J Korean Med Sci.
2013 Feb;28(2):336-339. 10.3346/jkms.2013.28.2.336.
Electrolyte Imbalances and Nephrocalcinosis in Acute Phosphate Poisoning on Chronic Type 1 Renal Tubular Acidosis due to Sjogren's Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Renal Division, Department of Internal Medicine, Hanyang University Guri Hospital, Guri, Korea. Joohark@hanyang.ac.kr
- KMID: 1429217
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2013.28.2.336
Abstract
- Although renal calcium crystal deposits (nephrocalcinosis) may occur in acute phosphate poisoning as well as type 1 renal tubular acidosis (RTA), hyperphosphatemic hypocalcemia is common in the former while normocalcemic hypokalemia is typical in the latter. Here, as a unique coexistence of these two seperated clinical entities, we report a 30-yr-old woman presenting with carpal spasm related to hypocalcemia (ionized calcium of 1.90 mM/L) due to acute phosphate poisoning after oral sodium phosphate bowel preparation, which resolved rapidly after calcium gluconate intravenously. Subsequently, type 1 RTA due to Sjogren's syndrome was unveiled by sustained hypokalemia (3.3 to 3.4 mEq/L), persistent alkaline urine pH (> 6.0) despite metabolic acidosis, and medullary nephrocalcinosis. Through this case report, the differential points of nephrocalcinosis and electrolyte imbalances between them are discussed, and focused more on diagnostic tests and managements of type 1 RTA.
MeSH Terms
-
Acidosis, Renal Tubular/*diagnosis/etiology
Acute Disease
Adult
Antibodies, Antinuclear/blood
Calcium Gluconate/therapeutic use
Chronic Disease
Female
Humans
Hydrogen-Ion Concentration
Hypocalcemia/*chemically induced/complications/drug therapy
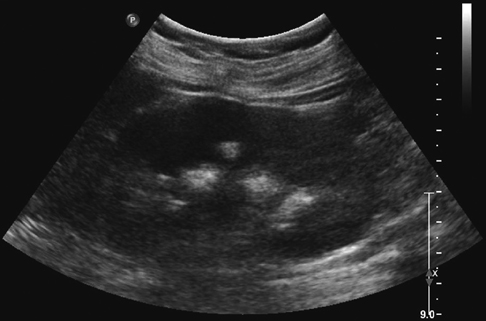
Nephrocalcinosis/complications/*diagnosis/ultrasonography
Parotid Gland/ultrasonography
Phosphates/*adverse effects
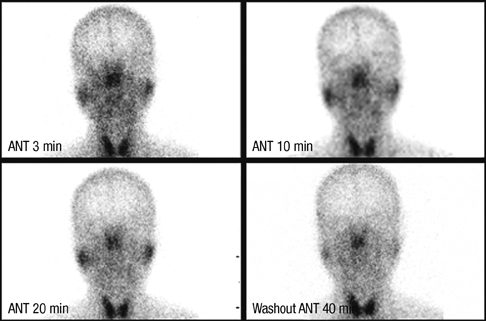
Salivary Glands/radionuclide imaging
Sjogren's Syndrome/complications/*diagnosis/metabolism
Submandibular Gland/ultrasonography
Antibodies, Antinuclear
Phosphates
Calcium Gluconate
Figure
Reference
-
1. Heher EC, Thier SO, Rennke H, Humphreys BD. Adverse renal and metabolic effects associated with oral sodium phosphate bowel preparation. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008. 3:1494–1503.2. Desmeules S, Gergeron MJ, Isenring P. Acute phosphate nephropathy and renal failure. N Engl J Med. 2003. 349:1006–1007.3. Markowitz GS, Perazella MA. Acute phosphate nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2009. 76:1027–1034.4. Beloosesky Y, Grinblat J, Weiss A, Grosman B, Gafter U, Chagnac A. Electrolyte disorders following oral sodium phosphate administration for bowel cleansing in elderly patients. Arch Intern Med. 2003. 163:803–808.5. Seamonds B, Towfighi J, Arvan DA. Determination of ionized calcium in serum by use of an ion-selective electrode. I. Determination of normal values under physiologic conditions, with comments on the effects of food ingestion and hyperventilation. Clin Chem. 1972. 18:155–160.6. Joo WC, Lee SW, Yang DH, Han JY, Kim MJ. A case of biopsy-proven chronic kidney disease on progression from acute phosphate nephropathy. Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2012. 31:124–127.7. Rodriguez Soriano J. Renal tubular acidosis: the clinical entity. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002. 13:2160–2170.8. Han SW, Kim HJ, Oh MS. Comparison of the urine acidification tests of torsemide vs furosemide in healthy volunteers. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2005. 20:2582–2583.9. Halperin ML, Goldstein MB, Haig A, Johnson MD, Stinebaugh BJ. Studies on the pathogenesis of type I (distal) renal tubular acidosis as revealed by the urinary PCO2 tensions. J Clin Invest. 1974. 53:669–677.10. Maripuri S, Grande JP, Osborn TG, Fervenza FC, Matteson EL, Donadio JV, Hogan MC. Renal involvement in primary Sjögren's syndrome: a clinicopathologic study. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009. 4:1423–1431.11. Cohen EP, Bastani B, Cohen MR, Kolner S, Hemken P, Gluck SL. Absence of H+-ATPase in cortical collecting tubules of a patient with Sjogren's syndrome and distal renal tubular acidosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1992. 3:264–271.12. Albright F, Burnett CH, Parson W, Reifenstein EC Jr, Roos A. Osteomalacia and late rickets: The various etiologies met in the United States with emphasis on that resulting from a specific form of renal acidosis, the therapeutic indications for each etiological sub-group, and the relationship between osteomalacia and Milkman's syndrome. Medicine. 1946. 25:399–479.13. Fourman P, Robinson JR. Diminished urinary excretion of citrate during deficiencies of potassium in man. Lancet. 1953. 265:656–657.14. Halperin ML, Carlisle EJF, Donnely AS, Kamel KS, Vasuvattakul S. Narins RG, editor. Renal tubular acidosis. Maxwell and Cleeman's Clinical Disorders of Fluid and Electrolyte Metabolism. 1994. 5th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Incorporated;875–910.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Distal Renal Tubular Acidosis with Nephrocalcinosis in a Patient with Primary Sjogren's Syndrome
- A Case Of Secondary Sjogren Syndrome Associated With Distal Renal Tubular Acidosis
- Two Cases of Distal Renal Tubular Acidosis accompanied by Sjogren's Syndrome
- A Case of Primary Sjiigren's Syndrome with Hypokalemic Paralysis and Renal Tubular Acidosis
- A Case of Type 1 Renal Tubular Acidosis and Osteomalacia in a Patient with Sjogren's Syndrome