Korean J Perinatol.
2013 Mar;24(1):20-28. 10.14734/kjp.2013.24.1.20.
Blood Urea Nitrogen Concentration and Aggressive Parenteral Amino Acid Administration in Extremely Low Birth Weight Infants during the First Week
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea. neopark@hanyang.ac.kr
- KMID: 1427070
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14734/kjp.2013.24.1.20
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Early administration of parenteral amino acids has been shown to limit catabolism and improve growth in extremely low birth weight infants (ELBWI). This study aimed to evaluate the relationship between an earlier aggressive administration of amino acids and blood urea nitrogen (BUN).
METHODS
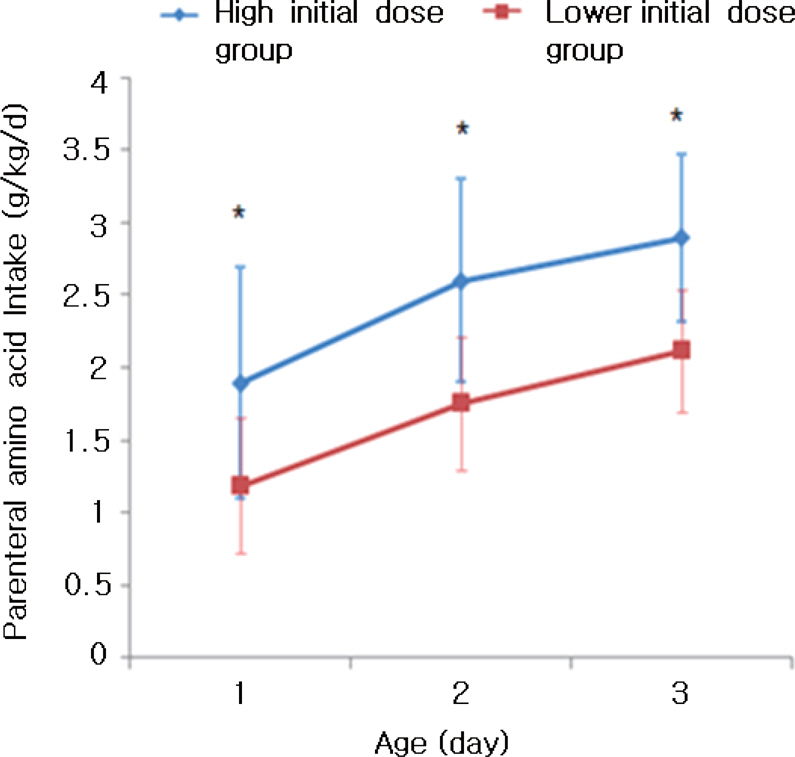
We retrospectively analyzed the medical records of all ELBWI who were born and admitted to Hanyang University Hospital from March 2007 to December 2009. The high initial dose group received > or =3.0 g/kg/d amino acids, while the lower initial dose group did not received a minimum of > or =3.0 g/kg/d parenteral AA at < or =3 days of age.
