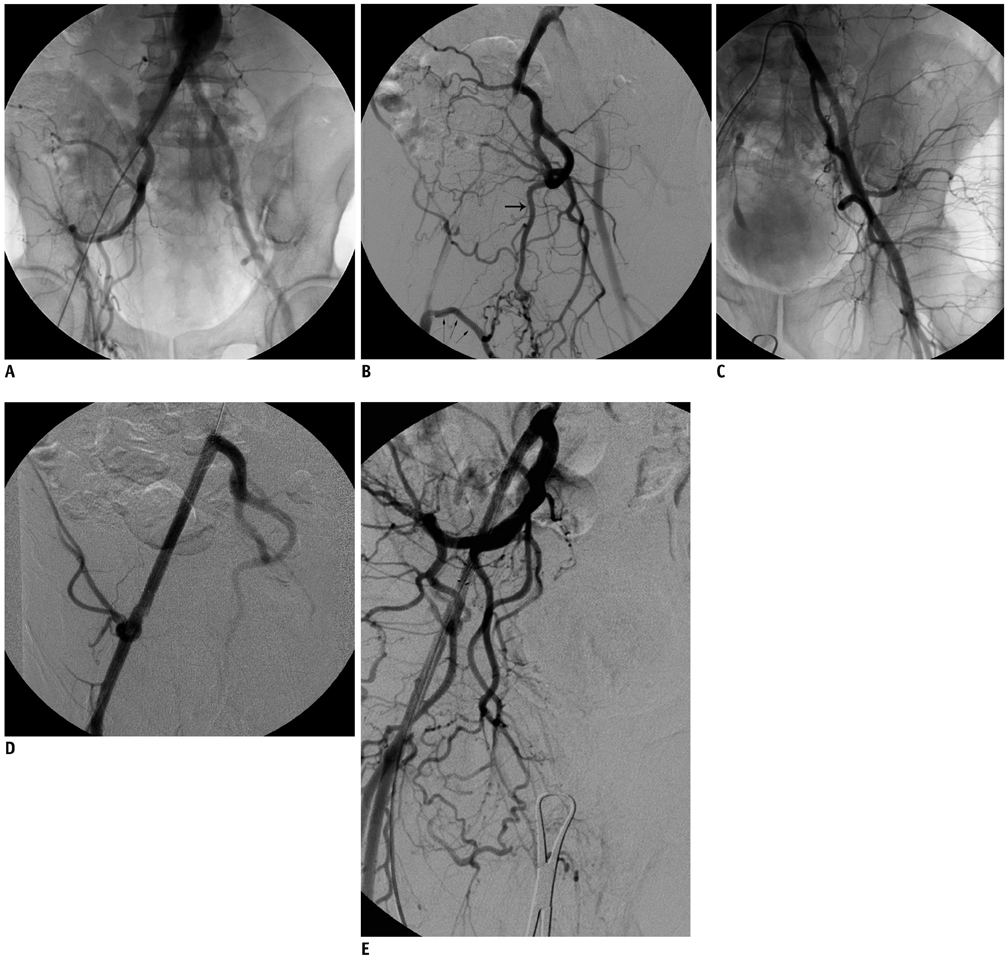
- We report a case of erectile dysfunction caused by external iliac artery occlusion, associated with pelvic steal syndrome; bilateral internal iliac arteries were patent. The patient stated that he had experienced erectile dysfunction at similar times along with claudication, but he did not mention it before angiography. He expressed that the erectile dysfunction did not last long and that he felt completely okay after the interventional procedure, in addition to his claudication. Successful treatment of the occlusion, by percutaneous transluminal angioplasty and stent implantation, helped resolve erectile dysfunction completely and treat the steal syndrome.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Feldman HA, Goldstein I, Hatzichristou DG, Krane RJ, McKinlay JB. Impotence and its medical and psychosocial correlates: results of the Massachusetts Male Aging Study. J Urol. 1994. 151:54–61.2. Yassin AA, Saad F. Testosterone and erectile dysfunction. J Androl. 2008. 29:593–604.3. Valji K, Bookstein JJ. Transluminal angioplasty in the treatment of arteriogenic impotence. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 1988. 11:245–252.4. Goldstein I, Siroky MB, Nath RL, McMillian TN, Menzoian JO, Krane RJ. Vasculogenic impotence: role of the pelvic steal test. J Urol. 1982. 128:300–306.5. Goldwasser B, Carson CC 3rd, Braun SD, McCann RL. Impotence due to the pelvic steal syndrome: treatment by iliac transluminal angioplasty. J Urol. 1985. 133:860–861.6. Kholoussy AM, Gain T, Matsumoto T. Impotence after aorto-iliac surgery: current concepts. Angiology. 1981. 32:589–594.7. Castaneda-Zuniga WR, Smith A, Kaye K, Rusnak B, Herrerra M, Miller R, et al. Transluminal angioplasty for treatment of vasculogenic impotence. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1982. 139:371–373.8. Angelini P, Fighali S. Early experience with balloon angioplasty of internal iliac arteries for vasculogenic impotence. Cathet Cardiovasc Diagn. 1987. 13:107–110.9. Van Unnik JG, Marsman JW. Impotence due to the external iliac steal syndrome treated by percutaneous transluminal angioplasty. J Urol. 1984. 131:544–545.10. Karkos CD, Wood A, Bruce IA, Karkos PD, Baguneid MS, Lambert ME. Erectile dysfunction after open versus angioplasty aortoiliac procedures: a questionnaire survey. Vasc Endovascular Surg. 2004. 38:157–165.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Placement of Balloon-Expandable Intraluminal Stent in Recurrent Iliac Artery Stenosis
- A Case of Renovascular Hypertension Cured by Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty
- Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty of Contralateral Iliac and Superficial Femoral Arteries via Graft Vessel in a Patient with FemoroFemoral Bypass Graft
- Cumulative Patency Rate of Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty and Stent Placement for Aortoiliac Occlusive Disease
- Interventional Radiology for Vascular Diseases