RESULTS
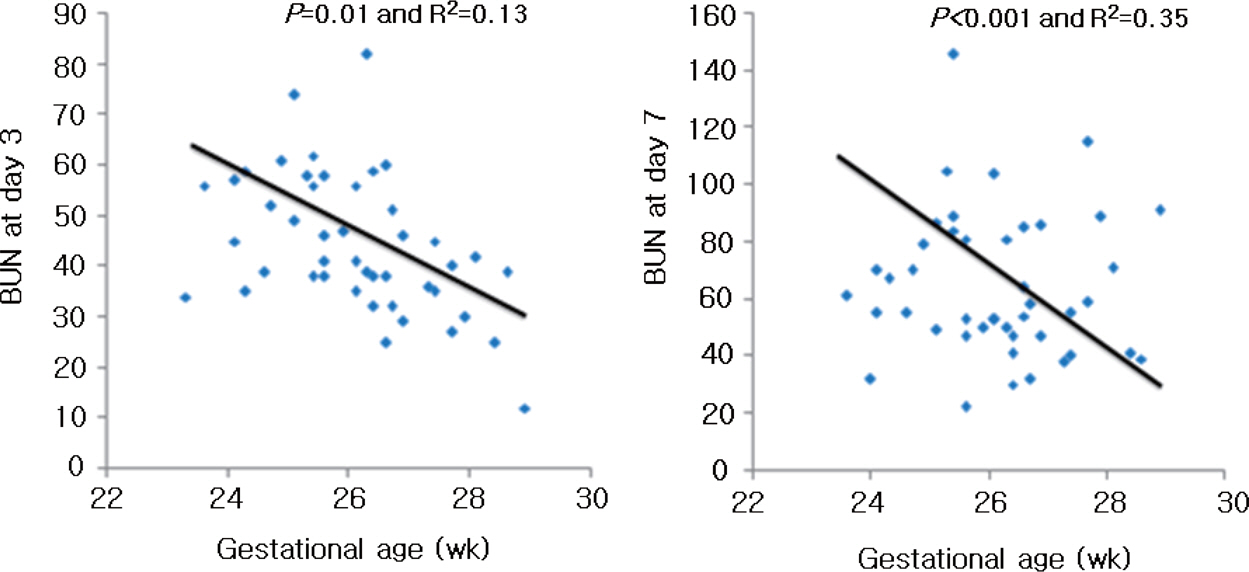
There were no differences in gestational age, birth weight and sex between the groups. Mean fluid intake and total calories during the first 48 hours of life were similar between two groups. There is no correlation between amino acid intake and BUN level in ELBWI during study period. However, gestational age showed a significant negative correlation with BUN level in ELBWI on day 3 and 7.
CONCLUSION
An earlier, more aggressive administration of amino acids was safe and well-tolerated. There is no correlation between amino acid intake and BUN level in ELBWI infants within 7 days of life.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Adamkin DH. Nutrition in very very low birth weight infants. Clin Perinatol. 1986. 13:419–43.
Article2). Bulbul A., Okan F., Bulbul L., Nuhoglu A. Effect of low versus high early parenteral nutrition on plasma amino acid profiles in very low birthweight infants. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012. 25:770–6.
Article3). Yu VY. Extrauterine growth restriction in preterm infants: importance of optimizing nutrition in neonatal intensive care units. Croat Med J. 2005. 46:737–43.4). Poindexter BB., Langer JC., Dusick AM., Ehrenkranz RA. Early provision of parenteral amino acids in extremely low birth weight infants: relation to growth and neurodevelop-mental outcome. J Pediatr. 2006. 148:300–5.
Article5). Thureen PJ., Melara D., Fennessey PV., Hay WW Jr. Effect of low versus high intravenous amino acid intake on very low birth weight infants in the early neonatal period. Pediatr Res. 2003. 53:24–32.
Article6). Porcelli Jr PJ., Sisk PM. Increased parenteral amino acid administration to extremely low-birthweight infants during early postnatal life. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2002. 34:174–9.7). Thureen PJ. Early aggressive nutrition in very preterm infants. Nestle Nutr Workshop Ser Pediatr Program. 2007. 59:193–204.
Article8). Yang S., Lee BS., Park HW., Choi YS., Jeong SH., Kim JH, et al. Effect of High vs Standard Early Parenteral Amino Acid Supplementation on the Growth Outcomes in Very Low Birth Weight Infants. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. In press. 2012.9). Kotsopoulos K., Benadiba-Torch A., Cuddy A., Shah PS. Safety and efficacy of early amino acids in preterm <28 weeks gestation: prospective observational comparison. J Perinatol. 2006. 26:749–54.10). Roggero P., Gianni ML., Morlacchi L., Piemontese P., Liotto N., Taroni F, et al. Blood urea nitrogen concentrations in low-birth-weight preterm infants during parenteral and enteral nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2010. 51:213–5.
Article11). Jobe AH., Bancalari E. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001. 163:1723–9.
Article12). Kamitsuka MD., Horton MK., Williams MA. The incidence of necrotizing enterocolitis after introducing standardized feeding schedules for infants between 1250 and 2500 grams and less than 35 weeks of gestation. Pediatrics. 2000. 105:379–84.
Article13). Papile LA., Burstein J., Burstein R., Koffler H. Incidence and evolution of subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhage: a study of infants with birth weights less than 1,500 gm. J Pediatr. 1978. 92:529–34.
Article14). Embleton ND. Optimal protein and energy intakes in pre-term infants. Early Hum Dev. 2007. 83:831–7.
Article15). Koletzko B., Goulet O., Hunt J., Krohn K., Shamir R. 1. Guidelines on Paediatric Parenteral Nutrition of the European Society of Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (ESPGHAN) and the European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism (ESPEN), Supported by the European Society of Paediatric Research (ESPR). J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2005. 41(Suppl 2):S1–87.16). Denne SC., Karn CA., Wang J., Liechty EA. Effect of intravenous glucose and lipid on proteolysis and glucose production in normal newborns. Am J Physiol. 1995. 269:E361–7.
Article17). Poindexter BB., Karn CA., Ahlrichs JA., Wang J., Leitch CA., Liechty EA, et al. Amino acids suppress proteolysis independent of insulin throughout the neonatal period. Am J Physiol. 1997. 272:E592–9.
Article18). Simmer K. Aggressive nutrition for preterm infants—benefits and risks. Early Hum Dev. 2007. 83:631–4.
Article19). Zlotkin SH., Bryan MH., Anderson GH. Intravenous nitrogen and energy intakes required to duplicate in utero nitrogen accretion in prematurely born human infants. J Pediatr. 1981. 99:115–20.
Article20). Denne SC., Poindexter BB. Evidence supporting early nutritional support with parenteral amino acid infusion. Semin Perinatol. 2007. 31:56–60.
Article21). Ziegler EE., Thureen PJ., Carlson SJ. Aggressive nutrition of the very low birthweight infant. Clin Perinatol. 2002. 29:225–44.
Article22). Ibrahim HM., Jeroudi MA., Baier RJ., Dhanireddy R., Krouskop RW. Aggressive early total parental nutrition in low-birth-weight infants. J Perinatol. 2004. 24:482–6.
Article23). Ridout E., Melara D., Rottinghaus S., Thureen PJ. Blood urea nitrogen concentration as a marker of amino-acid intolerance in neonates with birthweight less than 1250 g. J Perinatol. 2005. 25:130–3.
Article24). Lemons JA., Adcock EW 3rd., Jones MD Jr., Naughton MA., Meschia G., Battaglia FC. Umbilical uptake of amino acids in the unstressed fetal lamb. J Clin Invest. 1976. 58:1428–34.
Article25). te Braake FW., van den Akker CH., Wattimena DJ., Huijmans JG., van Goudoever JB. Amino acid administration to premature infants directly after birth. J Pediatr. 2005. 147:457–61.
Article26). Clark RH., Chace DH., Spitzer AR. Effects of two different doses of amino acid supplementation on growth and blood amino acid levels in premature neonates admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit: a randomized, controlled trial. Pediatrics. 2007. 120:1286–96.
Article27). Hay WW Jr., Lucas A., Heird WC., Ziegler E., Levin E., Grave GD, et al. Workshop summary: nutrition of the extremely low birth weight infant. Pediatrics. 1999. 104:1360–8.
Article28). Stephens BE., Walden RV., Gargus RA., Tucker R., McKinley L., Mance M, et al. First-week protein and energy intakes are associated with 18-month developmental outcomes in extremely low birth weight infants. Pediatrics. 2009. 123:1337–43.
Article29). Can E., Bulbul A., Uslu S., Comert S., Bolat F., Nuhoglu A. Effects of aggressive parenteral nutrition on growth and clinical outcome in preterm infants. Pediatr Int. In press. 2012.30). Blanco CL., Gong AK., Schoolfield J., Green BK., Daniels W., Liechty EA, et al. Impact of early and high amino acid supplementation on ELBW infants at 2 years. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2012. 54:601–7.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Early Parenteral Nutrition for Extremely Low Birth Weight Infants
- Nutritional strategy of early amino acid administration in very low birth weight infants
- Early Effective Parenteral Nutrition for Preterm Infants
- Comparison of total parenteral nutrition-associated cholestasis according to amino acid mixtures in very low birth weight infants
- Tolerability and Effect of Early High-Dose Amino Acid Administration in Extremely Low Birth Weight Infants